Sample code analysis of how to use bash to parse xml
最初的需求是希望bash能提供完整成熟的xml解析工具来解析xml,但是并没有找到这样的工具。后来在StackOverFlow上找到一个简单的处理xml的方法,即:
rdom () { local IFS=\> ; read -d \< E C ;}方法只有一行!(当然,两条语句应该算是两行……)
当然,这也只能处理最简单原始的xml,不能处理带属性的,不能有注释等等。
由于楼主过于懒惰,不想引入(学习)新的脚本语言,所以打算改造上面的方法。
改造之前,先来解释一下上面那行语句的意义。
其实很简单,这行命令的作用就是读取<与下一个<之间的字符
(xml中,如果在节点本身之外存在<或者>,属性值含有空格,则函数失效,所以我们假设xml中没有此情况)
有了上面的假设,那么两个<字符直接,就一定会有一个>字符,>将read读取的内容分为两部分,分别记做E和C,举个简单的例子:
<tag>value</tag>
第一次执行rdom时,read读取到<即结束了,所以E和C都是空字符串。
第二次执行rdom时,read读取到的内容为:tag>value,然后是<字符,read结束。所以E=tag;C=value
第三次执行rdom时,read读取到的内容为:/tag>到下一个<或文件末尾。所以E=/tag,C为空白符。
所以这种方式并不实用,我们想支持带属性的节点,我们也不想删除xml中的注释,我们甚至还想解析xml的声明,我们……好了,我们想的太多了。我们还是看看能做些什么吧。
我们可以看出,<>里面的部分是作为整体赋值给E的,那么解析属性就要对E做手脚。
(我们假设xml中,在节点本身之外存在没有<和>,属性值中也没有空格)
下面我们来操作一下,首先先引入一个输入空格,用来显示层级的函数echo_tabs
echo_tabs() {
local tabs="";
for((i = 0; i < $1; i++)); do
tabs=$tabs' ' #4个空格
done
echo -n "$tabs" #一定要加双引号
}然后我们来解析xml中的声明,就是下面这部分
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
声明与其他标签闭合方式不同,并且尖括号内两端是?,所以这里要把它与普通节点区分。
read_dom() {
#备份IFS
local oldIFS=$IFS
local IFS=\> #字段分割符改为>
read -d \< ENTITY CONTENT #read分隔符改为<
local ret=$?
local ELEMENT=''
#第一次执行时,第一个字符为<.
#所以read执行完毕,ENTITY和CONTENT都是空白符
if [[ $ENTITY =~ ^[[:space:]]*$ ]] && [[ $CONTENT =~ ^[[:space:]]*$ ]]; then
return $ret
fi
# ENTITY = ?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?
#解析xml声明,并非普通节点,闭合方式与节点不同
if [[ "$ENTITY" =~ ^\?xml[[:space:]]*(.*)\?$ ]]; then #使用正则去除问号和xml字符
ENTITY=''
ELEMENT='' #不是普通节点
ATTRIBUTES="${BASH_REMATCH[1]}" #获取声明中的属性
else #普通节点
ELEMENT=${ENTITY%% *} #获取节点名称,如果ENTITY中有空格,则第一个空格前面部分即为节点名称
ATTRIBUTES=${ENTITY#* } #获取节点所有属性,如果ENTITY中有空格,则第一个空格后面部分为所有属性(#2和#4,#4情况下,会多出/)
fi
}下面我们来解析注释。注释让人烦恼的地方是,注释内可以包含尖括号!这里只做最简单处理,只解析不含尖括号的注释!
