Detailed instructions on CSS floating and positioning
Detailed description of CSS floating and positioning
1. What does the concept of document flow mean? Is there any way to get elements out of the document flow?
Document flow refers to the process of element typesetting and layout, where elements will automatically flow from left to right and top to bottom. arrangement. And finally the form is divided into rows from top to bottom, and the elements are arranged in order from left to right in each row. Breaking out of the document flow means that the element disrupts this arrangement, or is taken away from the layout.
Methods to get elements out of the document flow are: floating and positioning.
2. There are several positioning methods, how to achieve positioning, and what are the usage scenarios?
CSS positioningThere are four methods: default positioning (static), relative positioning (relative), absolute positioning (absolute) and fixed Positioning (fixed)
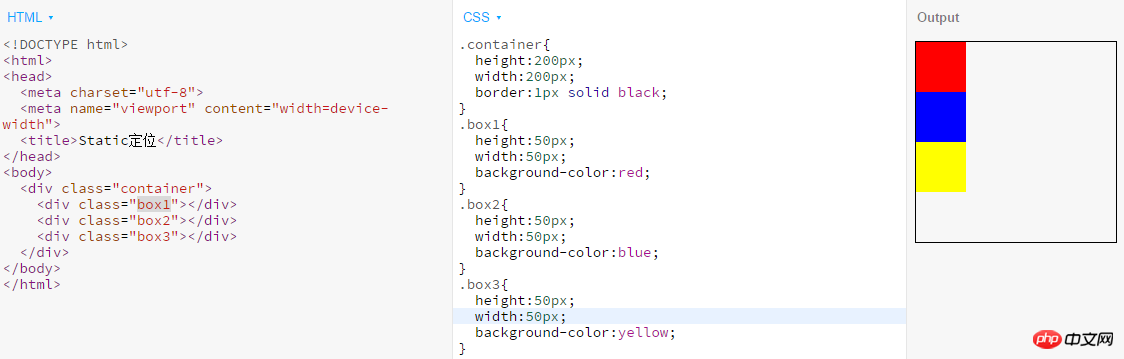
static: Default value. There is no positioning, the element is in the normal flow, top, right, bottom, left and z-index attributesinvalid. Examples are as follows:
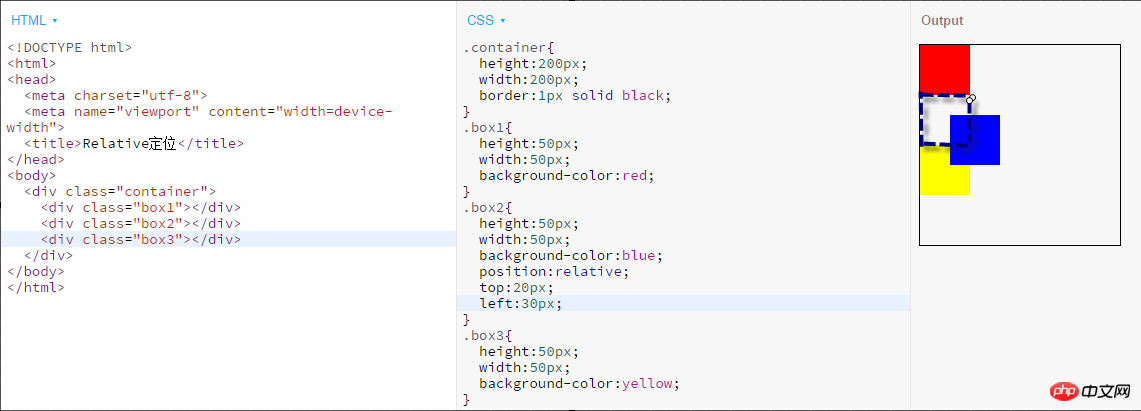
- ##relative: Generates relatively positioned elements, using the positions of top, bottom, left, and right relative to its normal position. The relative refers to the element's position in the default flow.
