 Backend Development
Backend Development
 XML/RSS Tutorial
XML/RSS Tutorial
 Detailed introduction to DTD document type definition in XML
Detailed introduction to DTD document type definition in XML
Detailed introduction to DTD document type definition in XML
This article mainly introduces the DTD document type definition in XML, which is the basic knowledge for introductory learning of XML. Friends who need it can refer to
XML document type definition, commonly known as DTD, it is a Accurately describe the way the XML language is used. DTDs check the validity of the vocabulary and structure of an XML document against the syntax rules of the appropriate XML language.
XML DTD can be specified inside the document, or it can be saved in a separate document and linked separately.
Syntax
The basic syntax of DTD is as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
In the above syntax:
DTD starts with < ;!DOCTYPE delimiter starts. <br/>element is used to tell the parser to start parsing the document from the specified root element. <br/>DTD identifier is an identifier used for document type definition. It can be a path to a file in the system or a URL connected to a file on the Internet. If the DTD points to an external path, it is called an external subset. Inside _[] is an optional list of entity declarations, called the inner subset. <br/>Internal DTD<br/>If an element is declared inside an XML document then the DTD is called an internal DTD. In order for this to be used as an internal DTD, the standalone attribute in the XML declaration must be set to yes. This means that the claimed work is independent of external sources.
Syntax
The internal DTD syntax is as follows:
1 |
|
Here root-element is the name of the root element, element -declarations represents the elements we declare.
Example
Here is a simple example of an internal DTD:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
|
Let’s take a look at the above code:
Start Declaration - Begin the XML declaration with the following statement:
1 |
|
DTD - Immediately after the XML header, the _Document Type Declaration_ is as follows, often referred to as DOCTYPE:
DTD Body - The DOCTYPE declaration is followed by the DTD body, where we declare elements, attributes, entities and symbols:
1 2 3 4 |
|
Many elements are passed here by
End declaration - Finally, the declaration part of the DTD is closed using square brackets and angle brackets (]>). This is a valid closing definition, followed immediately by the XML document content.
Rules
The document type declaration must appear at the beginning of the document (only with the XML header) and is not allowed to appear anywhere else in the document. <br/>Similar to DOCTYPE declarations, element declarations must begin with an exclamation point. <br/>The Name in the document type declaration must match the type of the root element. <br/>External DTD<br/>In an external DTD elements are declared outside the XML document. Accessed by specifying the system attribute, which can be a valid .dtd file or a valid URL. To indicate that it is an external DTD, the XML declaration's standalone attribute must be set to no. This means that the statement contains information from an external source.
Syntax
The following is the syntax of external DTD:
1 |
|
Here file-name is the file with .dtd extension. <br/>
Example
The following example shows the use of an external DTD:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
|
Type
We can reference an external DTD by using the system identifier or the public identifier.
System Identifier
The system identifier allows us to specify the location of an external file that contains the DTD declaration. The syntax is as follows:
1 |
|
As we can see, it contains the SYSTEM keyword and a URI reference pointing to the location of the document.
Public Identifier
The public identifier provides a mechanism for locating DTD resources. It is written as follows:
1 |
|
As we can see, it starts with the PUBLIC keyword, followed by the specialized identifier. Public identifiers are used to identify entries in the directory. Public identifiers can follow any format, but a commonly used format is Formal Public Identifiers (or FPIs).
Declare elements<br/>Declare elements in dtd (in an xml, if you want an element to be legal, you need to declare it in dtd)<br/> Syntax:< ;!ELEMENT element name category> and these two methods<br/>
For example:
1 |
|
The xml can be written as:
1 |
|
注意点
在dtd中
所有的 XML 文档(以及 HTML 文档)均由以下简单的构建模块构成:
元素
属性
实体
PCDATA
CDATA
下面是一些注意点:
(1)实体是用来定义普通文本的变量。实体引用是对实体的引用。
大多数同学都了解这个 HTML 实体引用:" "。这个“无折行空格”实体在 HTML 中被用于在某个文档中插入一个额外的空格。
当文档被 XML 解析器解析时,实体就会被展开。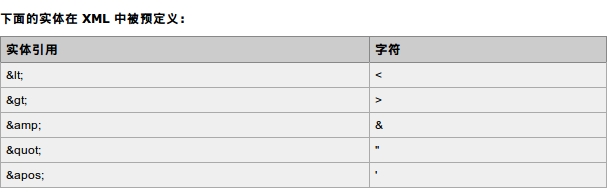
(2) PCDATA
PCDATA 的意思是被解析的字符数据(parsed character data)。
可把字符数据想象为 XML 元素的开始标签与结束标签之间的文本。
PCDATA 是会被解析器解析的文本。这些文本将被解析器解析成实体以及标记。
文本中的标签会被当作标记来处理,而实体会被展开。
不过,被解析的字符数据不应当包含任何 &、< 或者 > 字符;需要使用 &、< 以及 > 实体来分别替换它们。
(3)CDATA
CDATA 的意思是字符数据(character data)。
CDATA 是不会被解析器解析的文本。在这些文本中的标签不会被当作标记来对待,其中的实体也不会被展开。
The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to DTD document type definition in XML. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1392
1392
 52
52
 Can I open an XML file using PowerPoint?
