 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Detailed introduction to python machine learning decision tree
Detailed introduction to python machine learning decision tree
Detailed introduction to python machine learning decision tree
Decision Trees (DTs) are an unsupervised learning method used for classification and regression.
Advantages: The computational complexity is not high, the output results are easy to understand, insensitive to missing intermediate values, and can handle irrelevant feature data
Disadvantages: Over-matching may occur
ApplicableData type: Numerical and nominal source code download https://www.manning.com/books/machine-learning-in-action
Run demo
Key algorithm
Find the best features to divide the dataset ##createBranch and add the return result to the branch node
return branch node
Corresponding codedef createTree(dataSet,labels):
class
List
if classList.
count(classList[0]) == len(classList): If the returned classified List count type is the same, then return this type! Whether it can be classified at the sub -node. If you return it, other types will be ceded
在 在 在 在 在 在 在 Return classList [0] #Stop Splitting When all of the classs are iF Len (dataSet [0]) == 1: #stop splitting when there are no more features in dataSet If there is only one element Return majorityCnt(classList) bestFeat = chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet) BestFeatLabel = labels[bestFeat ] And get this label flippers or no surfaces?
myTree = {bestFeatLabel:{}} Then create a subtree of the best category del(labels[bestFeat]) Delete the best category featValues = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet] uniqueVals = set(featValues) set is a classification, see how many types there are for value in uniqueVals:
subLabels = labels[:] #copy all of labels, so trees do mess up existing labels
MyTree [Bestfeatlabel] [Value] = Createtree (SPLITDATASET (DataSET, Bestfeat, Value), Sublabels)
rn mytree
is dividing data The change in information before and after a set is called information gain. The biggest principle for dividing a data set is to make disordered data more orderly. This is understood as the pie-cutting principle:
# Use unit entropy to describe the complexity and amount of information. Corresponding to the density of the cake, if it is a vertically cut cake of equal density,
The weight of each part g = total G * its proportion in the great circle! Analogously, if the information entropy is the same after partitioning, the small h of each small part of the data = pro * total H, and the sum h[i] = H.
DebuggingProcess
calcShannonEnt
log(prob,2) log(1,2) = 0;2^0=1, because prob
25 lines for featVec in dataSet: Frequency counting for prop
chooseBestFeatureToSplit()
0.9709505944546686 = calcShannonEnt(dataSet)
#Detection Whether each sub-item of the data set belongs to the same category: If the values are all a, and the results are all y or n, it is a category. Therefore, just two parameter inputs
0.5509775004326937 = += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet) separated After subsetting, the probability * Shannon drop is obtained, and the original overall Shannon drop ratio is
1 2 3 |
|
0.4199730940219749 infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy
Summary:
At first, I couldn’t understand the code and didn’t understand what it was supposed to do! Classification, our goal is to classify a bunch of data and label it with labels.
Like k-nearby classify([0, 0], group, labels, 3), it means that the new data [0,0] is classified in the group, labels data according to the k=3 neighbor algorithm! Group corresponds to label!
I saw
later. , result label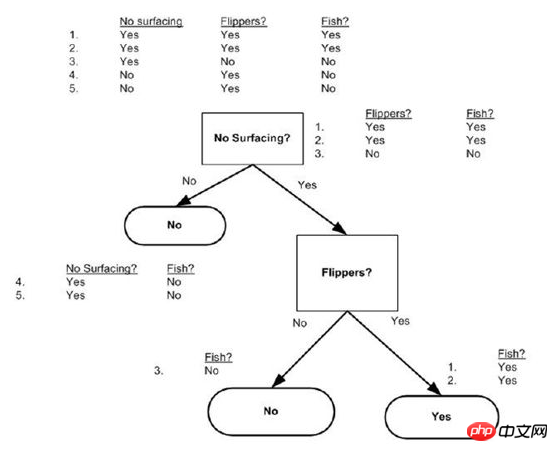
So, we need to cut out each dimension + result label into a two-dimensional array to compare and classify
The test should be to divide the first n dimensions Value, vector input, output is yes or no!It seems dizzy at first, but it is clearer. It is easier to understand after straightening out your ideas and looking at the code!
After understanding the target and initial data, you understand that classList is the result label! , is the corresponding result label corresponding to the dataset to be classified, and labels is the feature name, corresponding to the dimension of the starting dataset, the name of the feature strname
bestFeatLabel is the dimension name of the best classification feature, whether it is the first dimension or the second dimension , the N
featValues is the value array under the dimension of bestFeatLabel. It is the groups under this dimension that are used to make new classification comparisons.
uniqueVals uses set to determine whether it is of the same type,
For example
DataSet = [[1, 1, 'yes'],[0, 1, 'yes'],[1, 0, 'no' ],[1, 0, 'no'],[0, 0, 'no']]
Labels = ['no surfacing','flippers',]
createTree like this:{'flippers': {0: 'no', 1: 'yes'}} directly omits the dimension of no surfacing
Finally, let me use a paragraph to talk about decision-making Tree:
The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to python machine learning decision tree. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to solve the permissions problem encountered when viewing Python version in Linux terminal?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
How to solve the permissions problem encountered when viewing Python version in Linux terminal?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
Solution to permission issues when viewing Python version in Linux terminal When you try to view Python version in Linux terminal, enter python...
 How to efficiently copy the entire column of one DataFrame into another DataFrame with different structures in Python?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 11:15 PM
How to efficiently copy the entire column of one DataFrame into another DataFrame with different structures in Python?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 11:15 PM
When using Python's pandas library, how to copy whole columns between two DataFrames with different structures is a common problem. Suppose we have two Dats...
 How to teach computer novice programming basics in project and problem-driven methods within 10 hours?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:18 AM
How to teach computer novice programming basics in project and problem-driven methods within 10 hours?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:18 AM
How to teach computer novice programming basics within 10 hours? If you only have 10 hours to teach computer novice some programming knowledge, what would you choose to teach...
 How to avoid being detected by the browser when using Fiddler Everywhere for man-in-the-middle reading?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:15 AM
How to avoid being detected by the browser when using Fiddler Everywhere for man-in-the-middle reading?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:15 AM
How to avoid being detected when using FiddlerEverywhere for man-in-the-middle readings When you use FiddlerEverywhere...
 How does Uvicorn continuously listen for HTTP requests without serving_forever()?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How does Uvicorn continuously listen for HTTP requests without serving_forever()?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How does Uvicorn continuously listen for HTTP requests? Uvicorn is a lightweight web server based on ASGI. One of its core functions is to listen for HTTP requests and proceed...
 What are some popular Python libraries and their uses?
Mar 21, 2025 pm 06:46 PM
What are some popular Python libraries and their uses?
Mar 21, 2025 pm 06:46 PM
The article discusses popular Python libraries like NumPy, Pandas, Matplotlib, Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, Django, Flask, and Requests, detailing their uses in scientific computing, data analysis, visualization, machine learning, web development, and H
 How to dynamically create an object through a string and call its methods in Python?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 11:18 PM
How to dynamically create an object through a string and call its methods in Python?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 11:18 PM
In Python, how to dynamically create an object through a string and call its methods? This is a common programming requirement, especially if it needs to be configured or run...
 How to solve permission issues when using python --version command in Linux terminal?
Apr 02, 2025 am 06:36 AM
How to solve permission issues when using python --version command in Linux terminal?
Apr 02, 2025 am 06:36 AM
Using python in Linux terminal...



