Detailed introduction to XML parsing (graphics and text)
This tutorial uses NSXMLParser Object to parse xml files. The parsing results are displayed by Table View. This tutorial is built on iOS 9.3 on Xcode 7.3.1.
Open Xcode and create a new single-window application. The name is IOS9XMLParserTutorial, and the organization name and organization logo are determined by yourself. Select Swift as the language and iPhone as the device.
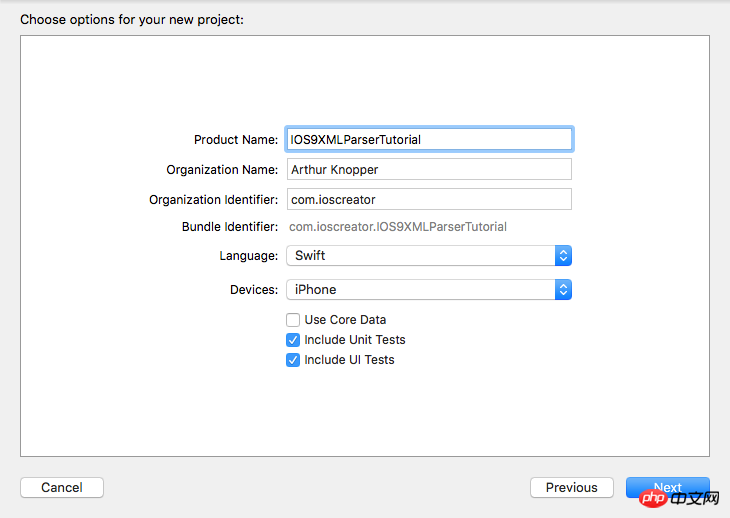
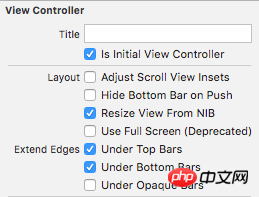
Remove the View Controller from the Storyboard and drag a Navigation Controller to the empty artboard. This Navigation Controller will automatically carry a Table View Controller. When you delete the initial View Controller the corresponding storyboard starting point is also removed. So we first select the newly added Navigation Controller and tick the "Is Initial View Controller" checkbox in the Attribute Inspector as the starting point of the new storyboard.
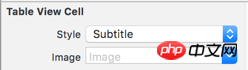
property to Subtitle in the Attributes Inspector.
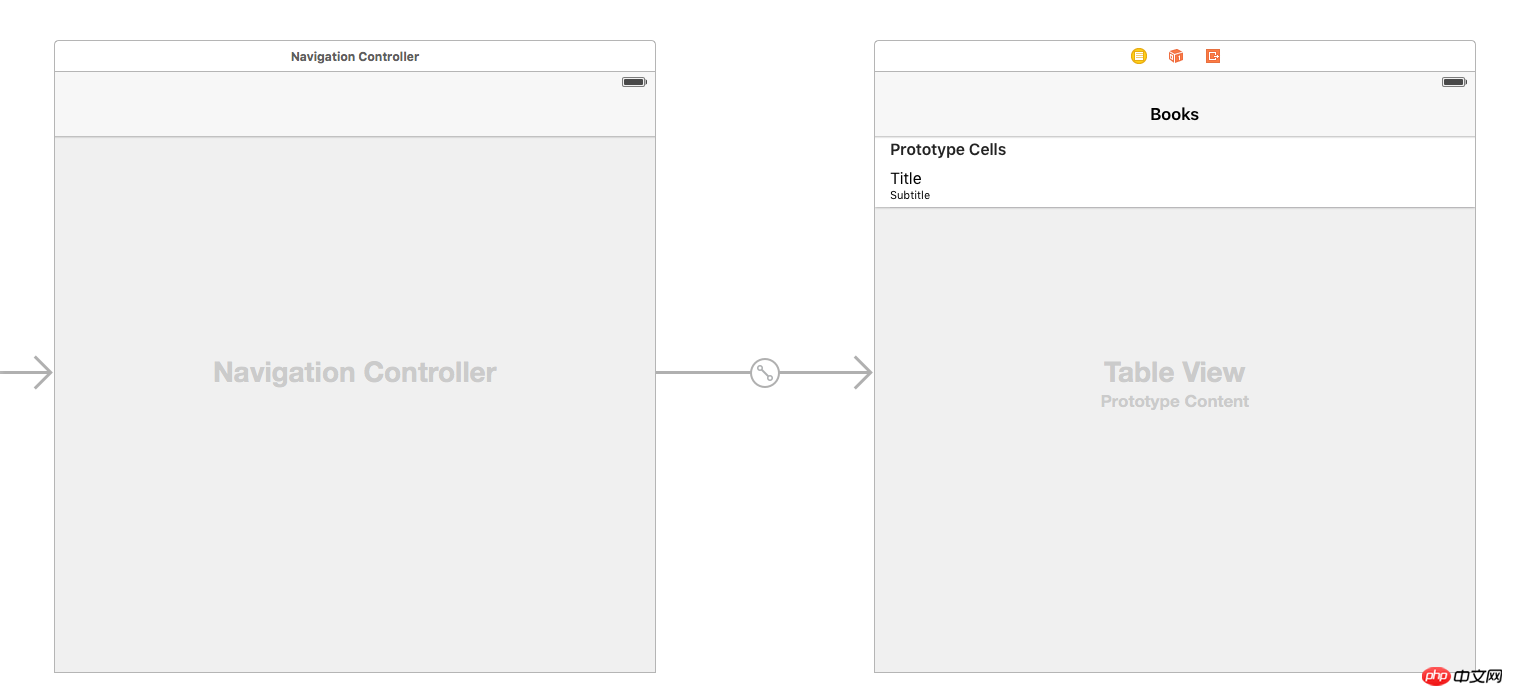
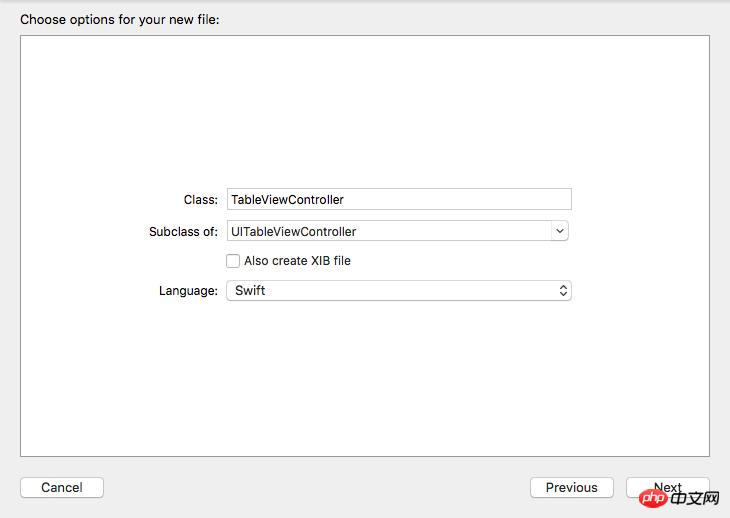
Class Add a new file, name it TableViewController, and set it as a subclass of UITableViewController.
File and add a new file. Name it Books.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<catalog>
<book id="1">
<title>To Kill a Mockingbird</title>
<author>Harper Lee</author>
</book>
<book id="2">
<title>1984</title>
<author>George Orwell</author>
</book>
<book id="3">
<title>The Lord of the Rings</title>
<author>J.R.R Tolkien</author>
</book>
<book id="4">
<title>The Catcher in the Rye</title>
<author>J.D. Salinger</author>
</book>
<book id="5">
<title>The Great Gatsby</title>
<author>F. Scott Fitzgerald</author>
</book>
</catalog>Model as different items in an xml file. Let’s call it Book.swift and replace it with the following code
import Foundation
class Book {
var bookTitle: String = String()
var bookAuthor: String = String()
}variables.
