 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 In-depth understanding of the difference between typeof and instanceof in JavaScript
In-depth understanding of the difference between typeof and instanceof in JavaScript
In-depth understanding of the difference between typeof and instanceof in JavaScript
This time I mainly talk about the usage and precautions of JavaScript's type judgment function typeof and judgment constructor prototype instanceof.
typeof
Let’s talk about typeof first. The first thing to note is that the typeof method returns a string to represent the type of the data.
Grammar explanation
Let’s first look at the value of typeof corresponding to each data type:
| Data type | Type |
|---|---|
| Undefined | “undefined” |
| Null | "object" |
| Boolean value | "boolean" |
| numeric value | "number " |
| string | "string" |
| Symbol (new in ECMAScript 6) | " symbol” |
| Host object (provided by the JS environment, such as the browser) | Implementation-dependent |
| Function object | "function" |
| Any other object | "object" |
Look again Specific example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 |
|
We will find a problem, that is, typeof is not accurate to determine the data type. For example, the typeof return value of arrays, regular expressions, dates, and objects is all object, which will cause some errors.
So on the basis of typeof judging the type, we also need to use the Object.prototype.toString method to further judge the data type.
Let’s take a look at the difference between the return values of the toString method and the typeof method in the case of the same data type:
##new Number(1.2)Number objecttrueBooleanbooleannew Boolean(true )Booleanobjectnew Date()Dateobjectnew Error()Errorobject##new Array(1, 2, 3)##/abc/gRegExpobjectnew RegExp(“meow”)RegExpobject可以看到利用toString方法可以正确区分出Array、Error、RegExp、Date等类型。
所以我们一般通过该方法来进行数据类型的验证
真题检测
但是既然今天说到了typeof,那这里就列出几道题目,来看看自己是否真正掌握了typeof的用法。
第一题:
1 2 |
|
第二题:
1 2 3 |
|
第三题:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
|
第四题:
1 2 3 4 5 |
|
第五题:
1 2 |
|
第六题:
1 2 3 4 5 |
|
第七题:
1 2 3 |
|
下面公布答案了,这七题的答案分别是:
1 |
|
做对了几道呢?是不是很大的困惑呢?这几题虽然都有typeof,但是考察了很多javascript的基础噢。下面我们来一一详解。
第一题:
1 2 |
|
表达式是从右往左的,x由于变量提升,类型不是null,而是undefined,所以x=y=”undefined”。
变量提升我在这篇文章中提到过,可以看看。
第二题:
1 2 3 |
|
传入的参数为f也就是function(){ return 1; }这个函数。通过f()执行后,得到结果1,所以typeof 1返回”number”。这道题很简单,主要是区分f和f()。
第三题:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
|
这一题考察的是this的指向。this永远指向函数执行时的上下文,而不是定义时的(ES6的箭头函数不算)。当arguments执行时,this已经指向了window对象。所以是”undefined”。对this执行不熟悉的同学可以看看这篇文章:深入理解this,对刚刚提到的箭头函数感兴趣的同学可以看看初步探究ES6之箭头函数。
第四题:
1 2 3 4 5 |
|
如果上面那一题做对了,那么这一题也应该不会错,同样是this的指向问题。
第五题:
1 2 |
|
这一题比较容易错,因为我在遇到这道题之前也从来没有遇到过javascript的分组选择符。什么叫做分组选择符呢?举一个例子就会明白了:
1 2 |
|
所以上面的题目会返回2,typeof 2当然是”number”啦。
第六题:
1 2 3 4 5 |
|
这是一个javascript语言规范上的问题,在条件判断中加入函数声明。这个声明语句本身没有错,也会返回true,但是javascript引擎在搜索的时候却找不到该函数。所以结果为”1undefined”。
第七题:
1 2 3 |
|
这题其实是一个考察心细程度的题目。形参的foo指向的是{ foo: { bar: 1 } }这个整体。相信这么说就明白了。
好啦。上面的题目都是很好的资源噢。
instanceof
接下来该说说instanceof方法了。instanceof运算符可以用来判断某个构造函数的prototype属性是否存在于另外一个要检测对象的原型链上。
如果对原型不太了解,可以看看深入理解原型。
下面我们看看instanceof的实例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
|
但是这里我们需要注意一个问题:
1 2 3 4 |
|
第一个为什么返回false呢?因为构造函数的原型被覆盖了,我们可以看看new f和new g的区别:
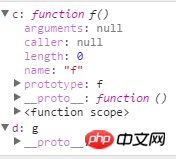
The above is the detailed content of In-depth understanding of the difference between typeof and instanceof in JavaScript. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1653
1653
 14
14
 1413
1413
 52
52
 1304
1304
 25
25
 1251
1251
 29
29
 1224
1224
 24
24
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
Usage: In JavaScript, the insertBefore() method is used to insert a new node in the DOM tree. This method requires two parameters: the new node to be inserted and the reference node (that is, the node where the new node will be inserted).
 How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
Introduction to the method of obtaining HTTP status code in JavaScript: In front-end development, we often need to deal with the interaction with the back-end interface, and HTTP status code is a very important part of it. Understanding and obtaining HTTP status codes helps us better handle the data returned by the interface. This article will introduce how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide specific code examples. 1. What is HTTP status code? HTTP status code means that when the browser initiates a request to the server, the service

| Data | toString | typeof |
|---|---|---|
| "foo" | String | string |
| new String(“foo”) | String | object |
| Array | object | |