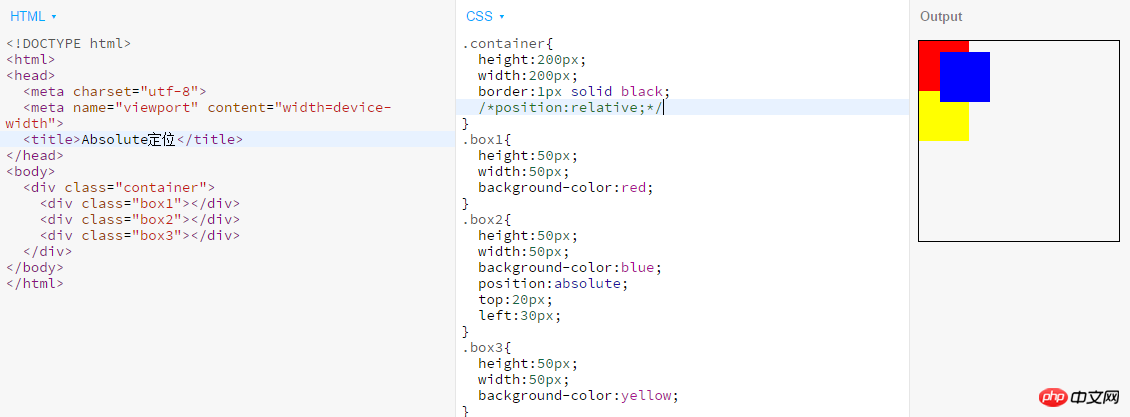
- absolute: Generate an absolutely positioned element, positioned relative to the first parent element outside of static positioning.
2. The position of an absolutely positioned element is relative to the nearest positioned ancestor element. If the element has no positioned ancestor element, its position is relative to the body; 3. Absolutely positioned Boxes can cover other elements of the page. Example:
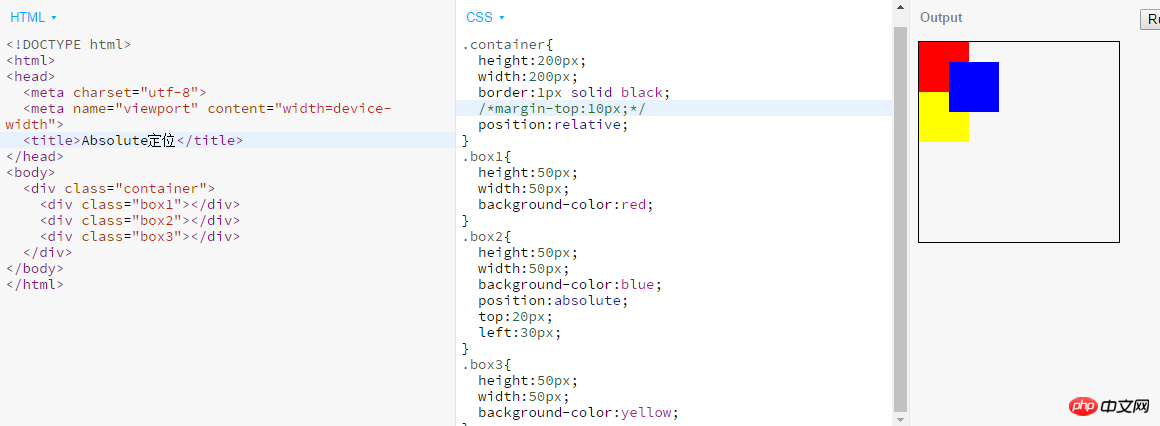
- fixed: It is essentially an absolute positioning that does not reserve space for the element. Specify the element's space by specifying its position relative to the screen viewport, and the element's position will not change when the screen scrolls. It is used in fixed
navigation at the top of many websites, fixed advertisements in the lower right corner, etc.
