
Contents of this chapter:
Knowledge point one:
Box Model: Box Model, consisting of element content, filling ( There are four components: padding, border, and margin. These four components include top/right/bottom/left.
The picture downloaded from w3school, let’s take a look at the four components of the box model
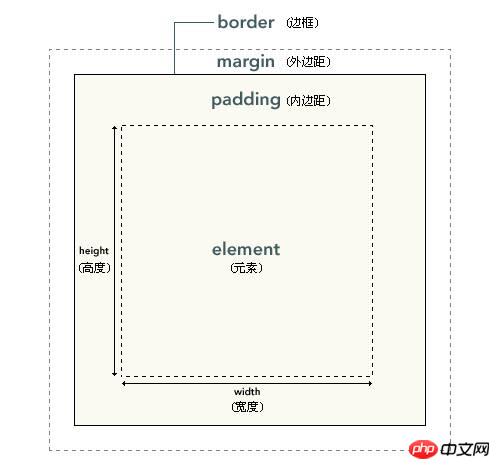
Description: The innermost part of the element box in the picture is the actual content (element); what directly surrounds the content is padding (padding), which presents the background of the element (background); the edge of the padding is Border; outside the border is margin (margin). The margin is transparent by default, so it will not block any elements behind it (in fact, the margin of an element is the padding of its parent element).
When placing an element on the page as to what size it needs to be, add all the declared padding, border, and margin values to the content area. Of course, if an element has no padding, borders, or margins, its size is determined solely by its content. Ignore the superposition effect of outer margins first. The calculation formula is as follows:
Total width = left margin + left border + left padding + width + right padding + right border + right margin
Total height = top margin + top border + top padding + height + bottom padding + bottom border + bottom margin
Take one of the examples as an example:
Introduction code:
<p style="width: 500px;"> <p style="margin: 10px; border: 5px solid blue; padding: 10px; "> 网上很多设置的方式,目前以二进制的方式来讲解(ID CLASS ELEMENT) 网上很多设置的方式,目前以二进制的方式来讲解(ID CLASS ELEMENT) 网上很多设置的方式,目前以二进制的方式来讲解(ID CLASS ELEMENT) </p> </p>
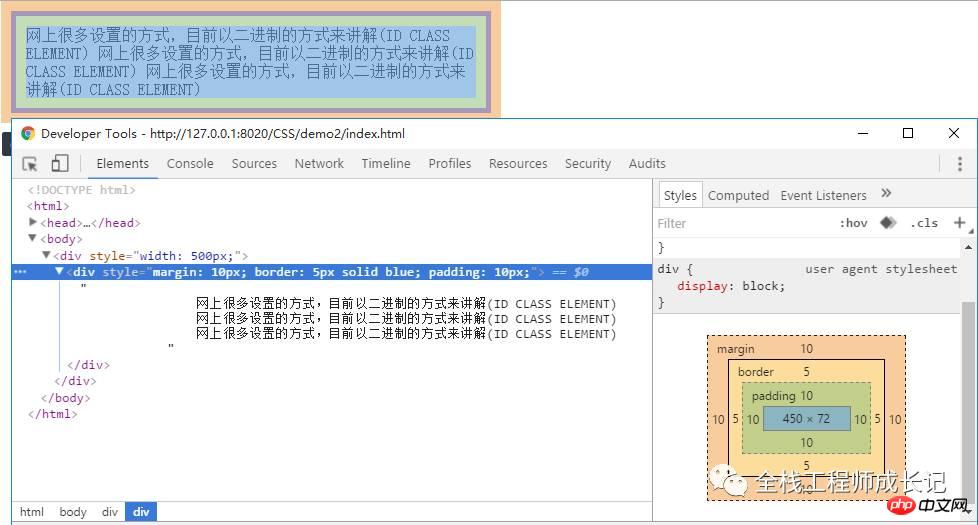
The total calculated size of the above elements is:
Total width = 10 + 5 + 10 + 450+ 10 + 5 + 10 = 500px
Total height = 10 + 5 + 10 + 72+ 10 + 5 + 10 = 122px
Knowledge point 2:
