
Vista and Windows 7 operating systems have added UAC (User Account Control) in order to enhance security Mechanism, if UAC is turned on, even if the user logs in with administrator privileges, his application will not be able to write to the system directory, system registry and other settings that may affect the operation of the system by default. This mechanism greatly enhances the system's security. Security, but for application developers, we cannot force users to turn off UAC, but sometimes the applications we develop need to be run as Administrator, that is, as administrator in Win7, so how do we achieve this? What about the function?
When we run some installation programs under win7, we will find that a dialog box will pop up first, asking the user to confirm whether to allow this program to change your computer configuration, but we The application written will not pop up this prompt by default, and it cannot be run with administrator privileges. This article introduces how to set up the C# program to prompt the user to run with administrator privileges.
First. Add an Application Manifest File

The default configuration is as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <asmv1:assembly manifestVersion="1.0" xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1"
xmlns:asmv1="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1" xmlns:asmv2="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v2"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<assemblyIdentity version="1.0.0.0" name="MyApplication.app"/>
<trustInfo xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v2">
<security>
<requestedPrivileges xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v3">
<!-- UAC Manifest Options
If you want to change the Windows User Account Control level replace the
requestedExecutionLevel node with one of the following.
<requestedExecutionLevel level="asInvoker" uiAccess="false" />
<requestedExecutionLevel level="requireAdministrator" uiAccess="false" />
<requestedExecutionLevel level="highestAvailable" uiAccess="false" />
If you want to utilize File and Registry Virtualization for backward
compatibility then delete the requestedExecutionLevel node.
-->
<requestedExecutionLevel level="asInvoker" uiAccess="false" />
</requestedPrivileges>
</security>
</trustInfo>
</asmv1:assembly>us You can see that there is a requestedExecutionLevel item in this configuration, which is used to configure the execution permission level requested by the current application. This item has 3 values to choose from, as shown in the following table:
| Value | Description | Comment |
| asInvoker | The application runs with the same access token as the parent process . | Recommended for standard user applications. Do refractoring with internal elevation points, as per the guidance provided earlier in this document. |
| highestAvailable | The application runs with the highest privileges the current user can obtain. | Recommended for mixed-mode applications. Plan to refractor the application in a future release. |
| requireAdministrator | The application runs only for administrators and requires that the application be launched with the full access token of an administrator. | Recommended for administrator only applications. Internal elevation points are not needed. The application is already running elevated. |
asInvoker : 如果选这个,应用程序就是以当前的权限运行。
highestAvailable: 这个是以当前用户可以获得的最高权限运行。
requireAdministrator: 这个是仅以系统管理员权限运行。
默认情况下是 asInvoker。
highestAvailable 和 requireAdministrator 这两个选项都可以提示用户获取系统管理员权限。那么这两个选项的区别在哪里呢?
他们的区别在于,如果我们不是以管理员帐号登录,那么如果应用程序设置为 requireAdministrator ,那么应用程序就直接运行失败,无法启动。而如果设置为 highestAvailable,则应用程序可以运行成功,但是是以当前帐号的权限运行而不是系统管理员权限运行。如果我们希望程序在非管理员帐号登录时也可以运行(这种情况下应该某些功能受限制) ,那么建议采用 highestAvailable 来配置。
关于requestedExecutionLevel 设置的权威文档请参考下面链接:
Create and Embed an Application Manifest (UAC)
下面是修改后的配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <asmv1:assembly manifestVersion="1.0" xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1"
xmlns:asmv1="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1" xmlns:asmv2="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v2"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<assemblyIdentity version="1.0.0.0" name="MyApplication.app"/>
<trustInfo xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v2">
<security>
<requestedPrivileges xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v3">
<!-- UAC Manifest Options
If you want to change the Windows User Account Control level replace the
requestedExecutionLevel node with one of the following.
<requestedExecutionLevel level="asInvoker" uiAccess="false" />
<requestedExecutionLevel level="requireAdministrator" uiAccess="false" />
<requestedExecutionLevel level="highestAvailable" uiAccess="false" />
If you want to utilize File and Registry Virtualization for backward
compatibility then delete the requestedExecutionLevel node.
