
When introducing the Array data structure in the previous section, we mentioned that it is static, each dimension The number of elements must be uniquely determined at compile time, and their type must be strongly typed.
So, in this section, we will talk about another data structure that is similar to Array, but overcomes the shortcomings of Array: ArrayList.
First of all, it is not static. The number of elements in each dimension does not need to be specified during compilation. The system default number of elements is 16. When the number of elements increases and is about to exceed 16, it will double and expand to 32, and will grow regularly. , becomes smaller, the opposite process is performed.
Secondly, the element type is a weak type, object. At runtime, the type of each element is determined based on the actual type assigned. In other words, the elements in this set can be a mixture of different elements.
Let’s first look at the interface of ArrayList provided by .NET: 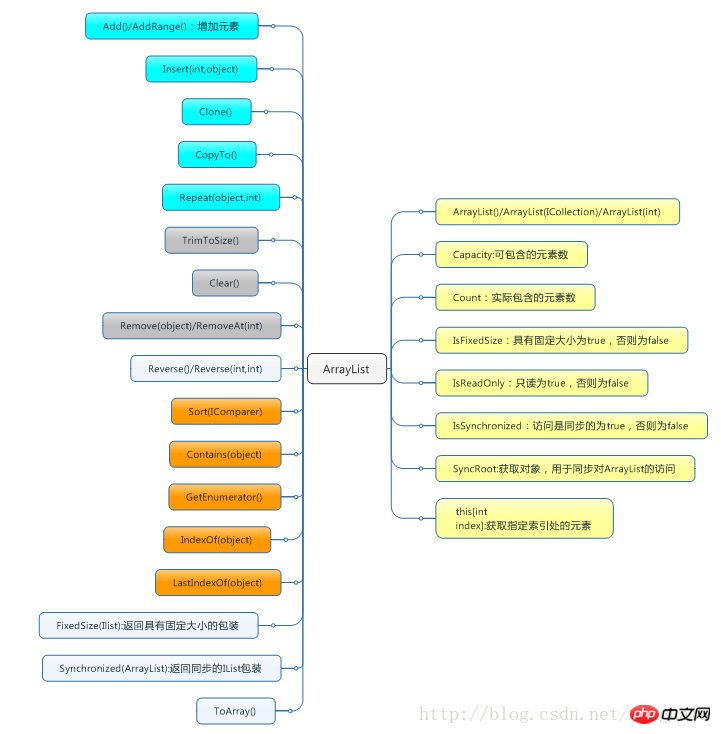
1) Object Creation and initialization
//对象创建
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList() {3.14, "vuefine"}; //添加元素
arrayList.Add("Hello wolrd");
arrayList.Add(5);2) Access element
//访问元素
object ele0 = arrayList[0];
Type t0 = ele0.GetType();//double3) Modify element
//修改元素
arrayList[0] = "Ni hao";4) Delete element
//删除元素
//移除已存在的对象
arrayList.Remove(5);
arrayList.RemoveAt(0); //移除不存在的对象
arrayList.Remove(12); //不抛异常5) ArrayList and other object relationships
object cloneAL = arrayList.Clone(); //创建浅表副本
Type tClone = cloneAL.GetType();
//Array是abstract,只能通过静态方法创建array
Array array = Array.CreateInstance(typeof(object),arrayList.Count);
arrayList.CopyTo(array);//复制到arrayThe above is the detailed content of .NET Framework-ArrayList Code Detailed Explanation. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 What are the common management systems?
What are the common management systems?
 mintui
mintui
 Which version of linux system is easy to use?
Which version of linux system is easy to use?
 What to do if an error occurs in the script of the current page
What to do if an error occurs in the script of the current page
 What are the requirements for Douyin live broadcast?
What are the requirements for Douyin live broadcast?
 Why can't I open pinterest?
Why can't I open pinterest?
 Introduction to Document in JS
Introduction to Document in JS
 What is the format of the account name of steam
What is the format of the account name of steam
 What are the enterprise erp systems?
What are the enterprise erp systems?