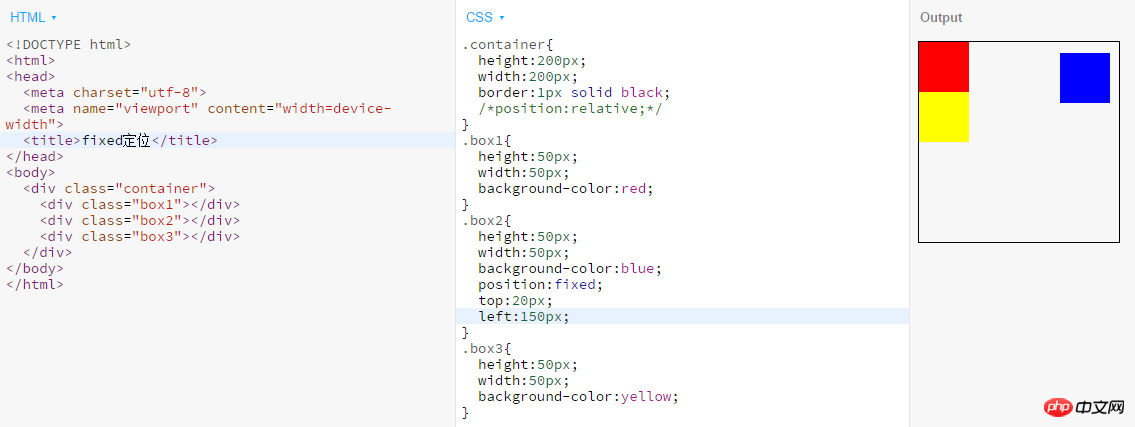
3. What are the reference points of absolute, relative, and fixed offsets?
The reference point of absolute offset is: relative to the nearest positioned parent element, if not, relative to the body element;
The reference point of relative offset is: relative to the element The original position in the normal stream; the reference point of the
fixed offset is: relative to the browser window.
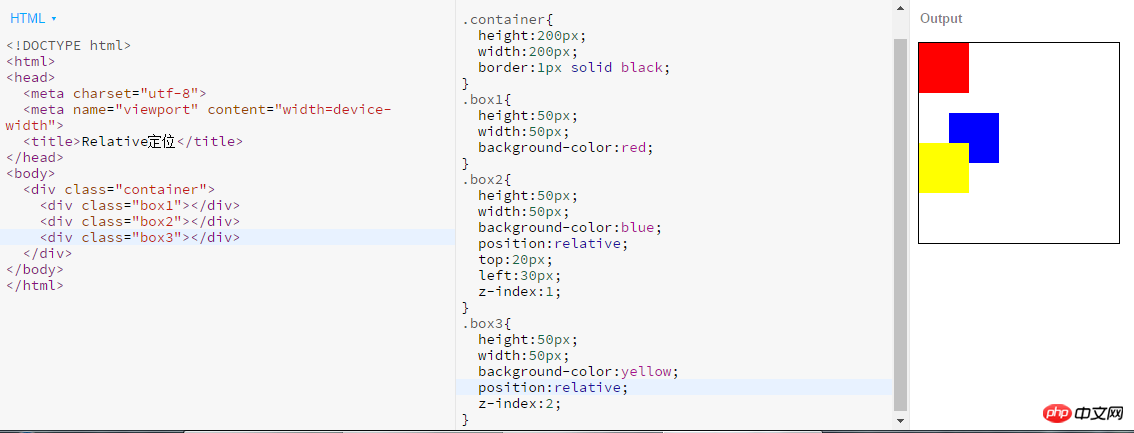
4. What is the role of z-index? How to use it?
The z-index attribute is used to set the stacking order of nodes. Nodes with higher stacking order will be displayed in lower stacking order. in front of the node.
Usage: Example
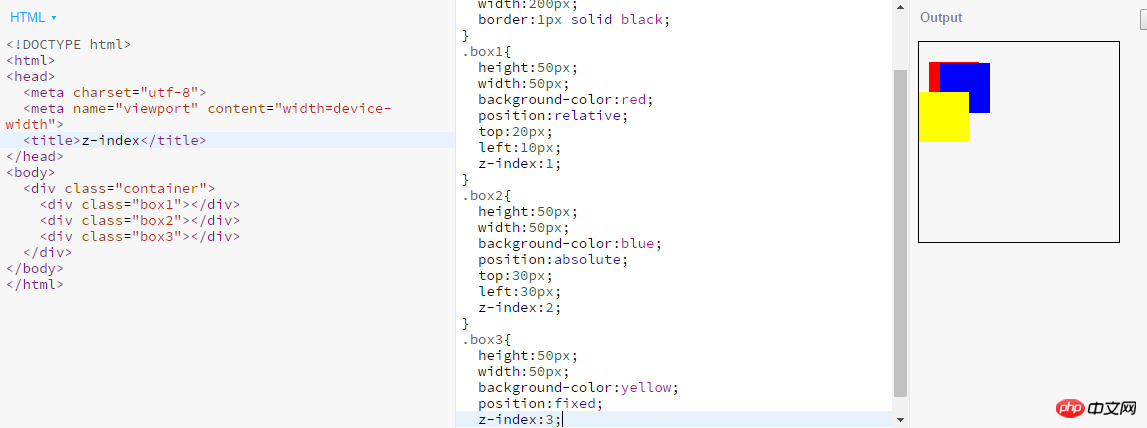
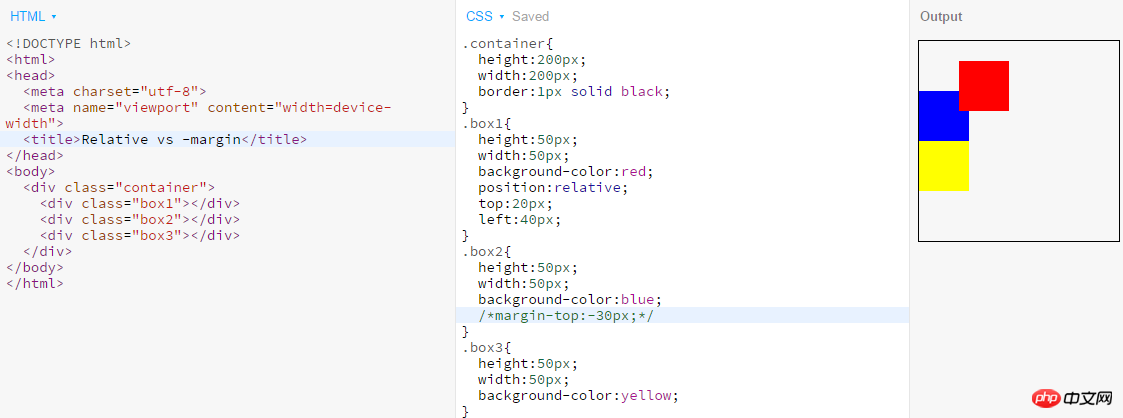
