 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 H5 Tutorial
H5 Tutorial
 HTML5 local storage-detailed explanation of the basic use of IndexedDB
HTML5 local storage-detailed explanation of the basic use of IndexedDB
HTML5 local storage-detailed explanation of the basic use of IndexedDB
In HTML5 Local Storage - Web SQL Database mentioned that Web SQL Database has actually been abandoned, and the local storage supported by HTML5 has actually become
Web Storage (Local Storage and Session Storage) with IndexedDB. Web Storage uses simple string key-value pairs to store data locally, which is convenient and flexible, but cannot store large amounts of structured data. IndexedDB is an API that can store large amounts of structured data on the client and use indexes for efficient retrieval.
Asynchronous API
Most operations in IndexedDB are not our commonly used calling methods and return result modes, but the request-response mode, such as the operation of opening a database
var request=window.indexedDB.open('testDB');
This command does not return a handle to the DB object. What we get is an IDBOpenDBRequest object, and the DB object we want to get is in its result attribute,
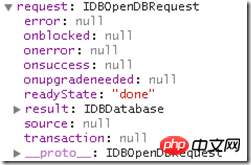
The response requested by this command is an IDBDatabase object, which is the IndexedDB object,
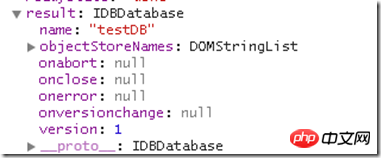
In addition to result, IDBOpenDBRequest interface Several important attributes are defined
onerror: callback function handle for failed request
onsuccess: callback function handle for successful request
onupgradeneeded: Request database version change handle
The so-called asynchronous API means that not after this instruction is executed, we can use request.result to obtain indexedDB Object, just like using ajax, completion of statement execution does not mean that the object has been obtained, so we usually handle it in its callback function.
Create database
The statement just now has shown how to open an indexedDB database. You can create or open an indexedDB by calling the indexedDB.open method. See a complete process
function openDB (name) {
var request=window.indexedDB.open(name);
request.onerror=function(e){
console.log('OPen Error!');
};
request.onsuccess=function(e){
myDB.db=e.target.result;
};
} var myDB={
name:'test',
version:1,
db:null
};
openDB(myDB.name);A myDB object is defined in the code. In the successful destruction function of creating indexedDB request, the DB object obtained by the request is assigned to the db attribute of myDB, so that myDB can be used. .db to access the created indexedDB.
version
We noticed that in addition to onerror and onsuccess, IDBOpenDBRequest also has a similar callback function handle - onupgradeneeded. This handle is called when the version number of the database we request to open is inconsistent with the version number of the existing database.
The indexedDB.open() method also has a second optional parameter, the database version number. When the database is created, the default version number is 1. When the version number we pass in is inconsistent with the current version number of the database, onupgradeneeded will be called. Of course, we cannot try to open a version lower than the current database version, otherwise onerror will be called. Modify the example just now
function openDB (name,version) {
var version=version || 1;
var request=window.indexedDB.open(name,version);
request.onerror=function(e){
console.log(e.currentTarget.error.message);
};
request.onsuccess=function(e){
myDB.db=e.target.result;
};
request.onupgradeneeded=function(e){
console.log('DB version changed to '+version);
};
} var myDB={
name:'test',
version:3,
db:null
};
openDB(myDB.name,myDB.version);Since a database with version 1 has just been created, open the version When it is 3, it will output on the console: DB version changed to 3
Close and delete the database
To close the database, you can directly call the close method of the database object
function closeDB(db){
db.close();
}Delete The database uses the deleteDatabase method of the indexedDB object
function deleteDB(name){
indexedDB.deleteDatabase(name);
}Simple call
var myDB={
name:'test',
version:3,
db:null
};
openDB(myDB.name,myDB.version);
setTimeout(function(){
closeDB(myDB.db);
deleteDB(myDB.name);
},500);Due to the asynchronous API, there is no guarantee that the db object can be obtained before the closeDB method is called (actually obtaining the db object is faster than executing a statement much slower), so I used setTimeout to delay it. Of course, we noticed that each indexedDB instance has an onclose callback function handle, which is used to process when the database is closed. Interested students can try it. The principle is very simple and will not be demonstrated.
object store
After having a database, we naturally want to create a table to store data, but there is no concept of table in indexedDB, but objectStore, a database Can contain multiple objectStore, objectStore is a flexible data structure that can store multiple types of data. In other words, an objectStore is equivalent to a table, and each piece of data stored in it is associated with a key.
