17 Python tricks and tricks to share
Showing a limited interface to the outside
When publishing a python third-party package, it is not expected that all ## in the code #Function or class can be imported externally, add all attribute in init.py, and fill in the list The imported class or function name can limit the import and prevent external import of other functions or classes.

#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from base import APIBase from client import Client from decorator import interface, export, stream from server import Server from storage import Storage from util import (LogFormatter, disable_logging_to_stderr, enable_logging_to_kids, info) all = ['APIBase', 'Client', 'LogFormatter', 'Server', 'Storage', 'disable_logging_to_stderr', 'enable_logging_to_kids', 'export', 'info', 'interface', 'stream']
object that supports the context management protocol , context management protocol Contains two methods, enter and exit. The with statement establishes the runtime context and needs to perform entry and exit operations through these two methods.
WhereContextExpression is the expression following with, which returns a context management object.
# 常见with使用场景
with open("test.txt", "r") as my_file: # 注意, 是enter()方法的返回值赋值给了my_file,
for line in my_file:
print line#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- class MyWith(object): def init(self): print "init method" def enter(self): print "enter method" return self # 返回对象给as后的变量 def exit(self, exc_type, exc_value, exc_traceback): print "exit method" if exc_traceback is None: print "Exited without Exception" return True else: print "Exited with Exception" return False def test_with(): with MyWith() as my_with: print "running my_with" print "------分割线-----" with MyWith() as my_with: print "running before Exception" raise Exception print "running after Exception" if name == 'main': test_with()
init method enter method running my_with exit method Exited without Exception ------分割线----- init method enter method running before Exception exit method Exited with Exception Traceback (most recent call last): File "bin/python", line 34, in <module> exec(compile(filef.read(), file, "exec")) File "test_with.py", line 33, in <module> test_with() File "test_with.py", line 28, in test_with raise Exception Exception</module></module>
It is proved that the enter method will be executed first, then the logic in with will be called, and finally exit will be executed for exit processing, and even if an exception occurs, it can Normal exitUsage of filterCompared with filter,
map and reduce will be used more frequently. Filter is just like its name, according to certain rules Filter Remove some elements.
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- lst = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] # 所有奇数都会返回True, 偶数会返回False被过滤掉 print filter(lambda x: x % 2 != 0, lst) #输出结果 [1, 3, 5]
lst = [1, 2, 3] new_lst = lst[0] if lst is not None else None print new_lst # 打印结果 1
Use decorator to implement simple# 单例装饰器 def singleton(cls): instances = dict() # 初始为空 def _singleton(*args, **kwargs): if cls not in instances: #如果不存在, 则创建并放入字典 instances[cls] = cls(*args, **kwargs) return instances[cls] return _singleton @singleton class Test(object): pass if name == 'main': t1 = Test() t2 = Test() # 两者具有相同的地址 print t1, t2Copy after login
static method decorator
Two commonly used decorations in classes, first distinguish them:- Ordinary member function, the first implicit parameter is
Object
classmethod decorator, class method (it feels very similar to the class method in OC), the first one is implicit The parameter is class
-
staticmethod decorator, without any implicit parameters. static in python The method is similar to the static method in C++
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- class A(object): # 普通成员函数 def foo(self, x): print "executing foo(%s, %s)" % (self, x) @classmethod # 使用classmethod进行装饰 def class_foo(cls, x): print "executing class_foo(%s, %s)" % (cls, x) @staticmethod # 使用staticmethod进行装饰 def static_foo(x): print "executing static_foo(%s)" % x def test_three_method(): obj = A() # 直接调用噗通的成员方法 obj.foo("para") # 此处obj对象作为成员函数的隐式参数, 就是self obj.class_foo("para") # 此处类作为隐式参数被传入, 就是cls A.class_foo("para") #更直接的类方法调用 obj.static_foo("para") # 静态方法并没有任何隐式参数, 但是要通过对象或者类进行调用 A.static_foo("para") if name == 'main': test_three_method() # 函数输出 executing foo(<main.a>, para) executing class_foo(<class>, para) executing class_foo(<class>, para) executing static_foo(para) executing static_foo(para)</class></class></main.a>Copy after loginproperty decorator
- Define private class properties
- Combine property with decorator to realize property privatization (
safe implementation of get and set methods). #python内建函数
property(fget=None, fset=None, fdel=None, doc=None)
attribute, doc is a string (like Comments are the same). From an implementation perspective, these parameters are optional. property has three methods getter(), setter() and
delete() to specify fget, fset and fdel. This means the following line: class Student(object):
@property #相当于property.getter(score) 或者property(score)
def score(self):
return self._score
@score.setter #相当于score = property.setter(score)
def score(self, value):
if not isinstance(value, int):
raise ValueError('score must be an integer!')
