Operator
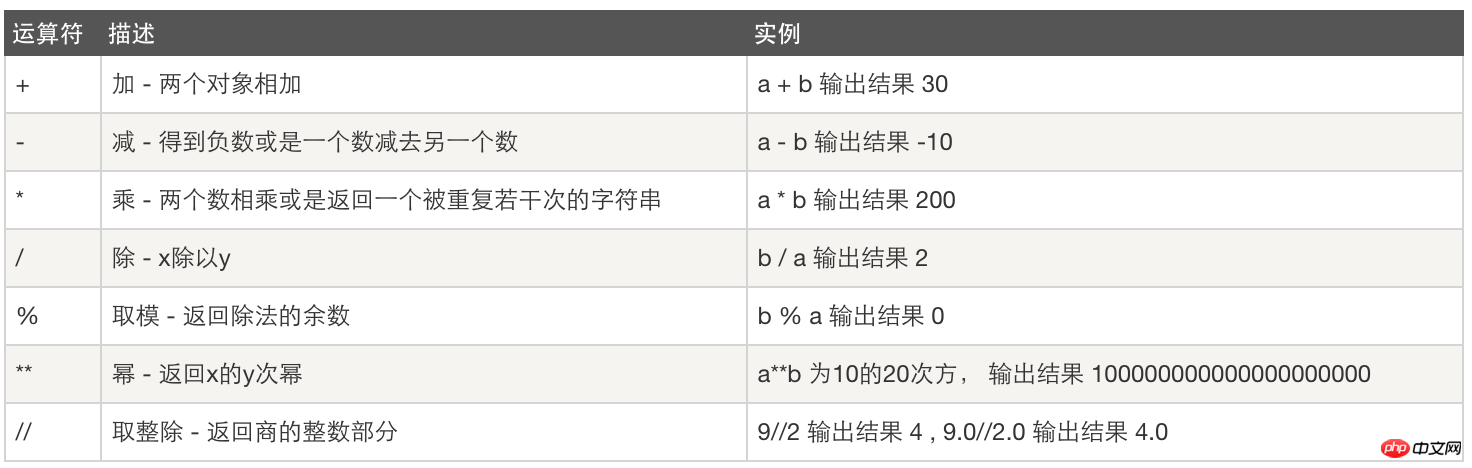
1. Arithmetic operations:

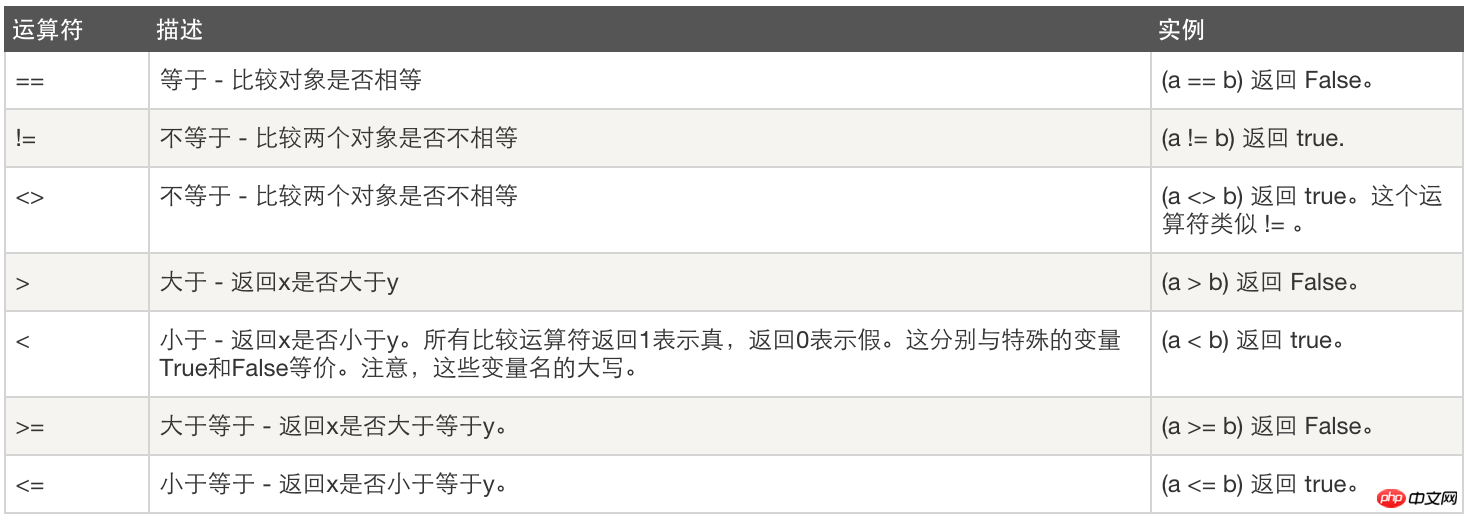
2. Comparison operations:

