
Basic environment: Python 3.5.1
mysql version: 5.6.35 (rpm installation method)
Operating system: Centos7.3 and windows7
1. python Introduction to the connection database module:
At present, the following are mainly used, MySQLdb and pymsql, as well as the mysql-connector-python driver officially provided by mysql. The MySQLdb module is more commonly used in python2.X, and python3.X I will use more pymsql, and I will study the official mysql-connector-python later. This learning and practice are all based on the pymsql module.
The usage of PyMySQL is almost the same as that of MySQLdb. If you are used to using MySQLdb, you only need to change import MySQLdb to import pymysql.
2. Introduction to the method and parameters of pymysql connecting to the database:
pymysql connects to mysql Using the pymysql.connect() method, many parameters can be adjusted:
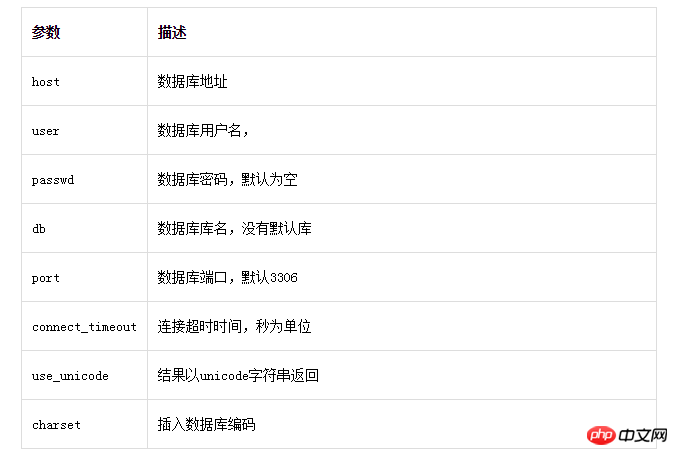
Connection example:
connect=pymysql.connect(host="192.168.186.157",port=3306,user="winner",passwd="123123",db="DB",charset ="utf8",connect_timeout=3000)
The example connection mainly includes parameters such as host, user, passwrd and port
Connection example 2:
connect=pymysql.connect( "192.168.186.157","winner","123123","test")
There is no need to add parameters such as host, but the format is fixed. The locations of the host, user, password and initial connection database cannot be interchanged. ,
The above example with parameters is relatively more casual.
Note: The port and connection timeout here are all int, so no quotes are needed
The connect() function returned by the connection object:
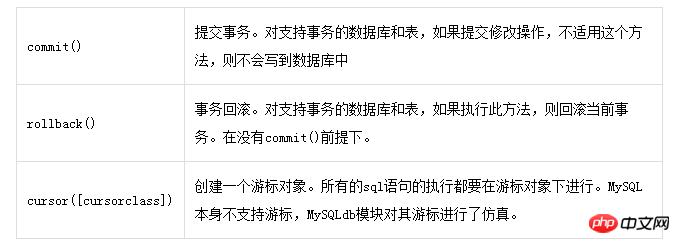
In the process of operating the mysql database in python, we mainly use the cursor acquisition method counect.cursor() and cursor.execute() methods to operate the database, such as creating databases and data tables. We generally directly Just connect to the mysql client and execute the SQL statement, so our more operations are operations such as adding, deleting, modifying, and checking.
