A detailed introduction to HTML5-creating HTML documents
One of the major changes in HTML5 is: Separating the semantics of an element from the impact of the element on the rendering results of its content. In principle, this makes sense. HTML elements are responsible for the structure and meaning of the document content, and the presentation of the content is controlled by CSS styles applied to the elements. The following introduces the most basic HTML elements: document elements and metadata elements.
1. Build the basic document structure
There are only 4 document elements: DOCTYPE element, html element, head element, and body element.
1. DOCTYPE element
Every HTML document must start with a DOCTYPE element. It tells the browser two things: first, that it is dealing with an HTML document; and second, the version of HTML used to mark up the document's content.
Note, the DTD required in HTML4 is no longer used in HTML5!
If the web page code contains the DOCTYPE element, the browser will parse it according to the standards you declare;
If you do not add the DOCTYPE element, the browser will Put the web page into quirks mode, there will be a certain difference between the two! !
<!-- HTML4 --><!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/strict.dtd">
<!-- HTML5 --><!DOCTYPE HTML>2. Other elements
<!DOCTYPE HTML><html>
<head>
<title>title</title>
</head>
<body>
文档内容 </body></html>It should be noted that there must be a title element in the head element!
2. Use metadata elements to describe documents
Metadata elements should be placed in the head element.
1. Set the document title: title element
2. Set the parsing base for relative URLs
The base element can be used to set a base URL for relative links in HTML documents Analyze on this basis. The base element also sets how the link opens when the user clicks it, and how the browser reacts when the form is submitted (described in Chapter 12, Forms).
<!doctype html><html lang="en"><head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Base Test</title>
<!-- 指定相对URL的基准URL -->
<base href="http://avatar.csdn.net">
<!-- 指定链接打开方式为:当前页面 -->
<base target="_self"></head><body>
<!-- 图片地址:http://www.php.cn/ -->
<img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="/1/4/A/1_ligang2585116.jpg" class="lazy" alt="奋飞">
<a href="http://http://www.php.cn/">PHP中文网</a></body></html>Note: If you do not specify a base URL, the browser will identify the URL of the current document as the parsing base for all relative URLs.
3. Use metadata to describe the document
The meta element can be used to define various metadata of the document; each meta element can only be used for one purpose.
(1) Specify the name/value metadata pair
You need to use its name and content attributes. 5 predefined metadata names are provided.
| Metadata name | Description |
|---|---|
| The name of the web application system to which the current page belongs | |
| The author name of the current page | |
| Description of the current page | |
| The name of the software used to generate HTML | |
| A batch of comma-separated strings used to describe the content of the page |
Description: Tell the browser how to classify and grade the content, In the past, the main method was to use keywords metadata. It is now devalued due to its misuse to create the illusion of page content and relevance. (2) Meta is widely used
<!-- 文档内容的字符编码 --> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html charset=UTF-8"> <!-- 5s后刷新当前页面 --> <meta http-equiv="refresh" content="5"> <!-- 5s后跳转到MyBlog --> <meta http-equiv="refresh" content="5; http://www.php.cn/">
(1) Specify the media to which the style applies
media attribute can be used to indicate under what circumstances the document should use the style defined in this element.
| Description | |
|---|---|
| All devices (Default) | ##aural |
| braille | |
| handheld | |
| projection | |
| #screen | |
| tty | |
| tv | |
It should be noted that 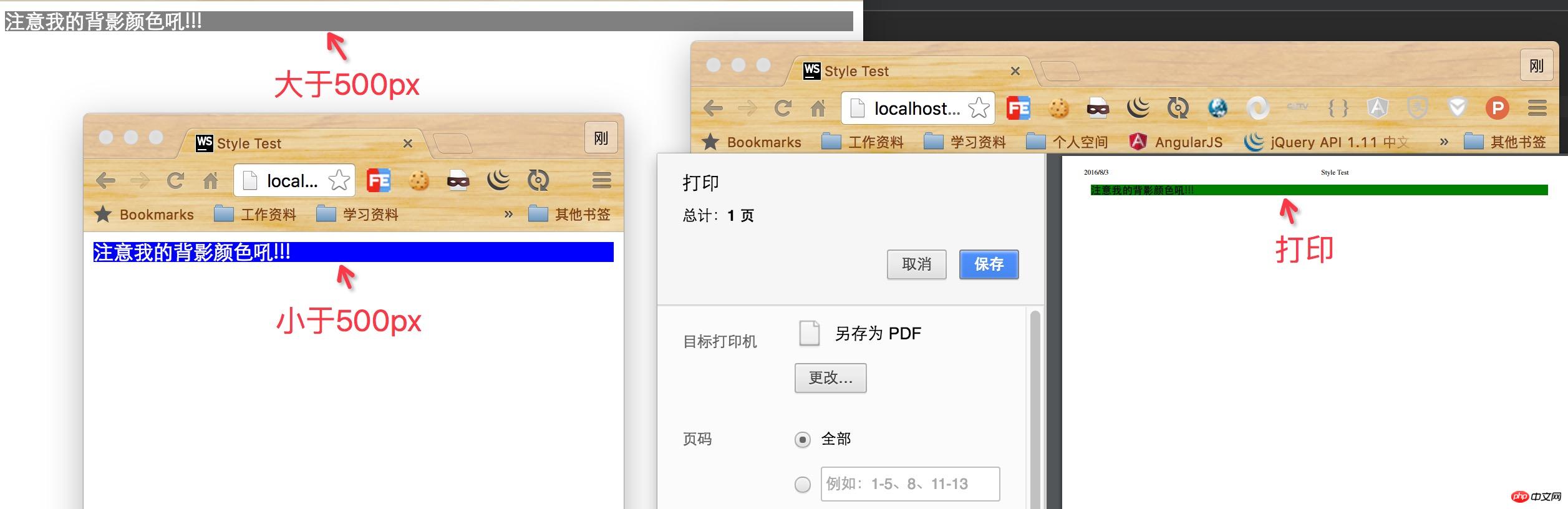 , when using the above media attributes, you need to conduct comprehensive testing and prepare unavailable backup styles.
