 Backend Development
Backend Development
 XML/RSS Tutorial
XML/RSS Tutorial
 Sample code of tree structure and DOM document object model in XML (picture)
Sample code of tree structure and DOM document object model in XML (picture)
Sample code of tree structure and DOM document object model in XML (picture)
This article mainly introduces the tree structure and DOM document object model in XML. The article gives an example of JavaScript parsing DOM objects. Friends in need can refer to the following
Tree structure
XML documents are always descriptive. Tree structures, often called XML trees, play an important role in describing XML documents.
This tree structure contains root (parent) elements, child elements, etc. By using a tree structure, we can understand all subsequent branches and sub-branches originating from the root element. Parsing starts at the root element and then moves down to the first branch pointing to an element, from where the first branch and its children are processed.
Example
The following example demonstrates a simple XML tree structure:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<Company>
<Employee>
<FirstName>Tanmay</FirstName>
<LastName>Patil</LastName>
<ContactNo>1234567890</ContactNo>
<Email>tanmaypatil@xyz.com</Email>
<Address>
<City>Bangalore</City>
<State>Karnataka</State>
<Zip>560212</Zip>
</Address>
</Employee>
</Company>The following tree structure represents the above XML document: 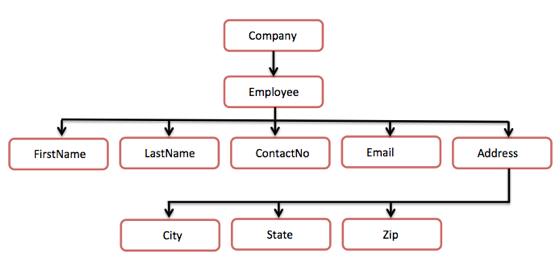
In the picture, there is a root element called
DOM Document Object Model
The Document Object Model (DOM) is the basis of XML. XML documents have a hierarchical unit of information called a node; the DOM is a way of describing these nodes and the relationships between them.
A DOM document is a collection of nodes or blocks of information organized in a hierarchical structure. This hierarchy allows developers to navigate this node tree to query specific information. Because it is based on an information hierarchy, the DOM is also considered node-tree-based.
On the other hand, XML DOM also provides an API that allows developers to add, edit, move or remove nodes anywhere in the node tree in order to create applications.
Sample
The following example (sample.htm) parses an XML document ("address.xml") into an XML DOM object and then extracts some information using JavaScript:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>TutorialsPoint DOM example </h1>
<div>
<b>Name:</b> <span id="name"></span><br>
<b>Company:</b> <span id="company"></span><br>
<b>Phone:</b> <span id="phone"></span>
</div>
<script>
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {// code for IE7+, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, Safari
xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else {// code for IE6, IE5
xmlhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xmlhttp.open("GET","/xml/address.xml",false);
xmlhttp.send();
xmlDoc=xmlhttp.responseXML;
document.getElementById("name").innerHTML=
xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("name")[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue;
document.getElementById("company").innerHTML=
xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("company")[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue;
document.getElementById("phone").innerHTML=
xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("phone")[0].childNodes[0].nodeValue;
</script>
</body
</html>The content of address.xml is as follows:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<contact-info>
<name>Tanmay Patil</name>
<company>TutorialsPoint</company>
<phone>(011) 123-4567</phone>
</contact-info>We can save these two files sample.htm and address.xml to the same directory/xml, Then execute the sample.htm file by opening it in a browser. It should produce a result like this: 
Here, you can see that we extracted each child node and displayed their value.
The above is the detailed content of Sample code of tree structure and DOM document object model in XML (picture). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1389
1389
 52
52
 Can I open an XML file using PowerPoint?
Feb 19, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Can I open an XML file using PowerPoint?
