HTML5 Guide (4) - Detailed explanation of using Geolocation
What we are going to learn today is to use Geolocation to implement positioning functions. We can obtain the Geolocation object through navigator.geolocation, which provides the following methods:
getCurrentPosition(callback,errorCallback,options): Get the current position;
watchPosition(callback,error,options): Start monitoring the current location;
clearWatch(id): Stop monitoring the current location.
Note: The browser used in the example below is chrome. If you use other browsers, I cannot guarantee that the running results will be consistent with the results displayed in the example.
1. Get the current position
We will use the getCurrentPosition method to obtain the current position. The location information will not be returned directly in the form of a result. We Need to use callback function for processing. There will be some delays in getting the coordinates, and you will be asked for access permissions. Let's look at the following example:
<!DOCTYPE HTML><html><head>
<title>Example</title>
<style>
table{border-collapse: collapse;}
th, td{padding: 4px;}
th{text-align: right;}
</style></head><body>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>Longitude:</th>
<td id="longitude">-</td>
<th>Latitude:</th>
<td id="latitude">-</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>Altitude:</th>
<td id="altitude">-</td>
<th>Accuracy:</th>
<td id="accuracy">-</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>Altitude Accuracy:</th>
<td id="altitudeAccuracy">-</td>
<th>Heading:</th>
<td id="heading">-</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>Speed:</th>
<td id="speed">-</td>
<th>Time Stamp:</th>
<td id="timestamp">-</td>
</tr>
</table>
<script>
navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(displayPosition);
function displayPosition(pos) {
var properties = ['longitude', 'latitude', 'altitude', 'accuracy', 'altitudeAccuracy', 'heading', 'speed'];
for (var i = 0, len = properties.length; i < len; i++) {
var value = pos.coords[properties[i]];
document.getElementById(properties[i]).innerHTML = value;
}
document.getElementById('timestamp').innerHTML = pos.timestamp;
} </script></body></html>The returned position object contains two attributes, coords: returns coordinate information; timestamp: the time when coordinate information was obtained. Among them, coords includes the following attributes: latitude: latitude; longitude: longitude; altitude: height; accuracy: accuracy (meters); altitudeAccuracy: altitude accuracy (meters); heading: direction of travel; speed: speed of travel (meters/second) .
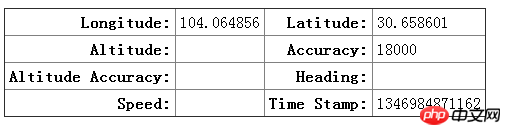
Not all information will be returned, depending on the device you are hosting your browser on. Mobile devices with GPS, accelerometer, and compass will return most of the information, but home computers will not. The location information obtained by the home computer depends on the network environment or wifi. Let's look at the results of the above example.
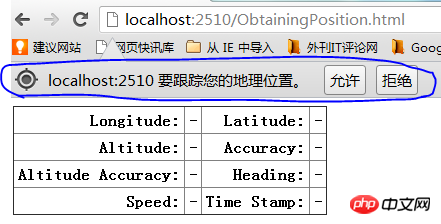
Click Allow to obtain coordinate information.
2. Handling exceptions
Now we introduce theException handling of getCurrentPosition, which is done by using errorCallback Callback function implemented. The parameter error returned by the function contains two attributes, code: error type code; message: error message. The code contains three values: 1: The user is not authorized to use geolocation; 2: Unable to obtain coordinate information; 3: Timeout for obtaining information.
Let’s look at an example:<!DOCTYPE HTML><html><head>
<title>Example</title>
<style>
table{border-collapse: collapse;}
th, td{padding: 4px;}
th{text-align: right;}
</style></head><body>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>Longitude:</th>
<td id="longitude">-</td>
<th>Latitude:</th>
<td id="latitude">-</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>Altitude:</th>
<td id="altitude">-</td>
<th>Accuracy:</th>
<td id="accuracy">-</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>Altitude Accuracy:</th>
<td id="altitudeAccuracy">-</td>
<th>Heading:</th>
<td id="heading">-</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>Speed:</th>
<td id="speed">-</td>
<th>Time Stamp:</th>
<td id="timestamp">-</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>Error Code:</th>
<td id="errcode">-</td>
<th>Error Message:</th>
<td id="errmessage">-</td>
</tr>
</table>
<script>
navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(displayPosition, handleError);
function displayPosition(pos) {
var properties = ["longitude", "latitude", "altitude", "accuracy", "altitudeAccuracy", "heading", "speed"];
for (var i = 0; i < properties.length; i++) {
var value = pos.coords[properties[i]];
document.getElementById(properties[i]).innerHTML = value;
}
document.getElementById("timestamp").innerHTML = pos.timestamp;
} function handleError(err) {
document.getElementById("errcode").innerHTML = err.code;
document.getElementById("errmessage").innerHTML = err.message;
} </script></body></html>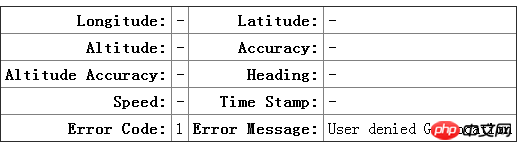
3 .Use geolocation optional parameter items
The options in getCurrentPosition(callback,errorCallback,options) have the following parameters that can be used, enableHighAccuracy: use the best effect; timeout: timeout time (milliseconds); maximumAge : Specifies thecache time (milliseconds). Let’s take the following example:
<!DOCTYPE HTML><html><head>
<title>Example</title>
<style>
table{border-collapse: collapse;}
th, td{padding: 4px;}
th{text-align: right;}
</style></head><body>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>Longitude:</th>
