A brief introduction to Java exceptions (picture)
What you see on paper is shallow, but you know you have to do it in detail
--Lu You Ask the canal how clear it is so that there is a source of running water --Zhu Xi
1. The super class of java exception is java.lang.Throwable
Exception handling Class structure composition:
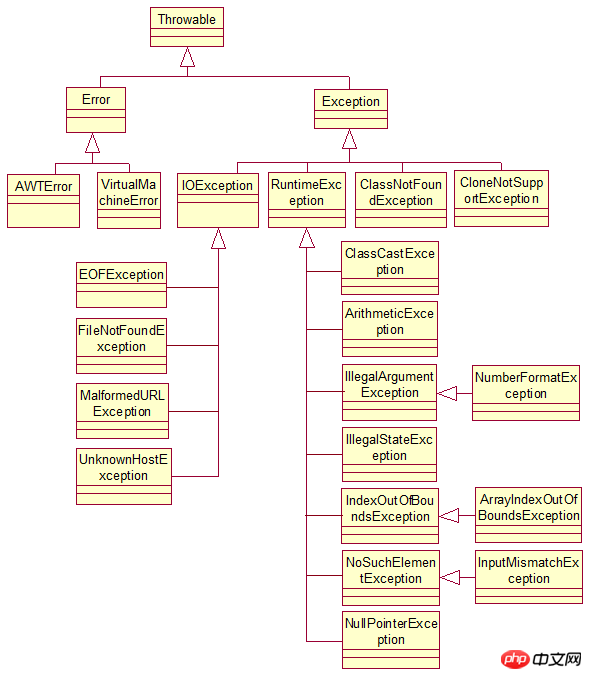
2. Java exceptions are divided into two categories: Error and Exception:
Error It is an error that the program cannot handle, such as OutOfMemoryError, ThreadDeath, etc. When these exceptions occur, the JVM selects the thread to terminate.
Exception is an exception that can be handled by the program itself. There are two types:
(1) Non-runtime exception (occurring in the compilation phase, called checkException ): Generally refers to errors that do not follow the Java language specifications, which are easier to see.
Such as NullPointerException, IndexOutOfBoundsException, these exceptions are unchecked exceptions, and the program can choose to capture them or not handle them.
These exceptions are generally caused by program logic errors. The program should avoid the occurrence of such exceptions as much as possible from a logical perspective.
(2) Runtime exception (occurring during the running of the program, called uncheckException): An exception that generally occurs during the running of the program, such as Null pointer errors and so on.
3. Java exceptions involve 5 keywords: try, catch,finally, throw, throws try{
尝试运行的程序代码
}
catch(异常类型 异常变量名)
{
异常处理代码,同时catch可以是多个,但只运行其中的一个
}
finally()
{
finally总在方法返回前运行,finally语句部分只有一个
}
The throws keyword is used in the method declaration part outside the method body to declare what exceptions the method may throw.
4. Common Exception:
NullPointException 空指针异常
ClassNotFoundException 找不到类
ClassCastException 类型转换
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 数组越界5. Finally()
When there are
return statements in try and catch, finally will be executed.
The above is the detailed content of A brief introduction to Java exceptions (picture). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to the Armstrong Number in Java. Here we discuss an introduction to Armstrong's number in java along with some of the code.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is