After having a preliminary understanding of the box model, we considered these scenarios:
1. Relative positioning or no positioning (the default position is static )
Introduction code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
.box {
background:black;
color:White;
height:100px;
padding:10px;
border:20px solid Red;
margin:30px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Static or Relative Box</h2>
<p class="box">不设置任何position属性及宽度</p>
</body>
</html>
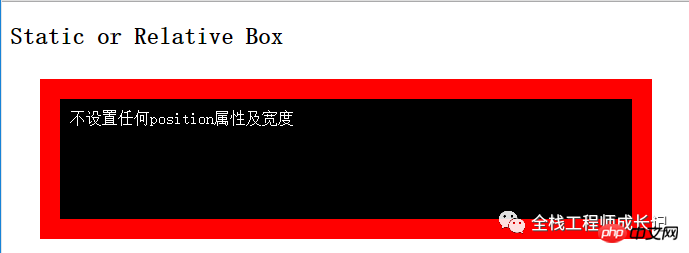
The width of the block is extended Automatically fill the width area of its parent element
2. Floating float elements and absolute positioning elements (have wrapping properties, and can also achieve wrapping effects by setting display: table;, you can Set it yourself and see the effect)
Introduction code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
.box {
background:black;
color:White;
height:100px;
padding:10px;
border:20px solid Red;
margin:30px;
position: absolute;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Absolute or Float Box</h2>
<p class="box">不设置任何position属性及宽度</p>
</body>
</html>

3 .Speciality: Set the style of p to box-sizing: border-box;
Introduction code:
<p style="width: 500px;"> <p style="margin: 10px; border: 5px solid blue; padding: 10px; width: 300px; box-sizing: border-box; "> 网上很多设置的方式,目前以二进制的方式来讲解(ID CLASS ELEMENT) 网上很多设置的方式,目前以二进制的方式来讲解(ID CLASS ELEMENT) 网上很多设置的方式,目前以二进制的方式来讲解(ID CLASS ELEMENT) </p> </p>
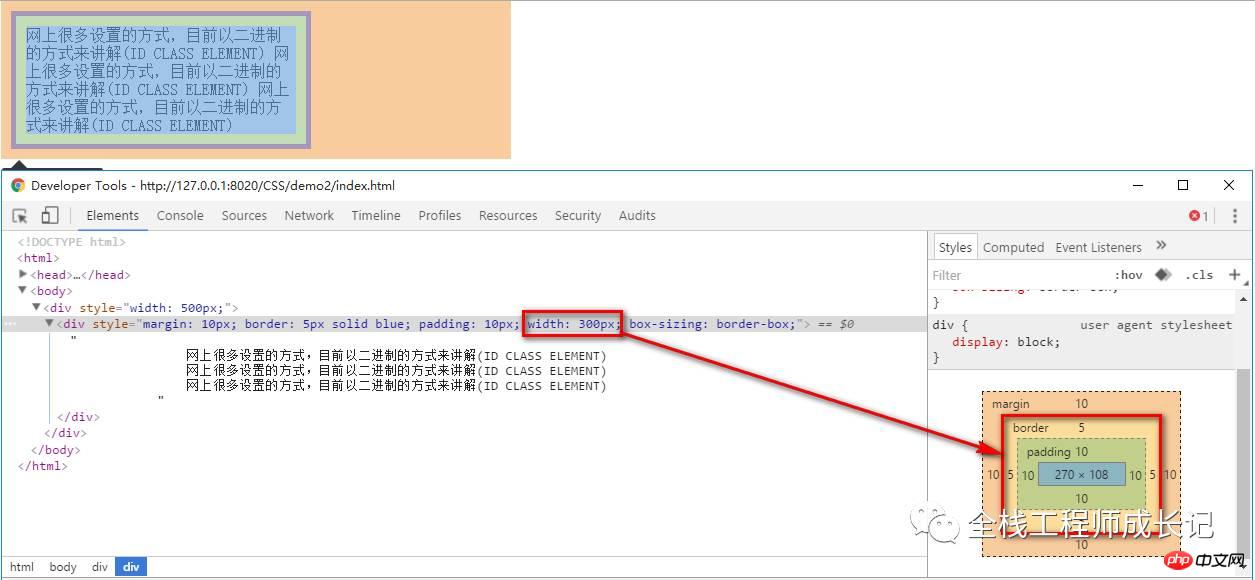
Found that the content width is: border width + padding width + content width
4. The margin attribute of the box model:
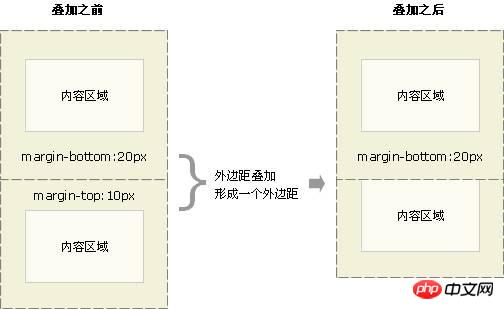
If two elements are placed together, the corresponding margin will only be the larger one
The above is the detailed content of CSS box model knowledge summary. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