2.z-index can only compare elements of the same level5. Both position: relative and negative
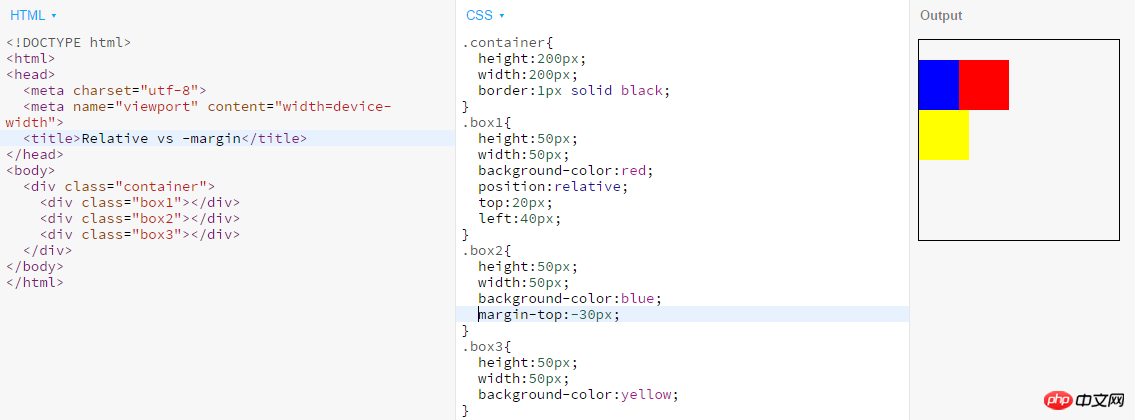
margin can offset the position of the element? What is the difference between the two?
Position:relative and negative margin can both offset the position of the element. The difference between the two is:- Negative margin will cause the element to move in the document flow. If the position is shifted, it will give up the space occupied before the shift, and the elements immediately following it will fill this space;
- If the element position is shifted after relative positioning, it will still It will stick to the space it originally occupied and will not let other elements of the document flow flow in.