Feb 19, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Can XML files be opened with PPT? XML, Extensible Markup Language (Extensible Markup Language), is a universal markup language that is widely used in data exchange and data storage. Compared with HTML, XML is more flexible and can define its own tags and data structures, making the storage and exchange of data more convenient and unified. PPT, or PowerPoint, is a software developed by Microsoft for creating presentations. It provides a comprehensive way of
 Convert XML data to CSV format in Python
Aug 11, 2023 pm 07:41 PM
Convert XML data to CSV format in Python
Aug 11, 2023 pm 07:41 PM
Convert XML data in Python to CSV format XML (ExtensibleMarkupLanguage) is an extensible markup language commonly used for data storage and transmission. CSV (CommaSeparatedValues) is a comma-delimited text file format commonly used for data import and export. When processing data, sometimes it is necessary to convert XML data to CSV format for easy analysis and processing. Python is a powerful
 Filtering and sorting XML data using Python
Aug 07, 2023 pm 04:17 PM
Filtering and sorting XML data using Python
Aug 07, 2023 pm 04:17 PM
Implementing filtering and sorting of XML data using Python Introduction: XML is a commonly used data exchange format that stores data in the form of tags and attributes. When processing XML data, we often need to filter and sort the data. Python provides many useful tools and libraries to process XML data. This article will introduce how to use Python to filter and sort XML data. Reading the XML file Before we begin, we need to read the XML file. Python has many XML processing libraries,
 Python implements conversion between XML and JSON
Aug 07, 2023 pm 07:10 PM
Python implements conversion between XML and JSON
Aug 07, 2023 pm 07:10 PM
Python implements conversion between XML and JSON Introduction: In the daily development process, we often need to convert data between different formats. XML and JSON are common data exchange formats. In Python, we can use various libraries to convert between XML and JSON. This article will introduce several commonly used methods, with code examples. 1. To convert XML to JSON in Python, we can use the xml.etree.ElementTree module
 Handling errors and exceptions in XML using Python
Aug 08, 2023 pm 12:25 PM
Handling errors and exceptions in XML using Python
Aug 08, 2023 pm 12:25 PM
Handling Errors and Exceptions in XML Using Python XML is a commonly used data format used to store and represent structured data. When we use Python to process XML, sometimes we may encounter some errors and exceptions. In this article, I will introduce how to use Python to handle errors and exceptions in XML, and provide some sample code for reference. Use try-except statement to catch XML parsing errors When we use Python to parse XML, sometimes we may encounter some
 Python parsing special characters and escape sequences in XML
Aug 08, 2023 pm 12:46 PM
Python parsing special characters and escape sequences in XML
Aug 08, 2023 pm 12:46 PM
Python parses special characters and escape sequences in XML XML (eXtensibleMarkupLanguage) is a commonly used data exchange format used to transfer and store data between different systems. When processing XML files, you often encounter situations that contain special characters and escape sequences, which may cause parsing errors or misinterpretation of the data. Therefore, when parsing XML files using Python, we need to understand how to handle these special characters and escape sequences. 1. Special characters and
 How to handle XML and JSON data formats in C# development
Oct 09, 2023 pm 06:15 PM
How to handle XML and JSON data formats in C# development
Oct 09, 2023 pm 06:15 PM
How to handle XML and JSON data formats in C# development requires specific code examples. In modern software development, XML and JSON are two widely used data formats. XML (Extensible Markup Language) is a markup language used to store and transmit data, while JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data exchange format. In C# development, we often need to process and operate XML and JSON data. This article will focus on how to use C# to process these two data formats, and attach
 Using Python to implement data verification in XML
Aug 10, 2023 pm 01:37 PM
Using Python to implement data verification in XML
Aug 10, 2023 pm 01:37 PM
Using Python to implement data validation in XML Introduction: In real life, we often deal with a variety of data, among which XML (Extensible Markup Language) is a commonly used data format. XML has good readability and scalability, and is widely used in various fields, such as data exchange, configuration files, etc. When processing XML data, we often need to verify the data to ensure the integrity and correctness of the data. This article will introduce how to use Python to implement data verification in XML and give the corresponding