-->
<requestedExecutionLevel level="requireAdministrator" uiAccess="false" />
</requestedPrivileges>
</security>
</trustInfo>
</asmv1:assembly>配置文件修改后,我们运行应用程序,就会首先弹出这样一个提示框,点 Yes 后,程序才可以继续运行,并且获得系统管理员的权限。
.csharpcode,
.csharpcode pre { font-size: small; color: black;
font-family: consolas, "Courier New", courier, monospace; background-color: #ffffff; /*white-space: pre;*/ }
.csharpcode pre { margin: 0em; }
.csharpcode .rem { color:
#008000; } .csharpcode .kwrd { color: #0000ff; } .csharpcode .str { color: #006080; } .csharpcode
.op { color: #0000c0; } .csharpcode .preproc { color: #cc6633; } .csharpcode .asp { background-color: #ffff00; }
.csharpcode .html { color: #800000; } .csharpcode
.attr { color: #ff0000; } .csharpcode .alt { background-color: #f4f4f4; width: 100%; margin: 0em; }
.csharpcode .lnum { color: #606060; }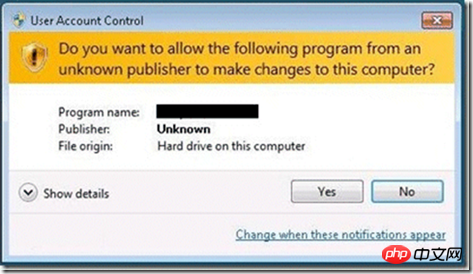
下面再来看看程序如何知道当前运行在系统管理员权限还是非系统管理员权限:
public static bool IsAdministrator()
{
WindowsIdentity identity = WindowsIdentity.GetCurrent();
WindowsPrincipal principal = new WindowsPrincipal(identity);
return principal.IsInRole(WindowsBuiltInRole.Administrator);
}.csharpcode,
.csharpcode pre { font-size: small; color: black; font-family: consolas, "Courier New", courier, monospace;
background-color: #ffffff; /*white-space: pre;*/ } .csharpcode pre { margin: 0em; } .csharpcode .rem { color:
#008000; } .csharpcode .kwrd { color: #0000ff; } .csharpcode .str { color: #006080; } .csharpcode
.op { color: #0000c0; } .csharpcode .preproc { color: #cc6633; } .csharpcode .asp { background-color: #ffff00; }
.csharpcode .html { color: #800000; } .csharpcode
.attr { color: #ff0000; } .csharpcode .alt { background-color: #f4f4f4; width: 100%; margin: 0em; }
.csharpcode .lnum { color: #606060; }这段代码可以用于判断当前程序是否运行在系统管理员权限下。如果配置为 asInvoker,在win7 下,这个函数会返回 false ,如果是 requireAdministrator 则返回 true。
在读写注册表“HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\”下的项时,明明注册表中有,但程序OpenSubKey始终返回Null,考虑到可能是因为权限的原因,于是我以管理员身份运行了一次,结果测试成功!原来真的是权限的问题,于是就在程序里面加入了默认以管理员身份运行的代码。下面让我们看看是怎么实现的吧!
程序默认以管理员身份运行
static void Main(string[] Args)
{
/**
* 当前用户是管理员的时候,直接启动应用程序
* 如果不是管理员,则使用启动对象启动程序,以确保使用管理员身份运行
*/
//获得当前登录的Windows用户标示
System.Security.Principal.WindowsIdentity identity = System.Security.Principal.WindowsIdentity.GetCurrent();
//创建Windows用户主题
Application.EnableVisualStyles();
System.Security.Principal.WindowsPrincipal principal = new System.Security.Principal.WindowsPrincipal(identity);
//判断当前登录用户是否为管理员
if (principal.IsInRole(System.Security.Principal.WindowsBuiltInRole.Administrator))
{
//如果是管理员,则直接运行
Application.EnableVisualStyles();
Application.Run(new Form1());
}
else
{
//创建启动对象
System.Diagnostics.ProcessStartInfo startInfo = new System.Diagnostics.ProcessStartInfo();
//设置运行文件
startInfo.FileName = System.Windows.Forms.Application.ExecutablePath;
//设置启动参数
startInfo.Arguments = String.Join(" ", Args);
//设置启动动作,确保以管理员身份运行
startInfo.Verb = "runas";
//如果不是管理员,则启动UAC
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start(startInfo);
//退出
System.Windows.Forms.Application.Exit();
}
}打开程序集里的Program.cs文件,并将其中Main方法中的代码替换为以上代码即可实现程序默认以管理员身份运行。
The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to the sample code of C# running the program as administrator by default. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