Feb 19, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Can I open an XML file using PowerPoint?
Feb 19, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Can XML files be opened with PPT? XML, Extensible Markup Language (Extensible Markup Language), is a universal markup language that is widely used in data exchange and data storage. Compared with HTML, XML is more flexible and can define its own tags and data structures, making the storage and exchange of data more convenient and unified. PPT, or PowerPoint, is a software developed by Microsoft for creating presentations. It provides a comprehensive way of
 Using Python to merge and deduplicate XML data
Aug 07, 2023 am 11:33 AM
Using Python to merge and deduplicate XML data
Aug 07, 2023 am 11:33 AM
Using Python to merge and deduplicate XML data XML (eXtensibleMarkupLanguage) is a markup language used to store and transmit data. When processing XML data, sometimes we need to merge multiple XML files into one, or remove duplicate data. This article will introduce how to use Python to implement XML data merging and deduplication, and give corresponding code examples. 1. XML data merging When we have multiple XML files, we need to merge them
 Convert XML data to CSV format in Python
Aug 11, 2023 pm 07:41 PM
Convert XML data to CSV format in Python
Aug 11, 2023 pm 07:41 PM
Convert XML data in Python to CSV format XML (ExtensibleMarkupLanguage) is an extensible markup language commonly used for data storage and transmission. CSV (CommaSeparatedValues) is a comma-delimited text file format commonly used for data import and export. When processing data, sometimes it is necessary to convert XML data to CSV format for easy analysis and processing. Python is a powerful
 Filtering and sorting XML data using Python
Aug 07, 2023 pm 04:17 PM
Filtering and sorting XML data using Python
Aug 07, 2023 pm 04:17 PM
Implementing filtering and sorting of XML data using Python Introduction: XML is a commonly used data exchange format that stores data in the form of tags and attributes. When processing XML data, we often need to filter and sort the data. Python provides many useful tools and libraries to process XML data. This article will introduce how to use Python to filter and sort XML data. Reading the XML file Before we begin, we need to read the XML file. Python has many XML processing libraries,
 Import XML data into database using PHP
Aug 07, 2023 am 09:58 AM
Import XML data into database using PHP
Aug 07, 2023 am 09:58 AM
Importing XML data into the database using PHP Introduction: During development, we often need to import external data into the database for further processing and analysis. As a commonly used data exchange format, XML is often used to store and transmit structured data. This article will introduce how to use PHP to import XML data into a database. Step 1: Parse the XML file First, we need to parse the XML file and extract the required data. PHP provides several ways to parse XML, the most commonly used of which is using Simple
 Python implements conversion between XML and JSON
Aug 07, 2023 pm 07:10 PM
Python implements conversion between XML and JSON
Aug 07, 2023 pm 07:10 PM
Python implements conversion between XML and JSON Introduction: In the daily development process, we often need to convert data between different formats. XML and JSON are common data exchange formats. In Python, we can use various libraries to convert between XML and JSON. This article will introduce several commonly used methods, with code examples. 1. To convert XML to JSON in Python, we can use the xml.etree.ElementTree module
 Handling errors and exceptions in XML using Python
Aug 08, 2023 pm 12:25 PM
Handling errors and exceptions in XML using Python
Aug 08, 2023 pm 12:25 PM
Handling Errors and Exceptions in XML Using Python XML is a commonly used data format used to store and represent structured data. When we use Python to process XML, sometimes we may encounter some errors and exceptions. In this article, I will introduce how to use Python to handle errors and exceptions in XML, and provide some sample code for reference. Use try-except statement to catch XML parsing errors When we use Python to parse XML, sometimes we may encounter some
 Python parsing special characters and escape sequences in XML
Aug 08, 2023 pm 12:46 PM
Python parsing special characters and escape sequences in XML
Aug 08, 2023 pm 12:46 PM
Python parses special characters and escape sequences in XML XML (eXtensibleMarkupLanguage) is a commonly used data exchange format used to transfer and store data between different systems. When processing XML files, you often encounter situations that contain special characters and escape sequences, which may cause parsing errors or misinterpretation of the data. Therefore, when parsing XML files using Python, we need to understand how to handle these special characters and escape sequences. 1. Special characters and