<td id="longitude">-</td>
<th>Latitude:</th>
<td id="latitude">-</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>Altitude:</th>
<td id="altitude">-</td>
<th>Accuracy:</th>
<td id="accuracy">-</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>Altitude Accuracy:</th>
<td id="altitudeAccuracy">-</td>
<th>Heading:</th>
<td id="heading">-</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>Speed:</th>
<td id="speed">-</td>
<th>Time Stamp:</th>
<td id="timestamp">-</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>Error Code:</th>
<td id="errcode">-</td>
<th>Error Message:</th>
<td id="errmessage">-</td>
</tr>
</table>
<script>
var options = {
enableHighAccuracy: false,
timeout: 2000,
maximumAge: 30000
};
navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(displayPosition, handleError, options);
function displayPosition(pos) {
var properties = ["longitude", "latitude", "altitude", "accuracy", "altitudeAccuracy", "heading", "speed"];
for (var i = 0; i < properties.length; i++) {
var value = pos.coords[properties[i]];
document.getElementById(properties[i]).innerHTML = value;
}
document.getElementById("timestamp").innerHTML = pos.timestamp;
} function handleError(err) {
document.getElementById("errcode").innerHTML = err.code;
document.getElementById("errmessage").innerHTML = err.message;
} </script></body></html>4. Monitor position changes
Below we introduce the use of watchPosition method to monitor position changes. Its usage is the same as getCurrentPosition. . Let’s look at an example:<!DOCTYPE HTML><html><head>
<title>Example</title>
<style>
table{border-collapse: collapse;}
th, td{padding: 4px;}
th{text-align: right;}
</style></head><body>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>Longitude:</th>
<td id="longitude">-</td>
<th>Latitude:</th>
<td id="latitude">-</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>Altitude:</th>
<td id="altitude">-</td>
<th>Accuracy:</th>
<td id="accuracy">-</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>Altitude Accuracy:</th>
<td id="altitudeAccuracy">-</td>
<th>Heading:</th>
<td id="heading">-</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>Speed:</th>
<td id="speed">-</td>
<th>Time Stamp:</th>
<td id="timestamp">-</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>Error Code:</th>
<td id="errcode">-</td>
<th>Error Message:</th>
<td id="errmessage">-</td>
</tr>
</table>
<button id="pressme">Cancel Watch</button>
<script>
var options = {
enableHighAccuracy: false,
timeout: 2000,
maximumAge: 30000
}; var watchID = navigator.geolocation.watchPosition(displayPosition, handleError, options);
document.getElementById("pressme").onclick = function (e) {
navigator.geolocation.clearWatch(watchID);
}; function displayPosition(pos) {
var properties = ["longitude", "latitude", "altitude", "accuracy", "altitudeAccuracy", "heading", "speed"];
for (var i = 0; i < properties.length; i++) {
var value = pos.coords[properties[i]];
document.getElementById(properties[i]).innerHTML = value;
}
document.getElementById("timestamp").innerHTML = pos.timestamp;
} function handleError(err) {
document.getElementById("errcode").innerHTML = err.code;
document.getElementById("errmessage").innerHTML = err.message;
} </script></body></html>The above is the detailed content of HTML5 Guide (4) - Detailed explanation of using Geolocation. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1379
1379
 52
52
 Table Border in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Table Border in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Guide to Table Border in HTML. Here we discuss multiple ways for defining table-border with examples of the Table Border in HTML.
 HTML margin-left
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
HTML margin-left
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
Guide to HTML margin-left. Here we discuss a brief overview on HTML margin-left and its Examples along with its Code Implementation.
 Nested Table in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Nested Table in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
This is a guide to Nested Table in HTML. Here we discuss how to create a table within the table along with the respective examples.
 HTML Table Layout
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML Table Layout
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Guide to HTML Table Layout. Here we discuss the Values of HTML Table Layout along with the examples and outputs n detail.
 HTML Input Placeholder
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML Input Placeholder
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Guide to HTML Input Placeholder. Here we discuss the Examples of HTML Input Placeholder along with the codes and outputs.
 HTML Ordered List
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
HTML Ordered List
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
Guide to the HTML Ordered List. Here we also discuss introduction of HTML Ordered list and types along with their example respectively
 Moving Text in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Moving Text in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Guide to Moving Text in HTML. Here we discuss an introduction, how marquee tag work with syntax and examples to implement.
 HTML onclick Button
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
HTML onclick Button
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Guide to HTML onclick Button. Here we discuss their introduction, working, examples and onclick Event in various events respectively.