The cursor object also provides several methods:
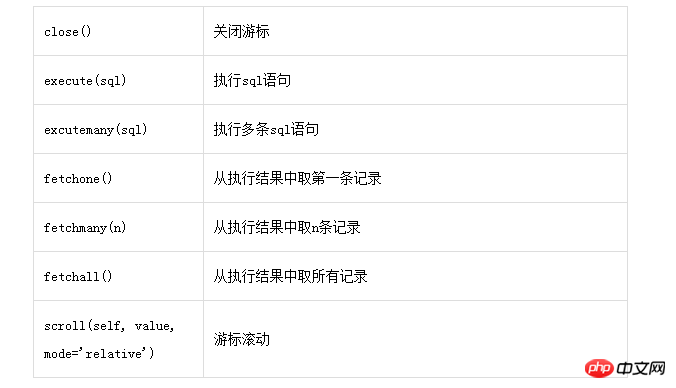
Example 1. Connect the mysql server of 192.168.186.157 to create the pymysql library character set as utf8
#/usr/bin/env python
#_*_coding :utf-8_*_
#Import pymysql module
import pymysql
#Use the pymysql.connect() method to create a database link
con=pymysql .connect(host='192.168.186.157',user='winner',passwd='123123',port=3306)
#Use the con.cursor() method to create a cursor
cursor =con.cursor()
sql=" create database If Not Exists pymysql default character set utf8;"
'''sql="""create table if not exists class (id int (10) primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20) not null ,address varchar(20) not null default "gansu")"""
'''
cursor.execute(sql)
cursor.execute("show databases")
dataname=cursor.fetchall()
print(dataname)
Execution results:
(('information_schema',), ('#mysql50#2017-03-16_09-38-47',), ('DB',), ('mysql',), ('performance_schema',),
('pymysql',), ('test',), ('winner_mas',))
Process finished with exit code 0
Example 2: Connect to the newly created pymysql database to create a class table
#/usr/bin/env python
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
#导入pymysql模块
import pymysql
#使用pymysql.connect()方法创建数据库链接
con=pymysql.connect(host='192.168.186.157',user='winner',passwd='123123',port=3306,db='pymysql')
#使用con.cursor()方法创建游标
cursor=con.cursor()
#sql=" create database If Not Exists pymysql default character set utf8;"
sql="""create table if not exists class (id int(10) primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20) not null ,address varchar(20) not null default "gansu")"""
cursor.execute(sql)
cursor.execute("show tables")
dataname=cursor.fetchall()
print(dataname)
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python35\python.exe C:/Users/Administrator/PycharmProjects/python/createdatabase.py
(('class',),)
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python35\lib\site-packages\pymysql\cursors.py:166: Warning: (1050, "Table 'class' already exists")
result = self._query(query)
Process finished with exit code 0
#/usr/bin/env python
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
#导入pymysql模块
import pymysql
#打开数据库链接
connect=pymysql.connect(host="192.168.186.157",port=3306,user="winner",passwd="123123",db="pymysql",charset="utf8",connect_timeout=3000)
#使用cursor方法获取操作游标
cursor=connect.cursor()
sql=''' insert into class (name,address)
values("JSP","go"),("winner","back"),("GOOD","contine"),("cursor","execute");
'''
#使用execute方法操作数据库
cursor.execute(sql)
#事务提交
#connect.commit()
data=cursor.execute("select * from class order by id desc" )
#使用fetchall方法获取操作结果
data=cursor.fetchmany(5)
print(data)
注意:在这里将事务提交的部分注释掉了,特演示一下不提交事务的情况。
执行结果(执行第四次时):
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python35\python.exe C:/Users/Administrator/PycharmProjects/python/insertmysql.py
((12, 'cursor', 'execute'), (11, 'GOOD', 'contine'), (10, 'winner', 'back'), (9, 'JSP', 'go'))
Process finished with exit code 0
由此我们发现数据库的事务关系在软件开发的过程当中是相当重要的一部分,所以在对事务处理的时候需要严谨。
提交事务的源代码:
#/usr/bin/env python
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
#导入pymysql模块
import pymysql
