
DTD is a set of grammatical rules for tags. It is part of the XML1.0 version specification, is the verification mechanism of html files, and is part of the composition of html files.
DTD: Three document types: S (Strict), T (Transitional), F (Frameset).
Strict: Use this type if you need clean markup without clutter in the presentation layer. Please use with Cascading Style Sheets (CSS)
Transitional: DTD can contain rendering attributes and elements that the W3C expects to be moved into the style sheet. If your readers are using browsers that do not support Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and you have to use HTML's rendering features use
Frameset: DTD should be used for documents with frames . Except that the frameset element replaces the body element, the Frameset DTD is equivalent to the Transitional DTD
html5 basically does not have the strict requirements of XHTML 1.0 Transitional, and simplifies many things and can be used directly
HTML5
—————————— ——————————————————————
xhtml 1.1:
xhtml 1.1 plus mathml plus svg:
————————————————————————————————
html 4.01 strict:
html 4.01 transitional:
html 4.01 frameset:
—————————— ————————————————————
xhtml 1.0 strict:
xhtml 1.0 transitional:
xhtml 1.0 frameset:
—— ——————————————————————————————
html 3.2:
< ;!doctype html public "-/w3c/dtd html 3.2 final/en">
—————————————————————— ————————
html 2 (the number 2 represents the version number):
Attached is an old version label comparison DTD document:
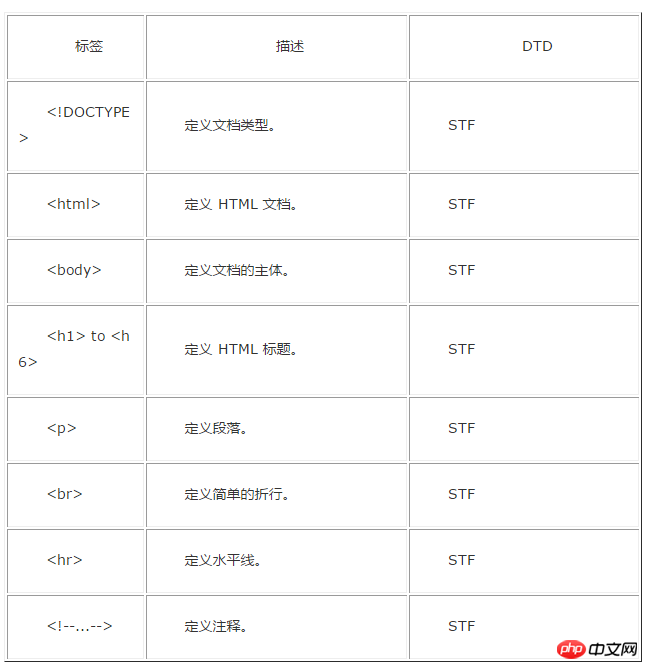
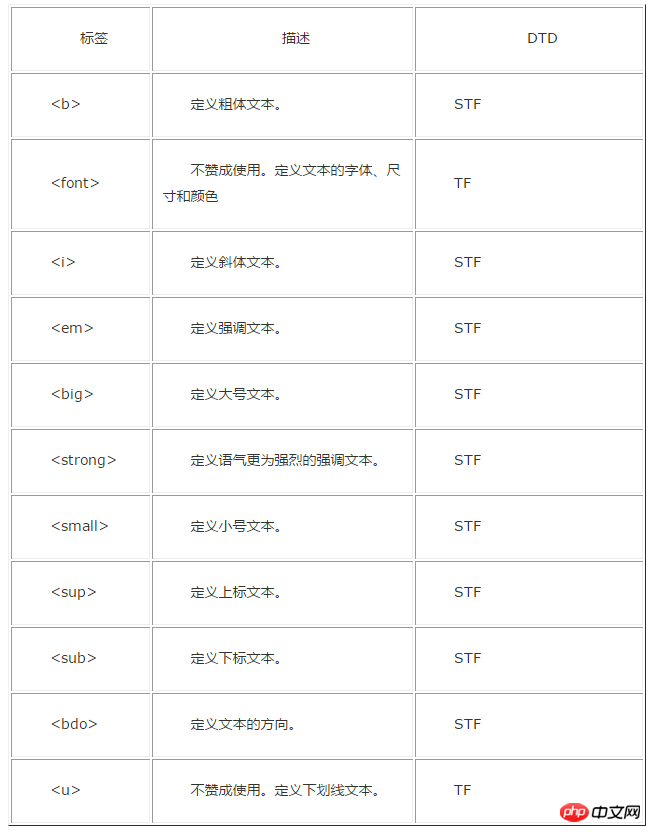
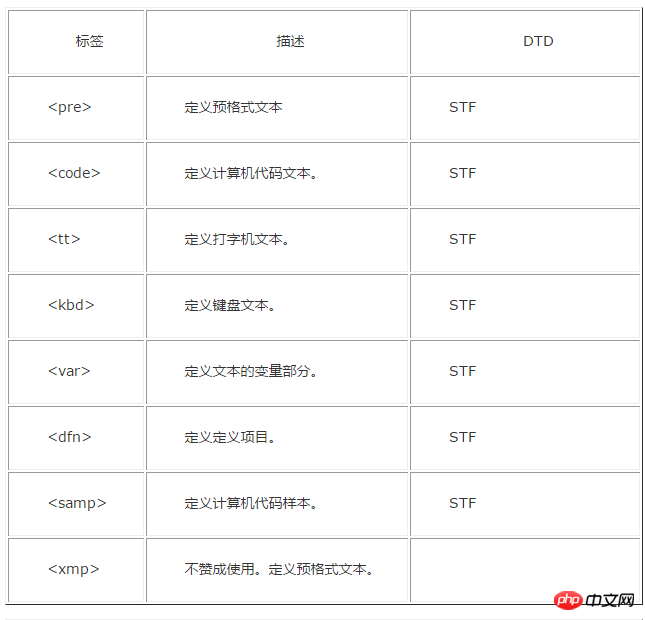