if value 100:
raise ValueError('score must between 0 ~ 100!')
self._score = value
- By combining yield and iter, we can turn an object into an iterable
-
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- class TestIter(object): def init(self): self.lst = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] def read(self): for ele in xrange(len(self.lst)): yield ele def iter(self): return self.read() def str(self): return ','.join(map(str, self.lst)) repr = str def test_iter(): obj = TestIter() for num in obj: print num print obj if name == 'main': test_iter()
Copy after loginMagical partial
partial is very similar to imitation in C++ function (function object).
In stack
overflow, a running method similar to partial is given: def partial(func, *part_args):
def wrapper(*extra_args):
args = list(part_args)
args.extend(extra_args)
return func(*args)
return wrapper
feature binding to pre-bind some Function parameters, returns a callable variable until the actual call is executed: eval我理解为一种内嵌的python解释器(这种解释可能会有偏差), 会解释字符串为对应的代码并执行, 并且将执行结果返回。 看一下下面这个例子: exec在Python中会忽略返回值, 总是返回None, eval会返回执行代码或语句的返回值 exec和eval在执行代码时, 除了返回值其他行为都相同 在传入字符串时, 会使用compile(source, ‘string#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from functools import partial
def sum(a, b):
return a + b
def test_partial():
fun = partial(sum, 2) # 事先绑定一个参数, fun成为一个只需要一个参数的可调用变量
print fun(3) # 实现执行的即是sum(2, 3)
if name == 'main':
test_partial()
# 执行结果
5
神秘eval
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
def test_first():
return 3
def test_second(num):
return num
action = { # 可以看做是一个sandbox
"para": 5,
"test_first" : test_first,
"test_second": test_second
}
def test_eavl():
condition = "para == 5 and test_second(test_first) > 5"
res = eval(condition, action) # 解释condition并根据action对应的动作执行
print res
if name == '_exec
>’, mode)编译字节码。 mode的取值为exec和eval
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
def test_first():
print "hello"
def test_second():
test_first()
print "second"
def test_third():
print "third"
action = {
"test_second": test_second,
"test_third": test_third
}
def test_exec():
exec "test_second" in action
if name == 'main':
test_exec() # 无法看到执行结果getattr
getattr(object, name[, default])返回对象的命名属性,属性名必须是字符串。如果字符串是对象的属性名之一,结果就是该属性的值。例如, getattr(x, ‘foobar’) 等价于 x.foobar。 如果属性名不存在,如果有默认值则返回默认值,否则触发 AttributeError 。
# 使用范例 class TestGetAttr(object): test = "test attribute" def say(self): print "test method" def test_getattr(): my_test = TestGetAttr() try: print getattr(my_test, "test") except AttributeError: print "Attribute Error!" try: getattr(my_test, "say")() except AttributeError: # 没有该属性, 且没有指定返回值的情况下 print "Method Error!" if name == 'main': test_getattr() # 输出结果 test attribute test method
命令行处理
def process_command_line(argv):
"""
Return a 2-tuple: (settings object, args list).
`argv` is a list of arguments, or `None` for ``sys.argv[1:]``.