if [[ "$ENTITY" = \!--*-- ]]; then #不检查注释
return 0
fi现在我们看xml中最关键的部分
我们知道,CONTENT为节点的内容,显示出来就可以了
if [[ ! "$CONTENT" =~ ^[[:space:]]*$ ]]; then
echo -n CONTENT=$CONTENT
fi节点自身属性都在ENTITY中,所以我们需要将节点名称与属性分开,然后再提取属性名和属性值
我们分别处理下面几种形式的节点
<test a="1"/> <test></test> <test>abc</test> <test/>
我们之前已经将节点名称与属性分开了
ELEMENT=${ENTITY%% *} #获取节点名称,如果ENTITY中有空格,则第一个空格前面部分即为节点名称
ATTRIBUTES=${ENTITY#* } #获取节点所有属性,如果ENTITY中有空格,则第一个空格后面部分为所有属性(#2和#4,#4情况下,会多出/)但是上面的ATTRIBUTES变量会有个小问题,稍后说明
ELEMENT如果以/开头,那么这是读取到节点的闭合标签了
ELEMENT如果以/结尾,那么这是一个空标签,类似
其他情况ELEMENT均为节点名称,但是读取
#!/usr/bin/env bash #只适合解析简单xml,若属性值带有空格,注释中含有尖括号等,则无法解析 #下面情况可以正常解析 #0.<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> #1.Only For Test #2.#3. #4. #Attribute=Attribute Name #VALUE=Attribute Value #ELEMENT=Element Name #CONTENT=Element Content #接受一个int层级参数,层级从0开始 echo_tabs() { local tabs=""; for((i = 0; i < $1; i++)); do tabs=$tabs' ' #4个空格 done echo -n "$tabs" #一定要加双引号 } read_dom() { #备份IFS local oldIFS=$IFS local IFS=\> #字段分割符改为> read -d \< ENTITY CONTENT #read分隔符改为< local ret=$? local ELEMENT='' #第一次执行时,第一个字符为<. #所以read执行完毕,ENTITY和CONTENT都是空白符 if [[ $ENTITY =~ ^[[:space:]]*$ ]] && [[ $CONTENT =~ ^[[:space:]]*$ ]]; then return $ret fi #第二次执行时,分为下面集中情况 #0.<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> #此时read结果为?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"? #CONTENT=若干空白符 #1. 1785 #此时read结果为Size,所以ENTITY=Size,CONTENT='1785' #第三次read结为/Size,所以ENTITY=/Size,CONTENT=若干空白符 #2.#此时read结果为ListBucketResult xmlns="http://s3.amazonaws.com/doc/2006-03-01/", 所以ENTITY=tListBucketResult xmlns="http://s3.amazonaws.com/doc/2006-03-01/",CONTENT=同#1 #3. #此时read结果为test/,所以ENTITY=test/,CONTENT=若干空白符 #4. #此时read结果为test name="xyz" age="21"/,所以ENTITY=test name="xyz"/,CONTENT=若干空白符 #5. #此时read结果为!--q1--,所以ENTITY=!--q1--,CONTENT='' # ENTITY = ?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"? #解析xml声明,并非普通节点,闭合方式与节点不同 if [[ "$ENTITY" =~ ^\?xml[[:space:]]*(.*)\?