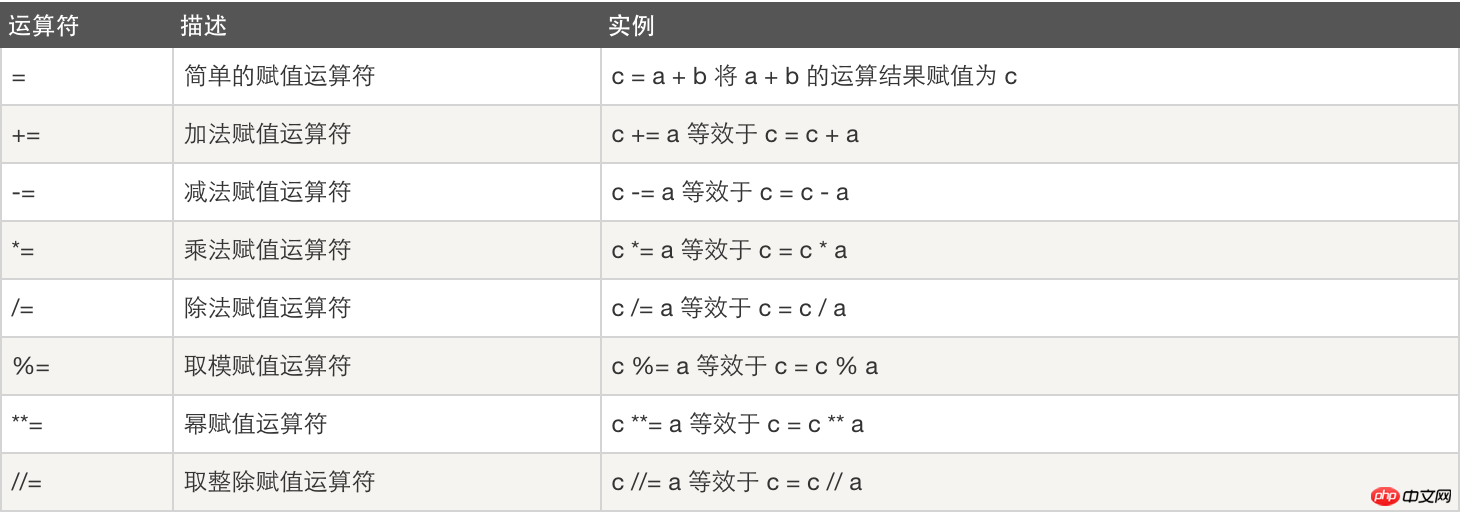
3. Assignment operation:

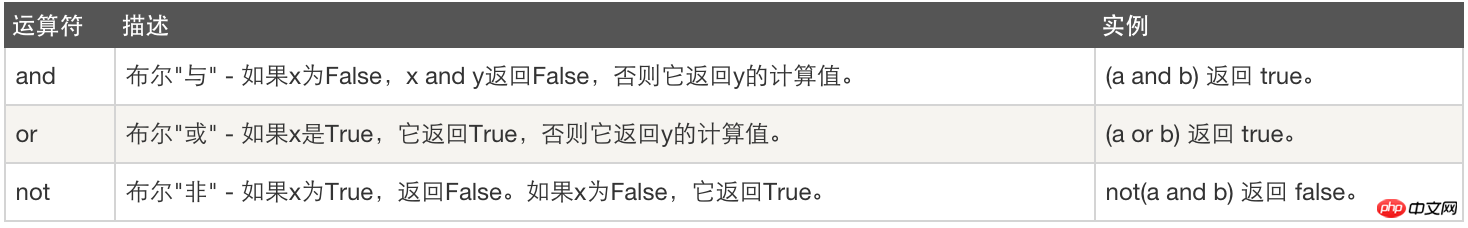
4. Logical operation:

