Java LinkedList source code analysis (picture)
Overall introduction
LinkedList implements both the List interface and the Deque interface, which means that it can be regarded as both a sequential container and a queue(Queue), and can also be regarded as a stack. From this point of view, LinkedList is simply an all-around champion. When you need to use a stack or queue, the first thing you should consider is LinkedList. Because Java has officially stated that it is not recommended to use the Stack class, and it is recommended to use LinkedList. What is even more regrettable is that there is no class called Queue in Java (it is an interface name).
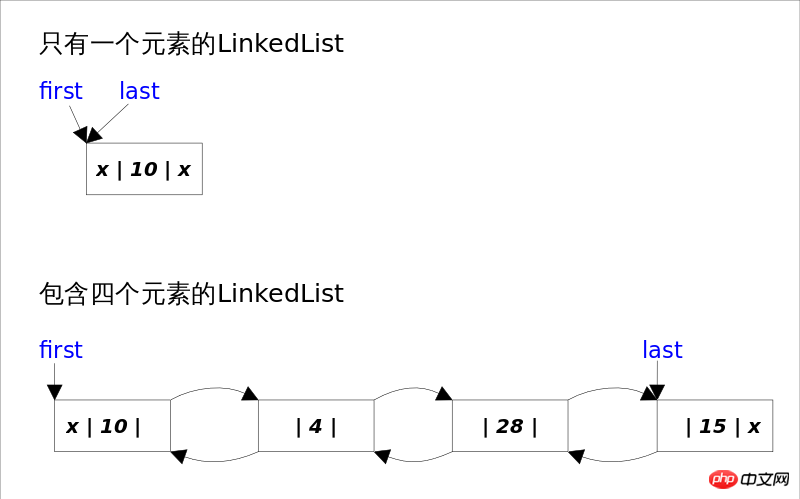
The bottom layer of LinkedList is implemented through a doubly linked list. This section will focus on the maintenance process of the doubly linked list when inserting and deleting elements, that is, the solution between Function related to the List interface, while the knowledge related to Queue, Stack and Deque will be discussed in the next section. Each node of a doubly linked list is represented by the inner class Node. LinkedList references through first and last to point to the first and last elements of the linked list respectively. Note that there is no so-called dummy variable here. When the linked list is empty, first and last both point to <a href="http://www.php.cn/wiki/62.html" target="_blank">null</a>.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
|
The implementation of LinkedList determines that all operations related to subscripts are linear time, and deleting elements at the beginning or end only requires constant time. In order to pursue efficiency, LinkedList does not implement synchronization (synchronized). If concurrent access by multiple threads is required, you can first use the Collections.synchronizedList() method to wrap it.
Method Analysis
add()
add() method has two versions, one is add(E e), this method is in LinkedList Insert elements at the end, because last points to the end of the linked list, and inserting elements at the end takes constant time. You only need to simply modify a few related references; the other is add(int index, E element). This method is to insert an element at the specified table below. You need to first find the specific position through linear search, and then Modify the relevant references to complete the insertion operation.
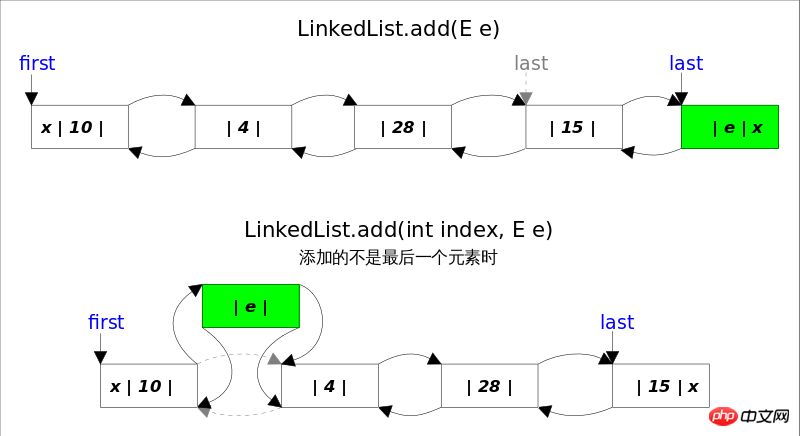
Combined with the above picture, we can see that the logic of add(E e) is very simple. The logic of
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
|
add(int index, E element) is slightly complicated and can be divided into two parts. 1. First find the location to be inserted according to the index; 2. Modify the reference and complete the insertion. operate.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
|
The node(int index) function in the above code is a little tricky, because the linked list is bidirectional, you can search from the beginning to the back, or you can search from the end to the front. The specific direction to look for depends on the condition index < (size >> 1), that is, whether the index is close to the front end or the back end.
remove()
remove()The method also has two versions, one is to delete the first element that is equal to the specified elementremove(<a href="http://www.php.cn/wiki/60.html" target="_blank"> Object</a> o), the other is to delete the element at the specified index remove(int index).
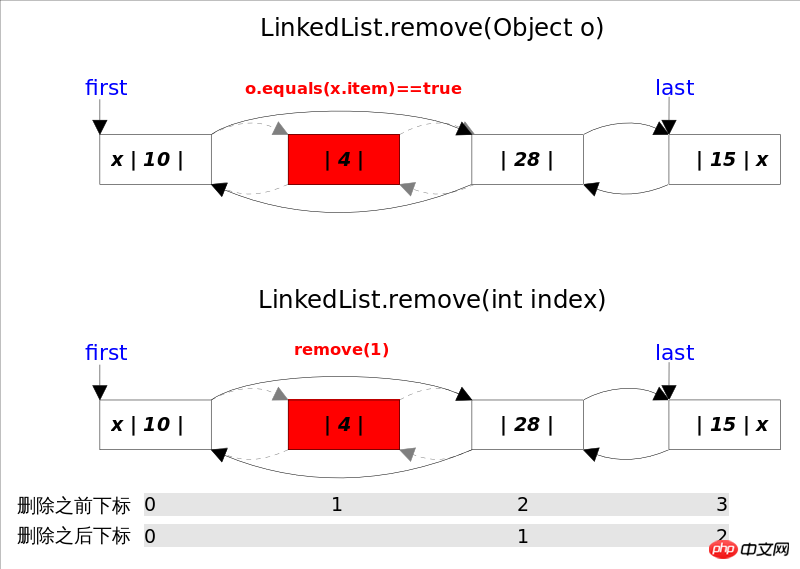
#Both deletion operations require 1. First finding the reference of the element to be deleted, 2. Modifying the relevant reference to complete the deletion operation. When looking for a reference to a deleted element, remove(Object o) calls the element's equals method, while remove(int index) uses the subscript Counting, both ways has linear time complexity. In step 2, both revome() methods are completed through the unlink(Node<E> x) method. Here you need to consider the boundary case when the deleted element is the first or last one.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
|
get()
get(int index)Get the reference to the element at the specified index by calling the node(int index mentioned above ) method implementation.
1 2 3 4 |
|
set()
set(int index, E element)The method modifies the element at the specified subscript to the specified value, and also first passes the node (int index)Find the reference corresponding to the element in the table below, and then modify the value of item in Node.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
|
The above is the detailed content of Java LinkedList source code analysis (picture). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1389
1389
 52
52
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.