$ ]]; then #使用正则去除问号和xml字符 ENTITY='' ELEMENT='' #不是普通节点 ATTRIBUTES="${BASH_REMATCH[1]}" #获取声明中的属性 else #普通节点 ELEMENT=${ENTITY%% *} #获取节点名称,如果ENTITY中有空格,则第一个空格前面部分即为节点名称 ATTRIBUTES=${ENTITY#* } #获取节点所有属性,如果ENTITY中有空格,则第一个空格后面部分为所有属性(#2和#4,#4情况下,会多出/) fi if [[ "$ENTITY" = \!--*-- ]]; then #不检查注释(#5) return 0 fi if [[ "$ELEMENT" = /* ]]; then #节点末尾 #1第三步 tabCount=$[$tabCount - 1] echo_tabs $tabCount echo END ${ELEMENT#*/} #删除/ return 0 elif [[ "$ELEMENT" = */ ]] || [[ $ATTRIBUTES = */ ]]; then #3或#4 empty=true #节点没有子节点,也没有value(自身为闭合标签) if [[ $ATTRIBUTES = */ ]]; then #如果是#4情况 ATTRIBUTES=${ATTRIBUTES%*/} #将末尾的/删除,提取所有属性 fi echo_tabs $tabCount echo -n ELEMENT=${ELEMENT%*/}' ' elif [ ! "$ELEMENT" = '' ]; then #第一次执行时,ENTITY和CONTENT都是空串 echo_tabs $tabCount echo -n ELEMENT="$ELEMENT"' ' #输出节点名 tabCount=$[$tabCount + 1] #新节点 else echo -n "XML declaration " #ELEMENT为空,不计算层级 fi local empty=false #没有子节点,没有value IFS=$oldIFS #属性之间由空白符分割,恢复IFS,IFS默认为空格/换行/制表符 local hasAttribute=false #节点是否有属性 for a in $ATTRIBUTES; do #循环所有属性 #echo ATTRIBUTES=$ATTRIBUTES ' -+-+-+- ' if [[ "$a" = *=* ]] #情况#2和#4 then hasAttribute=true ATTRIBUTE_NAME=${a%%=*} #提取属性名 ATTRIBUTE_VALUE=`tr -d '"' <<< ${a#*=}` #提取属性值并去掉双引号 echo -n ATTRIBUTE=$ATTRIBUTE_NAME VALUE=$ATTRIBUTE_VALUE' ' #输出属性名/属性值 fi done if [[ ! "$CONTENT" =~ ^[[:space:]]*$ ]]; then echo -n CONTENT=$CONTENT fi if [ "$empty" = true ]; then echo echo_tabs $tabCount echo -n END ${ELEMENT%/*} #删除/ # echo -n ' (empty node)' fi echo return $ret } read_xml() { local tabCount=0 #用来格式化输出,计算节点层级 while read_dom; do : done < test.xml } read_xml
对下面xml执行此脚本
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>Only For Test abc
输出结果为
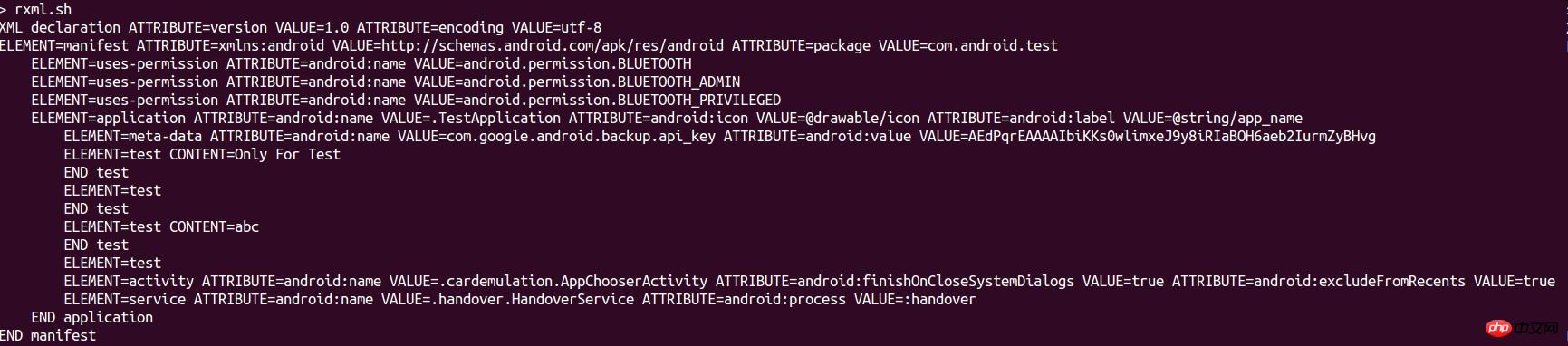
The above is the detailed content of Sample code analysis of how to use bash to parse xml. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1393
1393
 52
52
 37
37
 110
110
 Can I open an XML file using PowerPoint?
Feb 19, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Can I open an XML file using PowerPoint?