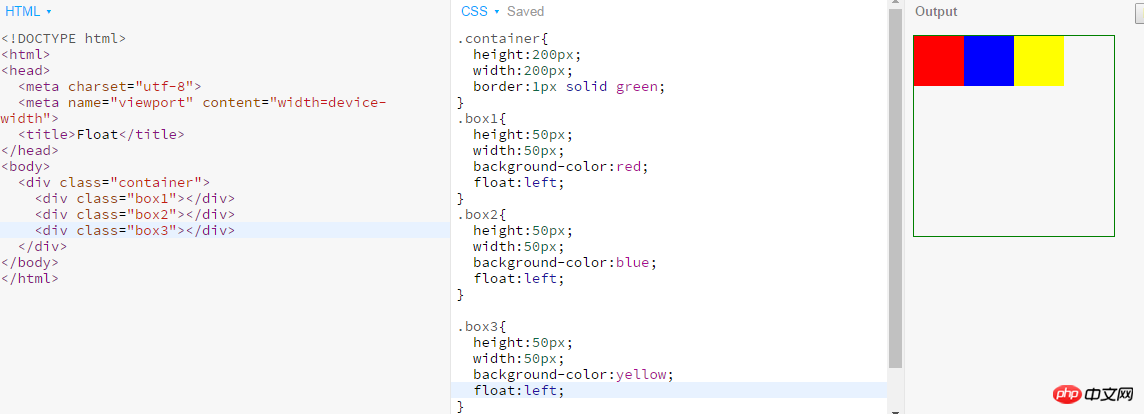
- The characteristics of floating elements are:
Inline elementsSupport width and height;
3.Whether it is a block element or an inline element, when there is no width, the default content will expand the width;4. Break away from the document flow; 5. Increase the level by half a level.- Influence on other floating elements: The element that floats later will never exceed the top of the element that floated first.
- Influence on ordinary elements: Floating elements will
- Influence on text: When the floating element extends downward, it will not affect the display of normal text, and the text will be offset relative to the floating element. But part of the text background will be obscured by floating elements. (Please refer to Dahua
FLOAT)
Clear Float# What does ## mean? How to clear floats? Clearing floats means: in non-
IE browsers(such as Firefox), when the height of the container is auto and the content of the container is There are floating elements (float is left or right). In this case, the height of the container cannot automatically extend to adapt to the height of the content, causing the content to overflow outside the container and affect the layout. In order to prevent this phenomenon from occurring, The CSS processing performed is called CSS clear float. Methods to clear floats:
1. Use empty elements with
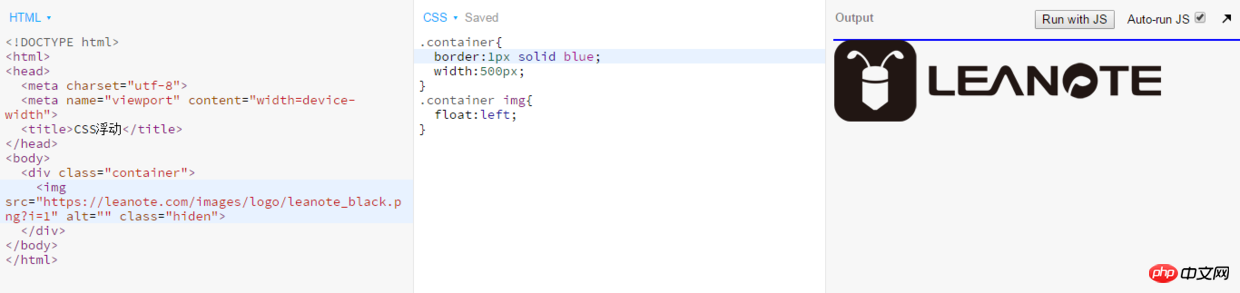
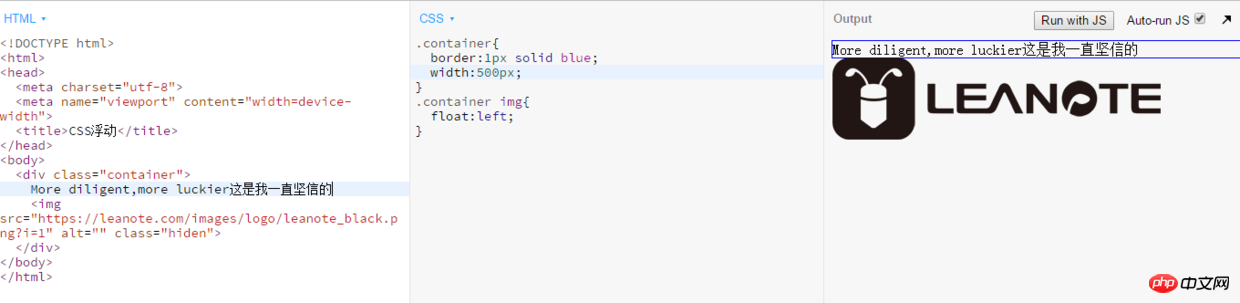
clear attributes Use an empty element after the floating element such as 2. Use the overflow attribute of CSS to add overflow:hidden; or overflow:auto; to the container of the floating element to clear the float. In addition, it is also required in IE6 Trigger hasLayout, such as setting the container width and height for the parent element or setting zoom:1. 3. Use CSS :afterpseudo-element Additional: I have never quite understood the use of clear:both to clear floats, and there is also the method of clearing floats. I misunderstood. I thought that after clearing floats, the rendering order of elements is the same as that of ordinary flow. This is not actually the case. Here is my own understanding. If there are any