Detailed introduction to C# generic types
This article mainly introduces C# generic types, which is very good and has reference value. Friends in need can refer to it
The previous article introduced you to a brief analysis of C# Type system (value type and reference type). Next, this article will introduce you to C# generic types.
Let’s talk about generics in C#. Proficient use of generics can improve the reusability of code. Using our code instantly makes you feel better, of course only a little bit, really only a little bit, because there is still a lot of knowledge to learn and master later. Let's first look at the next example of using Dictionary
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Dictionary<int, string> result = GetAll();
}
public static Dictionary<int, string> GetAll()
{
var dic = new Dictionary<int, string>();
dic.Add(1, "aaa");
dic.Add(1, "aaa");
dic.Add(1, "aaa");
return dic;
}Two forms of generics: generic types (classes, interfaces, delegates and structures) and generic methods, such as TKey and TValue are type parameters, and the int passed in and string are real types. It can be seen that the type parameters are just placeholders for the real type. Generics that do not provide real parameters for type parameters are called unconstructed generic types. If type parameters are specified, they are called constructed types, and instances of the type are the objects we use. The relationship diagram below.
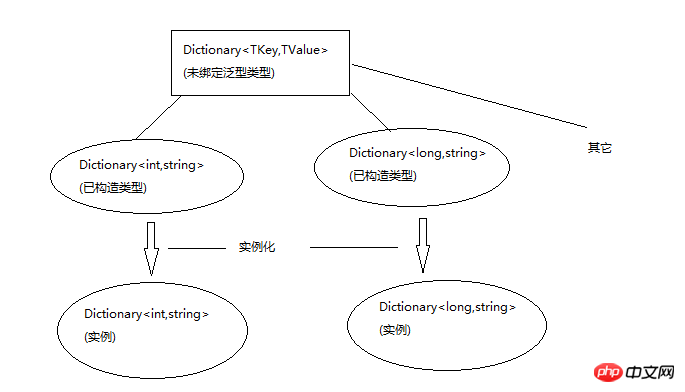
The judgment of generics is a headache. Next, we will explain it carefully. It may not be very clear, but try your best, because the book I don’t quite understand what you are saying, so let me explain it first. If you are not sure, you can read the explanation in the book. First look at the picture below
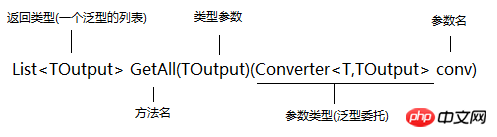
When we look at such a generic method, we need to replace the parameter type inside it in actual use (as mentioned before, the parameter type is actually Type parameter placeholder), use string to replace T, use int to replace TOutput
public static List<int> GetAll(Converter<string, int> conv)
{
} Where Converter
The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to C# generic types. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Active Directory with C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Active Directory with C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Guide to Active Directory with C#. Here we discuss the introduction and how Active Directory works in C# along with the syntax and example.
 Random Number Generator in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Random Number Generator in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in C#. Here we discuss how Random Number Generator work, concept of pseudo-random and secure numbers.
 C# Serialization
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:30 PM
C# Serialization
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:30 PM
Guide to C# Serialization. Here we discuss the introduction, steps of C# serialization object, working, and example respectively.
 C# Data Grid View
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:32 PM
C# Data Grid View
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:32 PM
Guide to C# Data Grid View. Here we discuss the examples of how a data grid view can be loaded and exported from the SQL database or an excel file.
 Patterns in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Patterns in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Guide to Patterns in C#. Here we discuss the introduction and top 3 types of Patterns in C# along with its examples and code implementation.
 Prime Numbers in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:35 PM
Prime Numbers in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:35 PM
Guide to Prime Numbers in C#. Here we discuss the introduction and examples of prime numbers in c# along with code implementation.
 Factorial in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Factorial in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Guide to Factorial in C#. Here we discuss the introduction to factorial in c# along with different examples and code implementation.
 The difference between multithreading and asynchronous c#
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
The difference between multithreading and asynchronous c#
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
The difference between multithreading and asynchronous is that multithreading executes multiple threads at the same time, while asynchronously performs operations without blocking the current thread. Multithreading is used for compute-intensive tasks, while asynchronously is used for user interaction. The advantage of multi-threading is to improve computing performance, while the advantage of asynchronous is to not block UI threads. Choosing multithreading or asynchronous depends on the nature of the task: Computation-intensive tasks use multithreading, tasks that interact with external resources and need to keep UI responsiveness use asynchronous.