#打开数据库链接
connect=pymysql.connect(host="192.168.186.157",port=3306,user="winner",passwd="123123",db="pymysql",charset="utf8",connect_timeout=3000)
#使用cursor方法获取操作游标
cursor=connect.cursor()
sql=''' insert into class (name,address)
values("JSP","go"),("winner","back"),("GOOD","contine"),("cursor","execute");
'''
#Use the execute method to operate the database
cursor.execute(sql)
#Transaction submission
connect.commit()
data=cursor.execute("select * from class order by id desc" )
#Use the fetchall method to obtain the operation result
data=cursor.fetchall()
print(data)
#!/usr/bin/python
#encoding=utf-8
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import os
import calendar
import datetime
import MySQLdb
import os, sys, re,string
import time, tarfile,getopt
import socket
import struct
reload(sys)
sys.setdefaultencoding('utf- 8')
optmap = {
'dbuser': 'tongji',
'dbpass': '64CE0CEE9A85F22C',
'dbhost': '192.168.1.10',
'dbport': 3306,
'dbname': 'web_basic'
}
code='201613'
now = int(time.time())
msgid=code+str(now)
print msgid
f = file('/home /haoren/nian/1550035_ACCOUNT_'+msgid+'_0001_V2.xml','w+')
f1 = file('/home/haoren/nian/1550035_RELATIONACCOUNTINFO_'+msgid+'_0001_V2.xml','w+' )
def log(line):
line = line + "\r\n"
f.write(line)
return
def log1(line):
line = line + "\r\n"
f1.write(line)
return
def sql_select(reqsql):
try:
db_conn = MySQLdb.connect(user=optmap['dbuser'], passwd=optmap['dbpass'], host=optmap[' dbhost'], port=optmap['dbport'], db=optmap['dbname'], charset='utf8')
db_cursor=db_conn.cursor()
db_conn.query ("use %s"%optmap['dbname'])
count = db_cursor.execute(reqsql)
ret = db_cursor.fetchall()
db_cursor.close ()
db_conn.close
return ret
except MySQLdb.Error,e:
print "Mysql ERROR %d:%s" %( e.args[0], e.args[1])
return ''
def getusercoin():
reqsql = "select * from singer_auth where status = 10 and ip !='NULL' AND (signtype = '1' OR signtype = '3') limit 150 ;"
#print reqsql
ret = sql_select(reqsql)
n = 0
for row in ret:
n += 1
if n
print str(row[ 1])+','+str(row[8])
print str(row[0])
print str(row[2])
print str(row[3])
if str(row[9]).strip() == '0' and str(row[10]).strip() == '0':
print str(row[9]) +','+ str(row[10])
elif str(row[9]).strip() == '0' and str(row[10]).strip() != '0':
print str(row[9]) +','+str(row[10]).split('/')[6]
elif str(row[9]).strip() != '0' and str(row[10]).strip() == '0':
print str(row[9]).split('/')[6] +','+str(row[10])
else:
print str(row[9]).split('/')[6] +','+str(row[10]).split('/')[6]
else:
n = 0
getusercoin()
f.close()
f1.close()
#!/usr/bin/env python
#-*-coding:utf-8-*-
#明细
import MySQLdb
import os, sys, re,string
import time, tarfile,getopt
optmap = {
'dbuser' : 'haoren',
'dbpass' : 'FqDxhG4d',
'dbhost' : '192.168.1.10',
'dbport' : 3306,
'dbname' : 'JSDB'
}
def get_files(dir, pattern):
res_file_list =[]
if os.path.exists(dir):
cur_file_list = os.listdir(dir)
for file_name in cur_file_list:
if re.search(pattern, file_name):
res_file_list.append(file_name)
return res_file_list
else:
return 'no'
def main():
cur_day = time.strftime("%Y%m%d", time.localtime(time.time()-86400))
opts, args = getopt.getopt(sys.argv[1:], 'd:')
for op, value in opts:
if op == '-d':
