
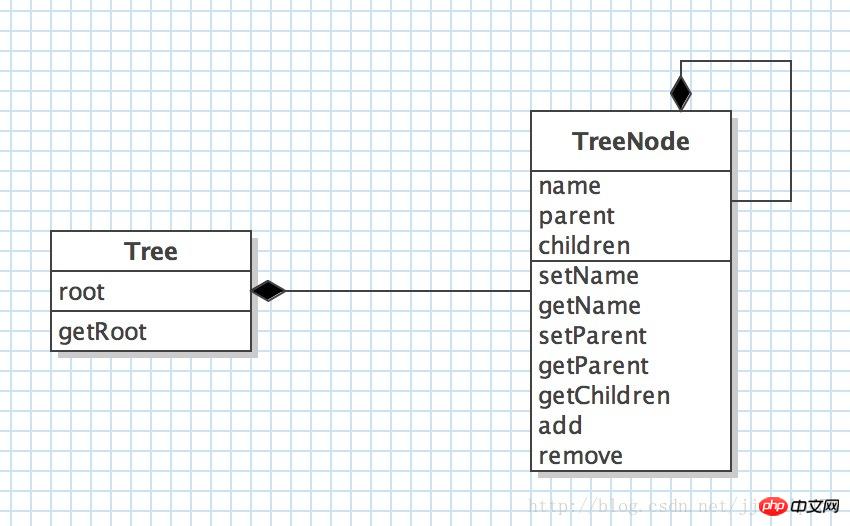
Class diagram
##
/**
* 树 整体
*
* @author stone
*
*/
public class Tree {
private TreeNode root; //根节点
public Tree(String name) {
this.root = new TreeNode(name);
}
public TreeNode getRoot() {
return root;
}
}/**
* 树节点 部份
* 也可以自身代表树:一堆节点组成了一颗树
*
* @author stone
*
*/
public class TreeNode {
private String name;
private TreeNode parent;
private List<TreeNode> children;
public TreeNode(String name) {
this.name = name;
this.children = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setParent(TreeNode parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
public TreeNode getParent() {
return parent;
}
public List<TreeNode> getChildren() {
return children;
}
public void add(TreeNode node) {
this.children.add(node);
}
public void remove(TreeNode node) {
this.children.remove(node);
}
}/*
* 组合(Composite)模式 又叫做部分-整体模式
* 它使我们层级、树形结构的问题中,模糊了简单元素和复杂元素的概念,客户程序可以像处理简单元素一样来处理复杂元素,从而使得客户程序与复杂元素的内部结构解耦
* 以下情况下适用Composite模式:
1.你想表示对象的部分-整体层次结构
2.你希望用户忽略组合对象与单个对象的不同,用户将统一地使用组合结构中的所有对象。
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Tree treeA = new Tree("A");
// treeA.getRoot().add(new TreeNode("B"));
// treeA.getRoot().add(new TreeNode("C"));
// TreeNode treeNodeD = new TreeNode("D");
// treeNodeD.add(new TreeNode("D1"));
// treeNodeD.add(new TreeNode("D2"));
// treeA.getRoot().add(treeNodeD);
// print(treeA.getRoot());
/*
* 上面使用了Tree对象,
* 下面只使用TreeNode对象,符合组合模式的定义,既代表部分也代表整体
*/
TreeNode treeA = new TreeNode("A");
treeA.add(new TreeNode("B"));
treeA.add(new TreeNode("C"));
TreeNode treeNodeD = new TreeNode("D");
treeNodeD.add(new TreeNode("D1"));
treeNodeD.add(new TreeNode("D2"));
treeA.add(treeNodeD);
print(treeA);
/*
* 其他示例:文件系统{目录、文件}, 类似这种可用递归遍历的结构,
* 用一个对象就能表示部分与整体,都可以用组合模式
*/
}
public static void print(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
LinkedList<TreeNode> linkedList = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
linkedList.add(root);
while (!linkedList.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = linkedList.removeFirst();
System.out.println(node.getName());
List<TreeNode> children = node.getChildren();
for (int i = 0; i < children.size(); i++) {
TreeNode next = children.get(i);
List<TreeNode> children2 = next.getChildren();
if (!children2.isEmpty()) {
linkedList.add(next);
} else {
System.out.println(next.getName());
}
}
}
}
}A B C D D1 D2
The above is the detailed content of A detailed introduction to the Composite pattern in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




