 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 A detailed introduction to understanding values and references in JavaScript parameter passing
A detailed introduction to understanding values and references in JavaScript parameter passing
A detailed introduction to understanding values and references in JavaScript parameter passing
Value and reference are common topics in various programming languages, and js is no exception.
I will analyze the actual running process of an example and share with you my understanding of values and references in js parameter passing.
Refer to the two classifications of data types on the official website. This article refers to these two classifications as basic types (boolean, null, undefined, string, number, symbol) and object types.
First, use an example to demonstrate the application of parameter passing:
var obj = {};
obj.inner = 10;
var num = 10;
var str = 'Hello';
var boo = true;
var oth = null;
var und = undefined;
var sym = Symbol('foo');
function passingobject(myobj){
myobj.inner = 1 + myobj.inner ;
}
function passingvalue(myvalue){
switch(typeof myvalue){
case 'number':
myvalue = myvalue + 1;
break;
case 'string':
myvalue = 'I am a new string now!';
break;
case 'boolean':
myvalue= false;
break;
default:
myvalue = 'Null, Undefined, or Symbol';
}
}
console.log("before num = " + num); // before num = 10
passingvalue(num);
console.log("after num = " + num); // after num = 10
console.log("before str = " + str); // before str = Hello
passingvalue(str);
console.log("after str = " + str); // after str = Hello
console.log("before boo = " + boo); // before boo = true
passingvalue(boo);
console.log("after boo = " + boo); // after boo = false
console.log("before oth = " + oth); // before oth = null
passingvalue(oth);
console.log("after oth = " + oth); // after oth = null
console.log("before und = " + und); // before und = undefined
passingvalue(und);
console.log("after und = " + und); // after und = undefined
console.log(sym); // Symbol(foo)
passingvalue(sym);
console.log(sym); // Symbol(foo)
console.log("before obj.inner = " + obj.inner); // before obj.inner = 10
passingobject(obj); // after obj.inner = 11
console.log("after obj.inner = " + obj.inner);It seems that the following two conclusions can be drawn from the results of example 1:
1. The data type passed It is a basic type (number, string boolean, null, undefined, symbol). During the parameter passing process, the operation of the passed value within the function does not affect the original value.
2. The data type passed is object. During the parameter passing process, the operation on the passed value inside the function will cause the original value to change.
However, are there any other special circumstances?
There is a usage that is very hotly discussed on stackoverflow, which goes against conclusion 2. example 2.
1 function changeStuff(a, b, c)
2 {
3 a = a * 10;
4 b.item = "changed";
5 c = {item: "changed"};
6 }
7
8 var num = 10;
9 var obj1 = {item: "unchanged"};
10 var obj2 = {item: "unchanged"};
11
12 console.log(obj1.item); // unchanged
13 console.log(obj2.item); // unchanged
14 changeStuff(num, obj1, obj2);
15 console.log(obj1.item); // changed
16 console.log(obj2.item); // unchangedIn example 2, obj2.item is not changed by the function changeStuff. The values of b and c are also changed internally in changeStuff. Why is obj1 changed (L15) but obj2 not changed?
I use the execution context of js to explain this phenomenon, as shown in the figure.
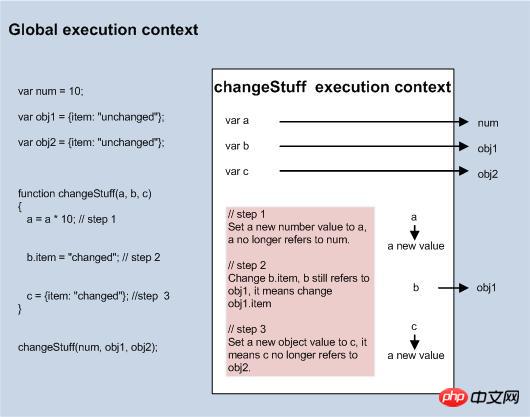
During the running of js, the editor dynamically generates an execution context (execution context). In example 2, the global execution context and the changeStuff execution context are first generated.