We can use a specified field in each record as the key value (keyPath), or we can use an automatically generated incrementing number as the key value (keyGenerator), or we can not specify it. Depending on the type of selection key, the data structures that objectStore can store are also different
| 键类型 | 存储数据 |
| 不使用 | 任意值,但是没添加一条数据的时候需要指定键参数 |
| keyPath | Javascript对象,对象必须有一属性作为键值 |
| keyGenerator | 任意值 |
| 都使用 | Javascript对象,如果对象中有keyPath指定的属性则不生成新的键值,如果没有自动生成递增键值,填充keyPath指定属性 |
事务
在对新数据库做任何事情之前,需要开始一个事务。事务中需要指定该事务跨越哪些object store。
事务具有三种模式
只读:read,不能修改数据库数据,可以并发执行
读写:readwrite,可以进行读写操作
版本变更:verionchange
var transaction=db.transaction([students','taecher']); //打开一个事务,使用students 和teacher object store var objectStore=transaction.objectStore('students'); //获取students object store
给object store添加数据
调用数据库实例的createObjectStore方法可以创建object store,方法有两个参数:store name和键类型。调用store的add方法添加数据。有了上面知识,我们可以向object store内添加数据了
keyPath
因为对新数据的操作都需要在transaction中进行,而transaction又要求指定object store,所以我们只能在创建数据库的时候初始化object store以供后面使用,这正是onupgradeneeded的一个重要作用,修改一下之前代码
function openDB (name,version) {
var version=version || 1;
var request=window.indexedDB.open(name,version);
request.onerror=function(e){
console.log(e.currentTarget.error.message);
};
request.onsuccess=function(e){
myDB.db=e.target.result;
};
request.onupgradeneeded=function(e){
var db=e.target.result;
if(!db.objectStoreNames.contains('students')){
db.createObjectStore('students',{keyPath:"id"});
}
console.log('DB version changed to '+version);
};
}这样在创建数据库的时候我们就为其添加了一个名为students的object store,准备一些数据以供添加
var students=[{
id:1001,
name:"Byron",
age:24
},{
id:1002,
name:"Frank",
age:30
},{
id:1003,
name:"Aaron",
age:26
}];function addData(db,storeName){
var transaction=db.transaction(storeName,'readwrite');
var store=transaction.objectStore(storeName);
for(var i=0;i<students.length;i++){
store.add(students[i]);
}
}
openDB(myDB.name,myDB.version);
setTimeout(function(){
addData(myDB.db,'students');
},1000);这样我们就在students object store里添加了三条记录,以id为键,在chrome控制台看看效果
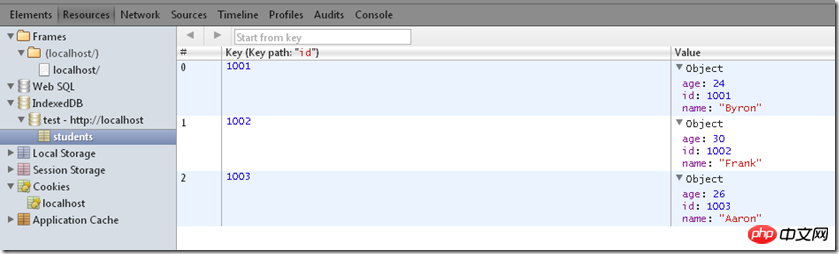
keyGenerate
function openDB (name,version) {
var version=version || 1;
var request=window.indexedDB.open(name,version);
request.onerror=function(e){
console.log(e.currentTarget.error.message);
};
request.onsuccess=function(e){
myDB.db=e.target.result;
};
request.onupgradeneeded=function(e){
var db=e.target.result;
if(!db.objectStoreNames.contains('students')){
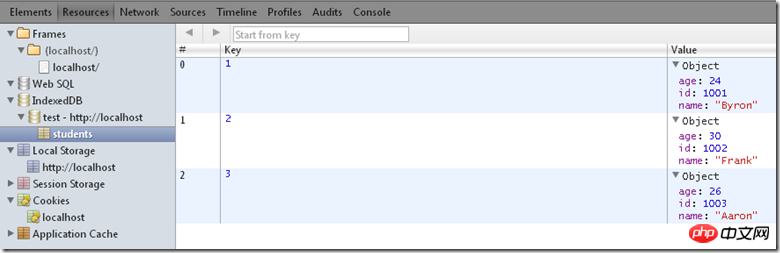
db.createObjectStore('students',{autoIncrement: true});
}
console.log('DB version changed to '+version);
};
}
剩下的两种方式有兴趣同学可以自己摸索一下了
查找数据
可以调用object store的get方法通过键获取数据,以使用keyPath做键为例
function getDataByKey(db,storeName,value){
var transaction=db.transaction(storeName,'readwrite');
var store=transaction.objectStore(storeName);
var request=store.get(value);
request.onsuccess=function(e){
var student=e.target.result;
console.log(student.name);
};
}更新数据
可以调用object store的put方法更新数据,会自动替换键值相同的记录,达到更新目的,没有相同的则添加,以使用keyPath做键为例
function updateDataByKey(db,storeName,value){ var transaction=db.transaction(storeName,'readwrite');
var store=transaction.objectStore(storeName);
var request=store.get(value);