deficiencies, everyone is welcome to criticize and correct me. About floating In the following code: Add a background in the parent containerPicture , the image will be rendered according to the normal flow If you add float to the background image on this basis, the effect will be as follows: We can see that the height of the parent element has collapsed and the background image is out of the document flow, so at this time the parent container p has replenished its height. Let us add some text to the parent container to see its height change The height of the parent container has been stretched, is there any! Is there any! So the reason why the child element floats and the parent element collapses is: because the p height is not set in advance, the p height is determined by the height of the child element it contains. Floating is out of the document flow, so the height of the image is not calculated. At this time, in p, it is equivalent to the height of the neutron element in p being 0. A problem that has troubled me for a long time, I would like to share it with you and give you the code: <p class="clear"></p>, and assign .clear{clear:both;} in CSS Properties can be used to clean up floats. You can also use <br class="clear"> or <hr class="clear"> to clean. 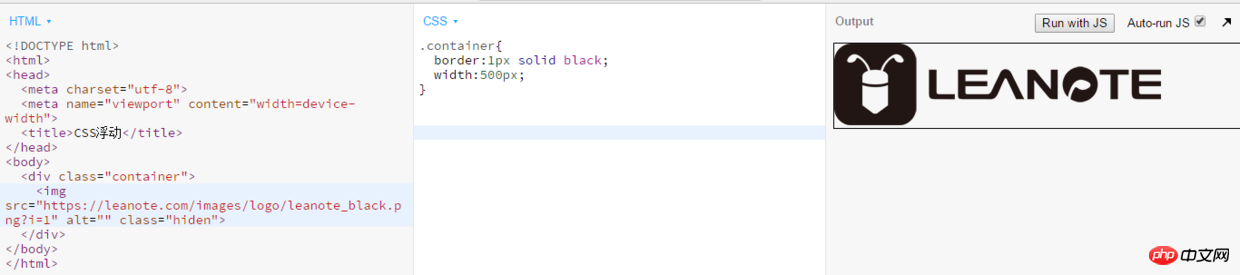
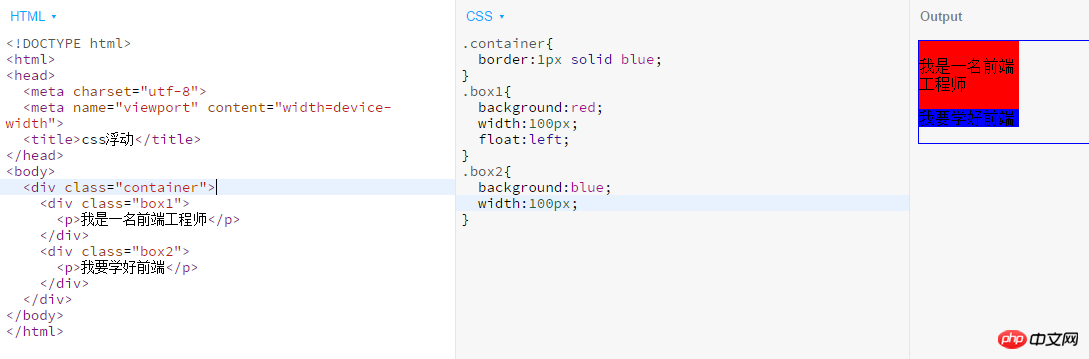
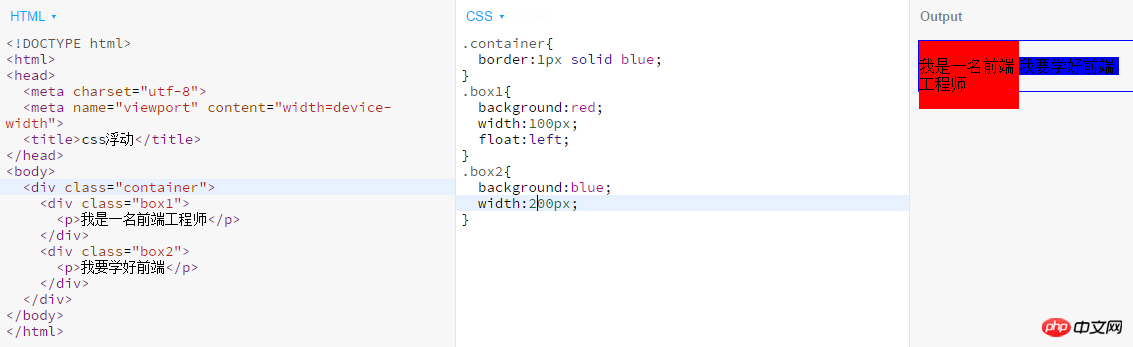
Clear :both; In fact, we use clear float to open the outer p. So sometimes, after we set all the inner p to float, we will find that the background of the outer p is not displayed. The reason is that the outer p It's not stretched out and is too small, so the visible background is limited to a line. Examples are as follows:

The above is the detailed content of Detailed instructions on CSS floating and positioning. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Demystifying Screen Readers: Accessible Forms & Best Practices
Mar 08, 2025 am 09:45 AM
Demystifying Screen Readers: Accessible Forms & Best Practices
Mar 08, 2025 am 09:45 AM
This is the 3rd post in a small series we did on form accessibility. If you missed the second post, check out "Managing User Focus with :focus-visible". In