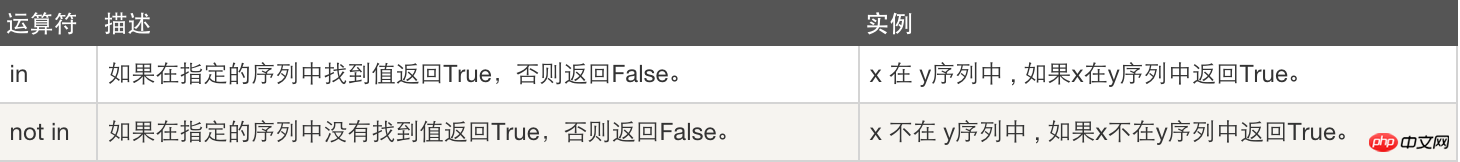
5. Member operation:

Basic data types
1. Number
int (integer type)
On a 32-bit machine, the number of digits in an integer It is 32 bits, and the value range is -2**31~2**31-1, that is, -2147483648~2147483647
On a 64-bit system, the number of digits in the integer is 64 bits, and the value range is -2* *63~2**63-1, that is -9223372036854775808~9223372036854775807
##2, Boolean value
True or False
1 Or 0
3, string
"hello world"
Common functions of strings:
Remove whitespace
Separation
Length
Index
Slice
4. List
Create a list:
name_list = ['alex', 'seven', 'eric']
or
name_list = list(['alex', 'seven', 'eric'])
##Basic operations:
Index
Slice
Append
Delete
Length
Slice
Loop
Contains
##5, Yuanzu
Create Yuanzu:
ages = (11, 22, 33, 44, 55)
or
ages = tuple((11, 22, 33, 44, 55))
Basic operations:
Index
Slice
Loop
Length
Contains
6, dictionary (unordered)
Create dictionary:
person = {"name": "mr.wu" , 'age': 18}
or
person = dict({"name": "mr.wu", 'age': 18})
Common operations:
Index
Add
Delete
Key, value, key-value pair
Loop
Length
PS: loop, range, continue and break
Others
1. for loop
The user loops the contents of the iterable object in order,
PS: break, continue
li = [11,22,33,44]
for item in li:
print item
2, enumrate
Add serial number to iterable object
li = [11,22,33 ]
for k,v in enumerate(li, 1):
print(k,v)
3, range and xrange
Specify range , generate the specified number
print range(1, 10)
# Result: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
print range(1, 10, 2)
# Result: [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
print range(30, 0, -2)
# Result: [30, 28, 26, 24, 22, 20, 18, 16, 14, 12, 10, 8, 6, 4, 2]
Exercise questions
1. Element classification
has the following value set [11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90... ], save all values greater than 66 to the first key of the dictionary, and save values less than 66 to the value of the second key.
That is: {'k1': all values greater than 66, 'k2': all values less than 66}
2. Search
Find the elements in the list and remove each elements, and finds all elements starting with a or A and ending with c.
li = ["alec", " aric", "Alex", "Tony", "rain"]
tu = ("alec", " aric", "Alex", "Tony", "rain")
dic = {'k1': "alex", 'k2': ' aric', "k3": "Alex", "k4": "Tony"}
3. Output the product list, the user enters the serial number, and the product selected by the user is displayed
Product li = ["Mobile phone", "Computer", 'Mouse pad', ' Yacht']
4. Shopping cart
Functional requirements:
Requires the user to enter total assets, for example: 2000
display The product list allows users to select products based on serial numbers and add them to the shopping cart
for purchase. If the total number of products is greater than the total assets, it will prompt that the account balance is insufficient. Otherwise, the purchase is successful.
Additional: Can be recharged, a certain product can be removed from the shopping cart
goods = [
{"name": "Computer", "price" : 1999},
{"name": "mouse", "price": 10},
{"name": "yacht", "price": 20},
{"name": "Beauty", "price": 998},
]
5. User interaction, displaying the selection of three-level linkage between provinces, cities and counties
dic = {
"Hebei": {
"Shijiazhuang": ["Luquan", "Gaocheng", "Yuanshi"],
"Handan": ["Yongnian", "Shexian", "Cixian"],
}
"Henan": {
...
}
"Shanxi": {
...
}
}
The above is the detailed content of Introduction to python basic data types. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!