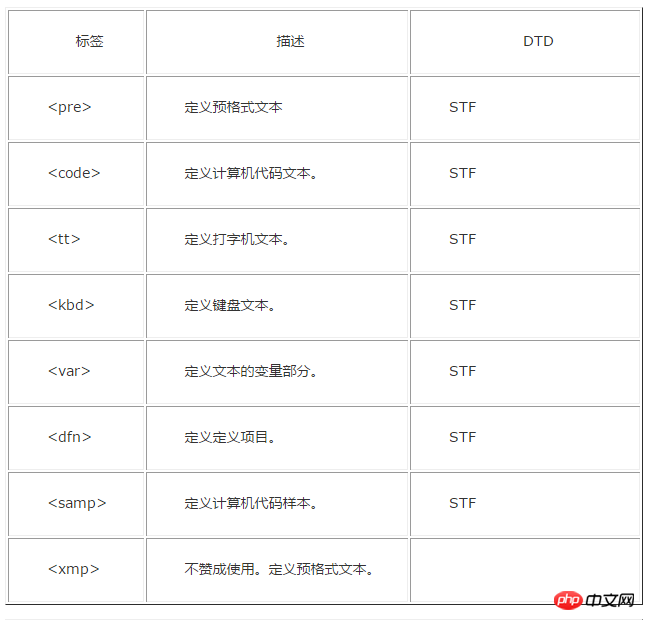
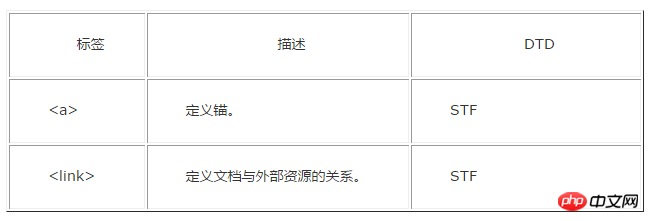
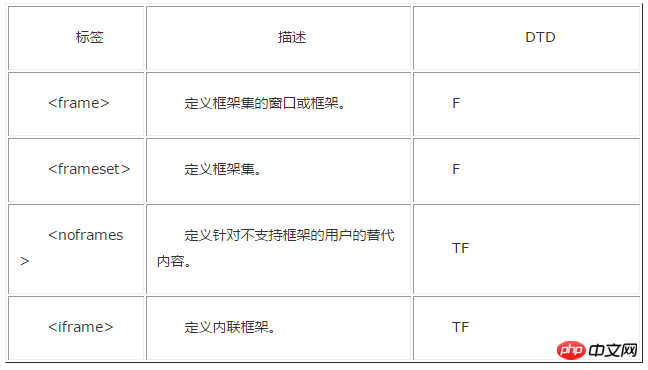
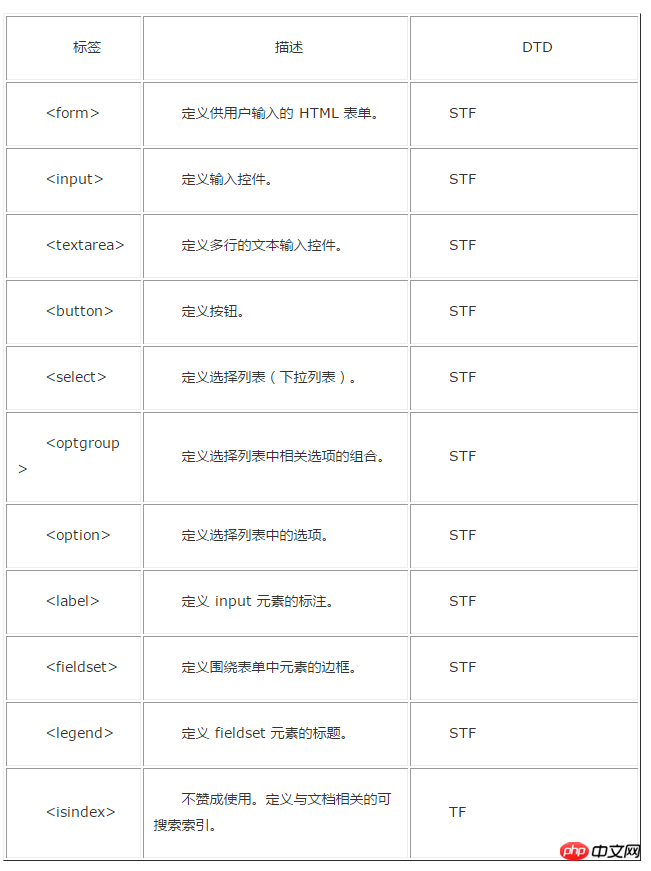
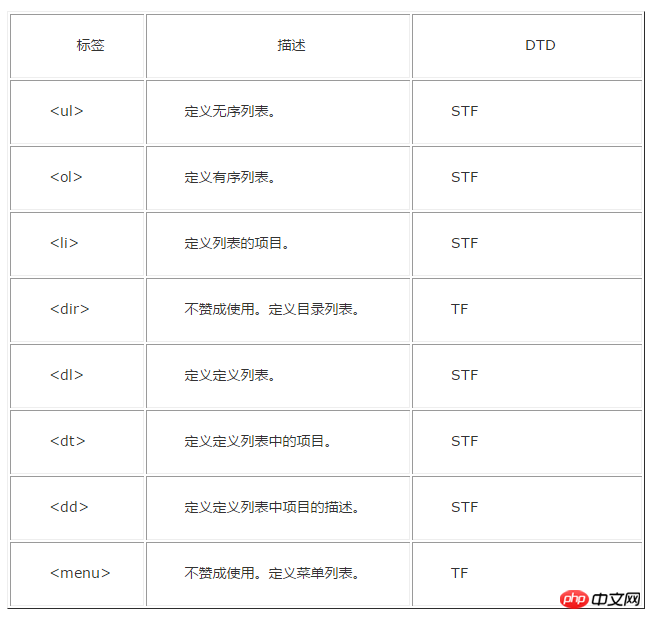
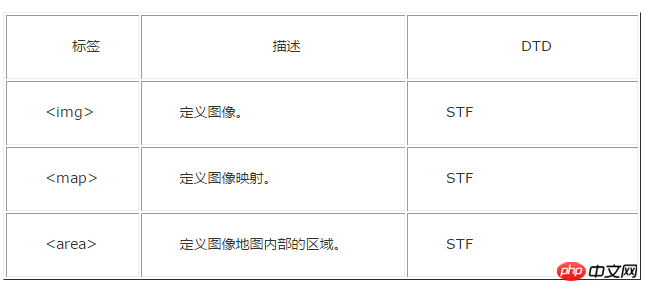
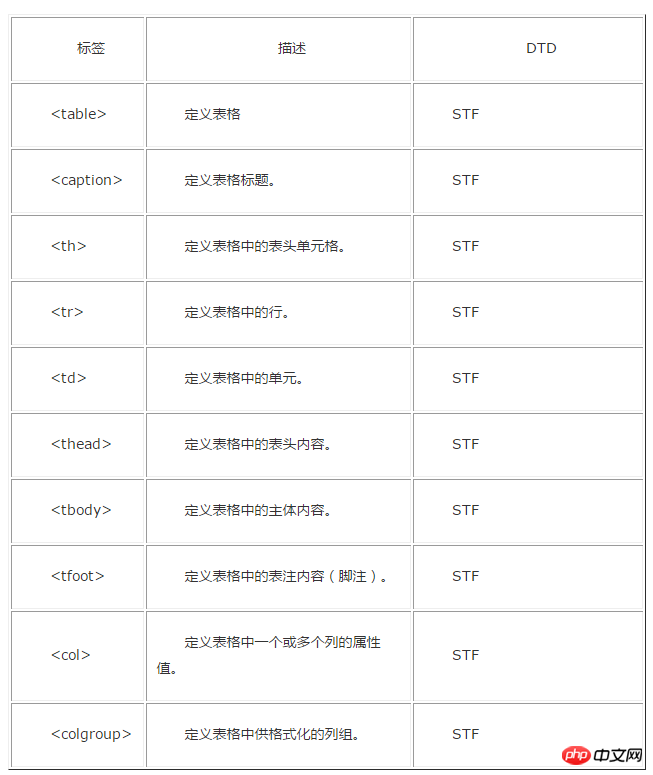
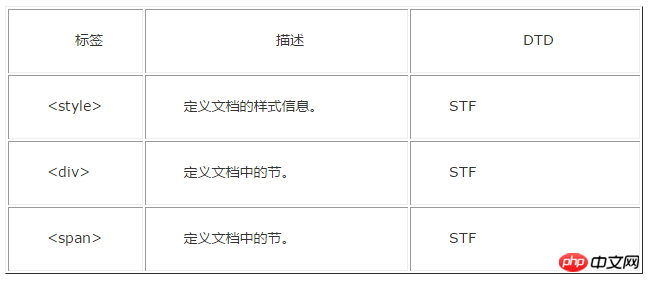
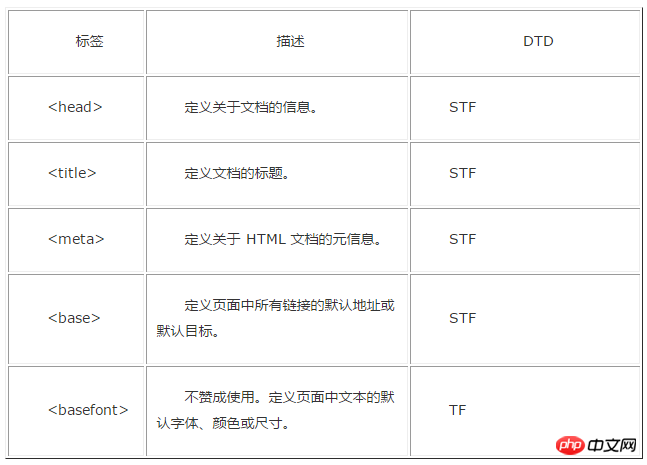
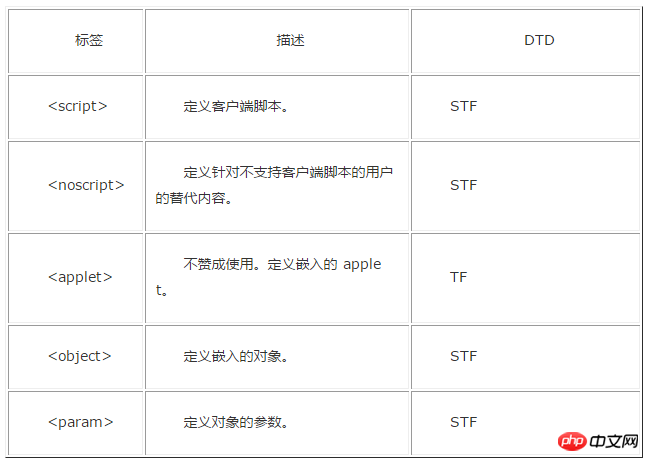
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of how to use DTD in HTML. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