 Create a JavaScript Contact Form With the Smart Forms Framework
Mar 07, 2025 am 11:33 AM
Create a JavaScript Contact Form With the Smart Forms Framework
Mar 07, 2025 am 11:33 AM
This tutorial demonstrates creating professional-looking JavaScript forms using the Smart Forms framework (note: no longer available). While the framework itself is unavailable, the principles and techniques remain relevant for other form builders.
 Adding Box Shadows to WordPress Blocks and Elements
Mar 09, 2025 pm 12:53 PM
Adding Box Shadows to WordPress Blocks and Elements
Mar 09, 2025 pm 12:53 PM
The CSS box-shadow and outline properties gained theme.json support in WordPress 6.1. Let's look at a few examples of how it works in real themes, and what options we have to apply these styles to WordPress blocks and elements.
 Working With GraphQL Caching
Mar 19, 2025 am 09:36 AM
Working With GraphQL Caching
Mar 19, 2025 am 09:36 AM
If you’ve recently started working with GraphQL, or reviewed its pros and cons, you’ve no doubt heard things like “GraphQL doesn’t support caching” or
 Making Your First Custom Svelte Transition
Mar 15, 2025 am 11:08 AM
Making Your First Custom Svelte Transition
Mar 15, 2025 am 11:08 AM
The Svelte transition API provides a way to animate components when they enter or leave the document, including custom Svelte transitions.
 Show, Don't Tell
Mar 16, 2025 am 11:49 AM
Show, Don't Tell
Mar 16, 2025 am 11:49 AM
How much time do you spend designing the content presentation for your websites? When you write a new blog post or create a new page, are you thinking about
 Classy and Cool Custom CSS Scrollbars: A Showcase
Mar 10, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Classy and Cool Custom CSS Scrollbars: A Showcase
Mar 10, 2025 am 11:37 AM
In this article we will be diving into the world of scrollbars. I know, it doesn’t sound too glamorous, but trust me, a well-designed page goes hand-in-hand
 What the Heck Are npm Commands?
Mar 15, 2025 am 11:36 AM
What the Heck Are npm Commands?
Mar 15, 2025 am 11:36 AM
npm commands run various tasks for you, either as a one-off or a continuously running process for things like starting a server or compiling code.