var books: [Book] = [] var eName: String = String() var bookTitle = String() var bookAuthor = String()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
if let path = NSBundle.mainBundle().URLForResource("books", withExtension: "xml") {
if let parser = NSXMLParser(contentsOfURL: path) {
parser.delegate = self
parser.parse()
}
}
}override func numberOfSectionsInTableView(tableView: UITableView) -> Int {
return 1
}
override func tableView(tableView: UITableView, numberOfRowsInSection section: Int) -> Int {
return books.count
}
override func tableView(tableView: UITableView, cellForRowAtIndexPath indexPath: NSIndexPath) -> UITableViewCell {
let cell = tableView.dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier("Cell", forIndexPath: indexPath)
let book = books[indexPath.row]
cell.textLabel?.text = book.bookTitle
cell.detailTextLabel?.text = book.bookAuthor
return cell
}array and presented by the Table View. Next, implement the delegate method of NSXMLParser.
// 1
func parser(parser: NSXMLParser, didStartElement elementName: String, namespaceURI: String?,
qualifiedName qName: String?, attributes attributeDict: [String : String]) {
eName = elementName
if elementName == "book" {
bookTitle = String()
bookAuthor = String()
}
}
// 2
func parser(parser: NSXMLParser, didEndElement elementName: String, namespaceURI: String?, qualifiedName qName: String?) {
if elementName == "book" {
let book = Book()
book.bookTitle = bookTitle
book.bookAuthor = bookAuthor
books.append(book)
}
}
// 3
func parser(parser: NSXMLParser, foundCharacters string: String) {
let data = string.stringByTrimmingCharactersInSet(NSCharacterSet.whitespaceAndNewlineCharacterSet())
if (!data.isEmpty) {
if eName == "title" {
bookTitle += data
} else if eName == "author" {
bookAuthor += data
}
}
}- This method is triggered when the parsing object encounters the start tag of "
" - This method is triggered when the parsing object encounters When the end tag of "
" is encountered, it is triggered. - The parsing process here is actually executed. The title and author tags will be parsed and the corresponding variables will be initialized.