"""
if argv is None:
argv = sys.argv[1:]
# initialize the parser object:
parser = optparse.OptionParser(
formatter=optparse.TitledHelpFormatter(width=78),
add_help_option=None)
# define options here:
parser.add_option( # customized description; put --help last
'-h', '--help', action='help',
help='Show this help message and exit.')
settings, args = parser.parse_args(argv)
# check number of arguments, verify values, etc.:
if args:
parser.error('program takes no command-line arguments; '
'"%s" ignored.' % (args,))
# further process settings & args if necessary
return settings, args
def main(argv=None):
settings, args = process_command_line(argv)
# application code here, like:
# run(settings, args)
return 0 # success
if name == 'main':
status = main()
sys.exit(status)读写csv文件
# 从csv中读取文件, 基本和传统文件读取类似
import csv
with open('data.csv', 'rb') as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
for row in reader:
print row
# 向csv文件写入
import csv
with open( 'data.csv', 'wb') as f:
writer = csv.writer(f)
writer.writerow(['name', 'address', 'age']) # 单行写入
data = [
( 'xiaoming ','china','10'),
( 'Lily', 'USA', '12')]
writer.writerows(data) # 多行写入各种时间形式转换
只发一张网上的图, 然后查文档就好了, 这个是记不住的
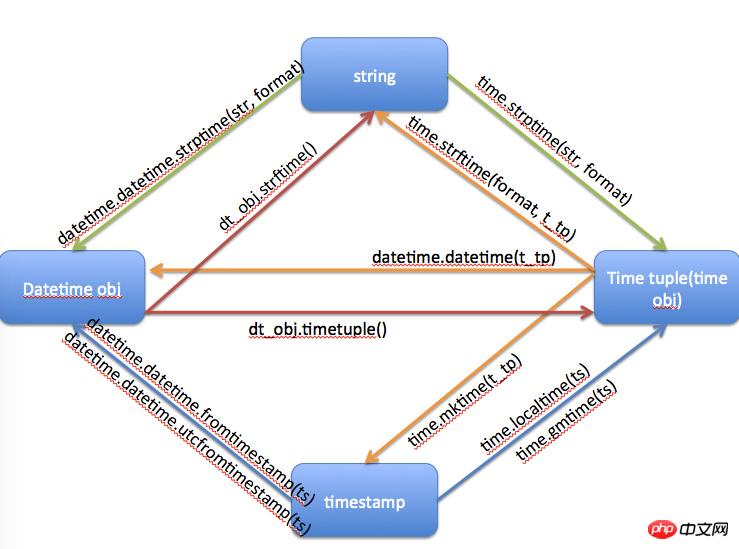
字符串格式化
一个非常好用, 很多人又不知道的功能:
>>> name = "andrew"
>>> "my name is {name}".format(name=name)
'my name is andrew'
The above is the detailed content of 17 Python tricks and tricks to share. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1.PHP is suitable for rapid development and maintenance of large-scale web applications. 2. Python dominates the field of data science and machine learning.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and Resources
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and Resources
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python and JavaScript have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of community, libraries and resources. 1) The Python community is friendly and suitable for beginners, but the front-end development resources are not as rich as JavaScript. 2) Python is powerful in data science and machine learning libraries, while JavaScript is better in front-end development libraries and frameworks. 3) Both have rich learning resources, but Python is suitable for starting with official documents, while JavaScript is better with MDNWebDocs. The choice should be based on project needs and personal interests.
 How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
In VS Code, you can run the program in the terminal through the following steps: Prepare the code and open the integrated terminal to ensure that the code directory is consistent with the terminal working directory. Select the run command according to the programming language (such as Python's python your_file_name.py) to check whether it runs successfully and resolve errors. Use the debugger to improve debugging efficiency.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.
 Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Docker uses Linux kernel features to provide an efficient and isolated application running environment. Its working principle is as follows: 1. The mirror is used as a read-only template, which contains everything you need to run the application; 2. The Union File System (UnionFS) stacks multiple file systems, only storing the differences, saving space and speeding up; 3. The daemon manages the mirrors and containers, and the client uses them for interaction; 4. Namespaces and cgroups implement container isolation and resource limitations; 5. Multiple network modes support container interconnection. Only by understanding these core concepts can you better utilize Docker.
 Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VS Code extensions pose malicious risks, such as hiding malicious code, exploiting vulnerabilities, and masturbating as legitimate extensions. Methods to identify malicious extensions include: checking publishers, reading comments, checking code, and installing with caution. Security measures also include: security awareness, good habits, regular updates and antivirus software.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in automation, scripting, and task management. 1) Automation: File backup is realized through standard libraries such as os and shutil. 2) Script writing: Use the psutil library to monitor system resources. 3) Task management: Use the schedule library to schedule tasks. Python's ease of use and rich library support makes it the preferred tool in these areas.