, when using the above media attributes, you need to conduct comprehensive testing and prepare unavailable backup styles.
(2) Specify external resources The link tag also supports the media attribute. Among them, the ref attribute determines how the browser treats the link element.
| #help | |
| icon | |
| license | |
| stylesheet | |
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Link Test</title>
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="favicon.ico" type="image/x-icon" /></head><body></body></html>Copy after login 注意:如果网站标志文件位于项目根目录下,就无需使用link元素加载,其会自动请求加载该文件。 三、使用脚本元素与脚本相关的有两个元素:第一个是script,定义脚本并控制其执行过程;第二个是noscript,规定浏览器不支持脚本或禁用脚本情况的处理方法。 <!-- 未启用或不支持脚本 --><noscript>
<!-- 5s后跳转到http://www.php.cn/ -->
<meta http-equiv="refresh" content="5; http://www.php.cn/"></noscript>Copy after login The above is the detailed content of A detailed introduction to HTML5-creating HTML documents. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website! Statement of this Website
The content of this article is voluntarily contributed by netizens, and the copyright belongs to the original author. This site does not assume corresponding legal responsibility. If you find any content suspected of plagiarism or infringement, please contact admin@php.cn

Hot AI Tools
Undresser.AI UndressAI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos 
AI Clothes RemoverOnline AI tool for removing clothes from photos. 
Undress AI ToolUndress images for free 
Clothoff.ioAI clothes remover 
AI Hentai GeneratorGenerate AI Hentai for free. 
Hot Article
R.E.P.O. Energy Crystals Explained and What They Do (Yellow Crystal)
2 weeks ago
By 尊渡假赌尊渡假赌尊渡假赌
Hello Kitty Island Adventure: How To Get Giant Seeds
1 months ago
By 尊渡假赌尊渡假赌尊渡假赌
How Long Does It Take To Beat Split Fiction?
4 weeks ago
By DDD
R.E.P.O. Save File Location: Where Is It & How to Protect It?
4 weeks ago
By DDD
Two Point Museum: All Exhibits And Where To Find Them
1 months ago
By 尊渡假赌尊渡假赌尊渡假赌

Hot Tools
Notepad++7.3.1Easy-to-use and free code editor 
SublimeText3 Chinese versionChinese version, very easy to use 
Zend Studio 13.0.1Powerful PHP integrated development environment 
Dreamweaver CS6Visual web development tools 
SublimeText3 Mac versionGod-level code editing software (SublimeText3) 
Hot Topics Table Border in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Table Border in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Guide to Table Border in HTML. Here we discuss multiple ways for defining table-border with examples of the Table Border in HTML.  Nested Table in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Nested Table in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
This is a guide to Nested Table in HTML. Here we discuss how to create a table within the table along with the respective examples.  HTML margin-left
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
HTML margin-left
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
Guide to HTML margin-left. Here we discuss a brief overview on HTML margin-left and its Examples along with its Code Implementation.  HTML Table Layout
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML Table Layout
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Guide to HTML Table Layout. Here we discuss the Values of HTML Table Layout along with the examples and outputs n detail.  HTML Ordered List
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
HTML Ordered List
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
Guide to the HTML Ordered List. Here we also discuss introduction of HTML Ordered list and types along with their example respectively  Moving Text in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Moving Text in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Guide to Moving Text in HTML. Here we discuss an introduction, how marquee tag work with syntax and examples to implement.  HTML Input Placeholder
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML Input Placeholder
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Guide to HTML Input Placeholder. Here we discuss the Examples of HTML Input Placeholder along with the codes and outputs.  HTML onclick Button
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
HTML onclick Button
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Guide to HTML onclick Button. Here we discuss their introduction, working, examples and onclick Event in various events respectively. 
|





