Detailed explanation of Java recursive algorithm (power node arrangement)
JavaRecursive algorithm is a recursive algorithm implemented based on Java language. Recursive algorithms are effective for solving a large class of problems, making the algorithm concise and easy to understand. Next, this article will introduce you to the knowledge about Java recursive algorithms. Friends who are interested can learn together.
The recursive algorithm is an algorithm that directly or indirectly calls its ownfunctionor method. Java recursive algorithm is a recursive algorithm implemented based on Java language. The essence of the recursive algorithm is to decompose the problem into sub-problems of the same type that are reduced in size, and then call methods recursively to represent the solution to the problem. Recursive algorithms are effective for solving a large class of problems, making the algorithm concise and easy to understand.
Features of recursive algorithm for solving problems:
1) Recursion is calling itself in the method.
2) When using the incremental recursion strategy, there must be a clear recursion end condition, called the recursion exit.
3) Recursive algorithm problem solving usually appears very simple, but the operating efficiency of recursive algorithm problem solving is low. Therefore, it is generally not recommended to use recursive algorithms to design programs.
4) During the recursive call process, the system opens a stack to store the return points, local quantities, etc. of each layer. Too many recursions can easily cause stack overflow, etc. Therefore, it is generally not recommended to use recursive algorithms to design programs.
The "repetition" embodied in the recursive algorithm generally has three requirements:
First, each call is reduced in scale ( Usually halved);
The second is that there is a close connection between two adjacent repetitions, and the previous one must be prepared for the next one (usually the output of the previous one is used as the input of the next one);
Third, when the scale of the problem is extremely small, the solution must be given directly instead of recursive calls. Therefore, each recursive call is conditional (provided that the scale does not reach the size of the direct answer), and unconditional recursion The call will become a dead loop and cannot end normally.
In order to understand the recursive algorithm, an example is given as follows:
Problem description:
Solve the Fibonacci sequence number The value of 10 positions? (Fibonacci Sequence (Fibonacci Sequence), also known as Golden Section Sequence, refers to such a sequence: 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21. ...In mathematics, the Fibonacci sequence is recursively defined as follows: F0=0, F1=1, Fn=F(n-1)+F(n-2) (n>=2 , n∈N*))
Java code list:
package com.bjpowernode.test;
public classFab {
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println(fab(5));
}
private static int fab(int index){
if(index==1 || index==2){
return 1;
}else{
return fab(index-1)+fab(index-2);
}
}
} Program analysis:
This example is a very classic example, mainly using Recursively implements the Fibonacci sequence. The exit of this recursive algorithm is in the code segment
if(index==1 || index==2){
return 1;
}. If the index of the program meets the conditions, the recursion will stop. So the running process of this program is:
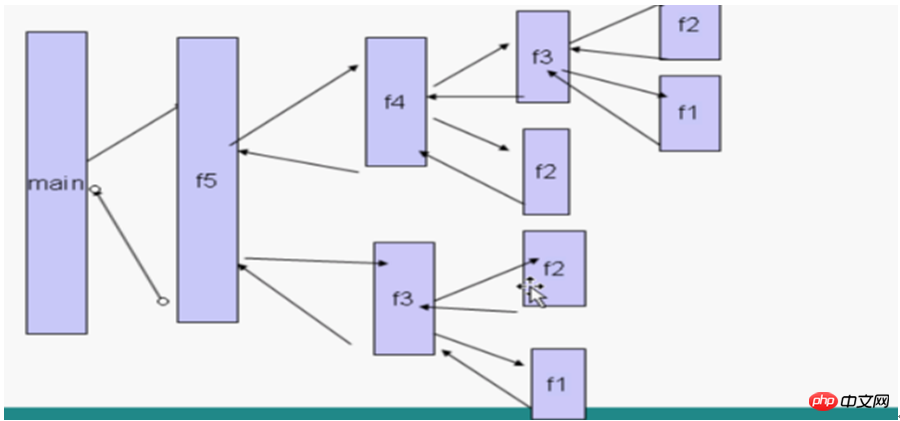
Up to this point in the program analysis, the recursive implementation is completed. Readers can simply make a demo to feel the algorithm. The subtlety, in fact, many people are saying that algorithms are difficult and difficult to reach the sky. In fact, mastering the root of the algorithm is the most important. What is the root of the algorithm? Take this recursive algorithm as an example. I feel that this root is that Exit, as long as you find the exit, the algorithm will naturally fall into place.
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of Java recursive algorithm (power node arrangement). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to the Armstrong Number in Java. Here we discuss an introduction to Armstrong's number in java along with some of the code.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is