Feb 19, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Can XML files be opened with PPT? XML, Extensible Markup Language (Extensible Markup Language), is a universal markup language that is widely used in data exchange and data storage. Compared with HTML, XML is more flexible and can define its own tags and data structures, making the storage and exchange of data more convenient and unified. PPT, or PowerPoint, is a software developed by Microsoft for creating presentations. It provides a comprehensive way of
 Using Python to merge and deduplicate XML data
Aug 07, 2023 am 11:33 AM
Using Python to merge and deduplicate XML data
Aug 07, 2023 am 11:33 AM
Using Python to merge and deduplicate XML data XML (eXtensibleMarkupLanguage) is a markup language used to store and transmit data. When processing XML data, sometimes we need to merge multiple XML files into one, or remove duplicate data. This article will introduce how to use Python to implement XML data merging and deduplication, and give corresponding code examples. 1. XML data merging When we have multiple XML files, we need to merge them
 Convert XML data to CSV format in Python
Aug 11, 2023 pm 07:41 PM
Convert XML data to CSV format in Python
Aug 11, 2023 pm 07:41 PM
Convert XML data in Python to CSV format XML (ExtensibleMarkupLanguage) is an extensible markup language commonly used for data storage and transmission. CSV (CommaSeparatedValues) is a comma-delimited text file format commonly used for data import and export. When processing data, sometimes it is necessary to convert XML data to CSV format for easy analysis and processing. Python is a powerful
 Filtering and sorting XML data using Python
Aug 07, 2023 pm 04:17 PM
Filtering and sorting XML data using Python
Aug 07, 2023 pm 04:17 PM
Implementing filtering and sorting of XML data using Python Introduction: XML is a commonly used data exchange format that stores data in the form of tags and attributes. When processing XML data, we often need to filter and sort the data. Python provides many useful tools and libraries to process XML data. This article will introduce how to use Python to filter and sort XML data. Reading the XML file Before we begin, we need to read the XML file. Python has many XML processing libraries,
 Python implements conversion between XML and JSON
Aug 07, 2023 pm 07:10 PM
Python implements conversion between XML and JSON
Aug 07, 2023 pm 07:10 PM
Python implements conversion between XML and JSON Introduction: In the daily development process, we often need to convert data between different formats. XML and JSON are common data exchange formats. In Python, we can use various libraries to convert between XML and JSON. This article will introduce several commonly used methods, with code examples. 1. To convert XML to JSON in Python, we can use the xml.etree.ElementTree module
 Handling errors and exceptions in XML using Python
Aug 08, 2023 pm 12:25 PM
Handling errors and exceptions in XML using Python
Aug 08, 2023 pm 12:25 PM
Handling Errors and Exceptions in XML Using Python XML is a commonly used data format used to store and represent structured data. When we use Python to process XML, sometimes we may encounter some errors and exceptions. In this article, I will introduce how to use Python to handle errors and exceptions in XML, and provide some sample code for reference. Use try-except statement to catch XML parsing errors When we use Python to parse XML, sometimes we may encounter some
 Python parsing special characters and escape sequences in XML
Aug 08, 2023 pm 12:46 PM
Python parsing special characters and escape sequences in XML
Aug 08, 2023 pm 12:46 PM
Python parses special characters and escape sequences in XML XML (eXtensibleMarkupLanguage) is a commonly used data exchange format used to transfer and store data between different systems. When processing XML files, you often encounter situations that contain special characters and escape sequences, which may cause parsing errors or misinterpretation of the data. Therefore, when parsing XML files using Python, we need to understand how to handle these special characters and escape sequences. 1. Special characters and
 How to handle XML and JSON data formats in C# development
Oct 09, 2023 pm 06:15 PM
How to handle XML and JSON data formats in C# development
Oct 09, 2023 pm 06:15 PM
How to handle XML and JSON data formats in C# development requires specific code examples. In modern software development, XML and JSON are two widely used data formats. XML (Extensible Markup Language) is a markup language used to store and transmit data, while JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data exchange format. In C# development, we often need to process and operate XML and JSON data. This article will focus on how to use C# to process these two data formats, and attach