Build and run the project. You can see the titles and authors of all books in the TableViewController. 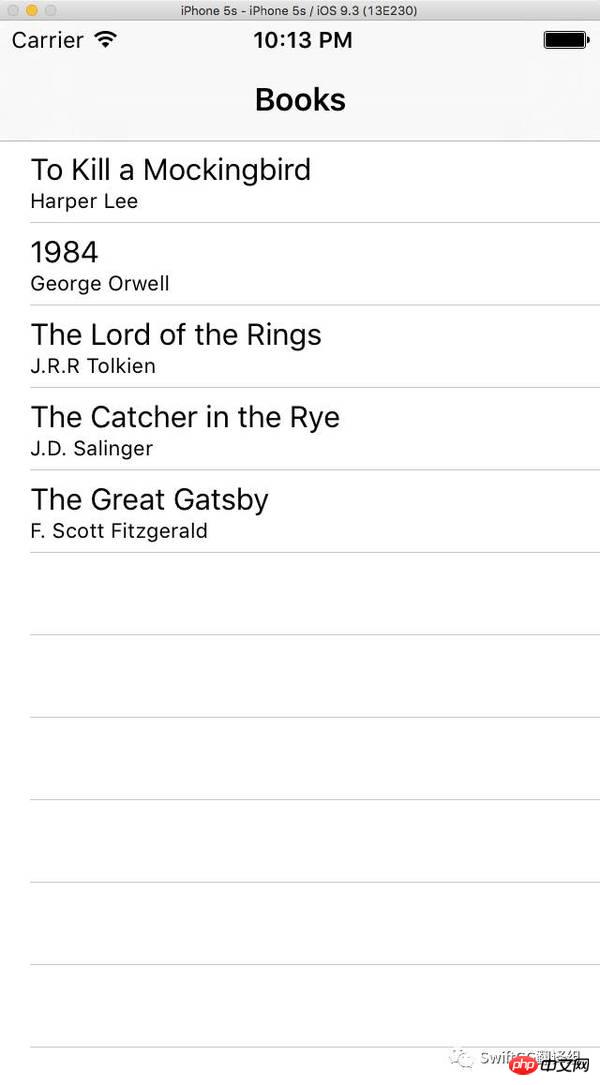
The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to XML parsing (graphics and text). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
The speed of mobile XML to PDF depends on the following factors: the complexity of XML structure. Mobile hardware configuration conversion method (library, algorithm) code quality optimization methods (select efficient libraries, optimize algorithms, cache data, and utilize multi-threading). Overall, there is no absolute answer and it needs to be optimized according to the specific situation.
 How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
It is impossible to complete XML to PDF conversion directly on your phone with a single application. It is necessary to use cloud services, which can be achieved through two steps: 1. Convert XML to PDF in the cloud, 2. Access or download the converted PDF file on the mobile phone.
 How to convert XML to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to convert XML to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
It is not easy to convert XML to PDF directly on your phone, but it can be achieved with the help of cloud services. It is recommended to use a lightweight mobile app to upload XML files and receive generated PDFs, and convert them with cloud APIs. Cloud APIs use serverless computing services, and choosing the right platform is crucial. Complexity, error handling, security, and optimization strategies need to be considered when handling XML parsing and PDF generation. The entire process requires the front-end app and the back-end API to work together, and it requires some understanding of a variety of technologies.
 Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
XML formatting tools can type code according to rules to improve readability and understanding. When selecting a tool, pay attention to customization capabilities, handling of special circumstances, performance and ease of use. Commonly used tool types include online tools, IDE plug-ins, and command-line tools.
 Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
An application that converts XML directly to PDF cannot be found because they are two fundamentally different formats. XML is used to store data, while PDF is used to display documents. To complete the transformation, you can use programming languages and libraries such as Python and ReportLab to parse XML data and generate PDF documents.
 How to open web.xml
Apr 03, 2025 am 06:51 AM
How to open web.xml
Apr 03, 2025 am 06:51 AM
To open a web.xml file, you can use the following methods: Use a text editor (such as Notepad or TextEdit) to edit commands using an integrated development environment (such as Eclipse or NetBeans) (Windows: notepad web.xml; Mac/Linux: open -a TextEdit web.xml)
 How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
Use most text editors to open XML files; if you need a more intuitive tree display, you can use an XML editor, such as Oxygen XML Editor or XMLSpy; if you process XML data in a program, you need to use a programming language (such as Python) and XML libraries (such as xml.etree.ElementTree) to parse.
 xml online formatting
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
xml online formatting
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
XML Online Format Tools automatically organizes messy XML code into easy-to-read and maintain formats. By parsing the syntax tree of XML and applying formatting rules, these tools optimize the structure of the code, enhancing its maintainability and teamwork efficiency.