When changeStuff(num, obj1, obj2) is executed, a, b, c point to the parameters num, obj1, obj2, a and num point to 10, b and obj1 point to the same value, and c and obj2 point to same value.
When executing step 1, reassign a to 10 times the value before a was assigned. From now on, a has nothing to do with num.
When executing step 2, reassign the item attribute of the value pointed to by b. This assignment only changes the value of item, while obj1 and b still point to the same value.
When step 3 is executed, c is reassigned. From then on, c has nothing to do with obj2. Therefore, even if c has an attribute called item, it has its own value with the item attribute of obj2, and it does not affect obj2. item.
In other words, during the js function parameter passing process, if the parameters are reassigned inside the function, this assignment process will not affect the value of the original variable.
This also well explains the phenomenon that basic type parameter variables (Conclusion 1) will not be affected. Every change of basic type parameter variables is a new assignment and will not affect the original variables. .
Summary
In js function transfer, when basic type (number, string, boolean, null, undefined, symbol) variables are passed as parameters, the function internal Any operation on the parameters will not change the value of the variable.
When an object type variable is passed as a parameter, the operation on the parameter inside the function will affect the value of the variable, Unless the parameter is reassigned (any type of value) inside the function.
Thank you!
Feel free to contact me if you have any question!
The above is a detailed introduction to the understanding of values and references in JavaScript parameter passing. For more related content, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website (www.php.cn)!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 Best practices for optimizing Golang function parameter passing performance
Apr 13, 2024 am 11:15 AM
Best practices for optimizing Golang function parameter passing performance
Apr 13, 2024 am 11:15 AM
In order to optimize Go function parameter passing performance, best practices include: using value types to avoid copying small value types; using pointers to pass large value types (structures); using value types to pass slices; and using interfaces to pass polymorphic types. In practice, when passing large JSON strings, passing the data parameter pointer can significantly improve deserialization performance.
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
Introduction to the method of obtaining HTTP status code in JavaScript: In front-end development, we often need to deal with the interaction with the back-end interface, and HTTP status code is a very important part of it. Understanding and obtaining HTTP status codes helps us better handle the data returned by the interface. This article will introduce how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide specific code examples. 1. What is HTTP status code? HTTP status code means that when the browser initiates a request to the server, the service
 Detailed explanation of C++ function parameters: Performance optimization of parameter passing in parallel programming
Apr 27, 2024 pm 02:09 PM
Detailed explanation of C++ function parameters: Performance optimization of parameter passing in parallel programming
Apr 27, 2024 pm 02:09 PM
In a multi-threaded environment, function parameter passing methods are different, and the performance difference is significant: passing by value: copying parameter values, safe, but large objects are expensive. Pass by reference: Passing by reference is efficient, but function modifications will affect the caller. Pass by constant reference: Pass by constant reference, safe, but restricts the function's operation on parameters. Pass by pointer: Passing pointers is flexible, but pointer management is complex, and dangling pointers or memory leaks may occur. In parallel summation, passing by reference is more efficient than passing by value, and passing by pointer is the most flexible, but management is complicated.
 Research on parameter passing methods in Go language
Apr 03, 2024 pm 02:48 PM
Research on parameter passing methods in Go language
Apr 03, 2024 pm 02:48 PM
In the Go language, there are two main ways to pass function parameters: value passing: passing a copy of the variable will not affect the original variable in the calling code. Pointer passing: Passing the address of a variable allows the function to directly modify the original variable in the calling code.
 C++ function pointer parameter passing mechanism
Apr 19, 2024 pm 02:06 PM
C++ function pointer parameter passing mechanism
Apr 19, 2024 pm 02:06 PM
The function pointer is used as a parameter passing mechanism in C++: the function pointer is passed as a constant pointer, a copy is created during the passing process, the received function formal parameter points to the copy, and the dereferenced copy can call the underlying function.