request.onsuccess=function(e){
var student=e.target.result;
student.age=35;
store.put(student);
};
}删除数据及object store
调用object store的delete方法根据键值删除记录
function deleteDataByKey(db,storeName,value){
var transaction=db.transaction(storeName,'readwrite');
var store=transaction.objectStore(storeName);
store.delete(value);
}调用object store的clear方法可以清空object store
function clearObjectStore(db,storeName){
var transaction=db.transaction(storeName,'readwrite');
var store=transaction.objectStore(storeName);
store.clear();
}调用数据库实例的deleteObjectStore方法可以删除一个object store,这个就得在onupgradeneeded里面调用了
if(db.objectStoreNames.contains('students')){
db.deleteObjectStore('students');
}最后
这就是关于indexedDB的基本使用方式,很多同学看了会觉得很鸡肋,和我们正常自己定义个对象使用没什么区别,也就是能保存在本地罢了,这是因为我们还没有介绍indexedDB之所以称为indexed的杀器——索引,这个才是让indexedDB大显神通的东西,下篇我们就来看看这个杀器。
The above is the detailed content of HTML5 local storage-detailed explanation of the basic use of IndexedDB. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1389
1389
 52
52
 Table Border in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Table Border in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Guide to Table Border in HTML. Here we discuss multiple ways for defining table-border with examples of the Table Border in HTML.
 Nested Table in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Nested Table in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
This is a guide to Nested Table in HTML. Here we discuss how to create a table within the table along with the respective examples.
 HTML margin-left
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
HTML margin-left
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
Guide to HTML margin-left. Here we discuss a brief overview on HTML margin-left and its Examples along with its Code Implementation.
 HTML Table Layout
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML Table Layout
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Guide to HTML Table Layout. Here we discuss the Values of HTML Table Layout along with the examples and outputs n detail.
 HTML Input Placeholder
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML Input Placeholder
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Guide to HTML Input Placeholder. Here we discuss the Examples of HTML Input Placeholder along with the codes and outputs.
 Moving Text in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Moving Text in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Guide to Moving Text in HTML. Here we discuss an introduction, how marquee tag work with syntax and examples to implement.
 HTML Ordered List
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
HTML Ordered List
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
Guide to the HTML Ordered List. Here we also discuss introduction of HTML Ordered list and types along with their example respectively
 HTML onclick Button
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
HTML onclick Button
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Guide to HTML onclick Button. Here we discuss their introduction, working, examples and onclick Event in various events respectively.