m = re.search('[0-9]{8}', value)
if m:
cur_day = value
else:
print "请输入8位日期(比如:20130215)"
return 'no'
log_day = time.strftime('%y%m%d', time.localtime(time.mktime(time.strptime(cur_day, '%Y%m%d'))))
fmt_day = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d', time.localtime(time.mktime(time.strptime(cur_day, '%Y%m%d'))))
print '结算统计日期:',fmt_day
#log_day = time.strftime("%y%m%d", time.localtime(time.time()-86400))
dirname="/home/haoren/logdir/%s_67"%log_day
print dirname
db_conn = MySQLdb.connect(user=optmap['dbuser'], passwd=optmap['dbpass'], host=optmap['dbhost'], port=optmap['dbport'], db=optmap['dbname'])
db_cursor=db_conn.cursor()
db_conn.query("use %s"%optmap['dbname'])
tabletime = time.strftime("%y%m%d", time.localtime(time.mktime(time.strptime(cur_day, "%Y%m%d"))))
sql="CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `JIESUANTONGJI_%s` like JIESUANTONGJISAMPLE"%tabletime
db_conn.query(sql)
db_conn.query("delete from JIESUANTONGJI_%s"%tabletime)
if os.path.exists("/tmp/JieSuanTongJi2016.txt"):
os.system("rm -f /tmp/JieSuanTongJi2016.txt")
file_list2=get_files(dirname,'billserver')
for file2 in file_list2:
command = "cat %s/%s | grep -h -w 结算统计 |grep -v 人民币消费结算统计 >> /tmp/JieSuanTongJi2016.txt"%(dirname,file2)
os.system(command)
#结算统计记录放在txt文档里面
filename='/tmp/JieSuanTongJi2016.txt'
record = {}
a_file = open(filename, 'r')
#160125-11:00:14 Bill[40268] INFO: [结算统计]时间(1453690814)类别(1)名称(购物卡收入)平台(3977962)等级(2)用户(65147500)赠送(1)个购物卡(39)给客户(65147500),客户等级(28),签约(1), 消耗人民币(100), 客户获得人民币(8000), 平台获得人民币(2000),客户当前人民币(1320960)平台当前人民币(335560)
for a_line in a_file.readlines():
m = re.search("^(\S+) Bill\[\d+\] INFO: \[结算统计\]时间\((\d+)\)类别\((\d+)\)名称\((\S+)\)平台\((\d+)\)等级\((\d+)\)用户\((\d+)\)赠送\((\d+)\)个购物卡\((\d+)\)给客户\((\d+)\),客户等级\((\d+)\),签约\((\d+)\), 消耗人民币\((\d+)\), 客户获得人民币\((\d+)\), 平台获得人民币\((\d+)\),客户当前人民币\((\d+)\)平台当前人民币\((\d+)\)", a_line)
if m:
#print "第一项:"+m.group(1)
#print "第二项:"+m.group(2)
#print "The third item:"+m.group(3)
#print "The 4th item:"+m.group(4)
#print "The fifth item Item: "+m.group (5)
#Print" Sixth Item: "+M.Group (6)
Print" seventh item: "+m.group ( 7)
#print "The eighth item:"+m.group(8)
#print "The 10th item:"+m.group(10)
#print "The 11th item: "+m.group(11)
:"+m.group(12)
#print "The 14th item:"+m.group(13)
(14)
using using using using ’ s ’ s through through ’ s ‐ out out ‐ ‐ ‐
m.group(14)) >0 or int(m.group(15)) >0 : PE,ITEMNAME,CHANNELID,CHANNELLEVEL ,PRESENTERID,ITEMNUM,ITEMID,SINGERID,SINGERLEVEL,SIGN,CONSUMECOIN,SINGERRECVGOLD,CHANNELRECVGOLD,CURRENTSINGERGOLD,CURRENTCHANNELGOLD) values(%d,%d,'%s',%d,%d,%d,%d,%d ,%d,%d,%d,%d,%d,%d,%d,%d)"%(tabletime,int(m.group(2)),int(m.group(3)), str(m.group(4)),int(m.group(5)),int(m.group(6)),int(m.group(7)),int(m.group(8)), int(m.group(9)),int(m.group(10)),int(m.group(11)),int(m.group(12)),int(m.group(13)), int(m.group(14)),int(m.group(15)),int(m.group(16)),int(m.group(17)))) a_file.close () db_conn.commit() db_cursor.close() db_conn.close()main() #if __name__ == "__main__":# main()The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of using python to operate mysql database. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




