Share a SQL statement optimization experience
The database I use is mysql5.6. Here is a brief introduction to the scenario
Course schedule
create table Course( c_id int PRIMARY KEY, name varchar(10) )
100 data items
Student table:
create table Student( id int PRIMARY KEY, name varchar(10) )
data 70000 entries
Student Score Table SC
CREATE table SC( sc_id int PRIMARY KEY, s_id int, c_id int, score int )
Data 70w entries
Purpose of query:
Find candidates who scored 100 points in the Chinese Language Test
Query statement:
select s.* from Student s where s.s_id in (select s_id from SC sc where sc.c_id = 0 and sc.score = 100 )
Execution time: 30248.271s
Halo, why is it so slow? Let’s check the query plan first:
EXPLAIN select s.* from Student s where s.s_id in (select s_id from SC sc where sc.c_id = 0 and sc.score = 100 )

It is found that no index is used, and the type is ALL, so the first thing that comes to mind is to create an index. The fields to be indexed are of course the fields in the where condition.
First create an index for the c_id and score of the sc table
CREATE index sc_c_id_index on SC(c_id); CREATE index sc_score_index on SC(score);
Execute the above query statement again, the time is: 1.054s
It is more than 30,000 times faster, greatly shortened Query time, it seems that indexes can greatly improve query efficiency. It is necessary to build indexes. Many times, we forget to build them
索引了,数据量小的的时候压根没感觉,这优化的感觉挺爽。
但是1s的时间还是太长了,还能进行优化吗,仔细看执行计划:

查看优化后的sql:
SELECT `YSB`.`s`.`s_id` AS `s_id`, `YSB`.`s`.`name` AS `name` FROM `YSB`.`Student` `s` WHERE < in_optimizer > ( `YSB`.`s`.`s_id` ,< EXISTS > ( SELECT 1 FROM `YSB`.`SC` `sc` WHERE ( (`YSB`.`sc`.`c_id` = 0) AND (`YSB`.`sc`.`score` = 100) AND ( < CACHE > (`YSB`.`s`.`s_id`) = `YSB`.`sc`.`s_id` ) ) ) )
补充:这里有网友问怎么查看优化后的语句
方法如下:
在命令窗口执行

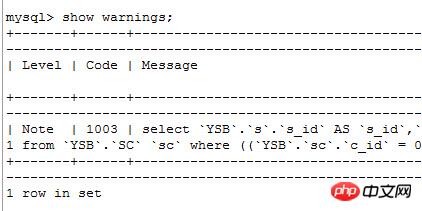
有type=all
按照我之前的想法,该sql的执行的顺序应该是先执行子查询
select s_id from SC sc where sc.c_id = 0 and sc.score = 100
耗时:0.001s
得到如下结果:
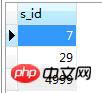
然后再执行
select s.* from Student s where s.s_id in(7,29,5000)
耗时:0.001s
这样就是相当快了啊,Mysql竟然不是先执行里层的查询,而是将sql优化成了exists子句,并出现了EPENDENT SUBQUERY,
mysql是先执行外层查询,再执行里层的查询,这样就要循环70007*11=770077次。
那么改用连接查询呢?
SELECT s.* from Student s INNER JOIN SC sc on sc.s_id = s.s_id where sc.c_id=0 and sc.score=100
这里为了重新分析连接查询的情况,先暂时删除索引sc_c_id_index,sc_score_index
执行时间是:0.057s
效率有所提高,看看执行计划:
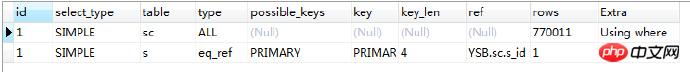
这里有连表的情况出现,我猜想是不是要给sc表的s_id建立个索引
CREATE index sc_s_id_index on SC(s_id); show index from SC
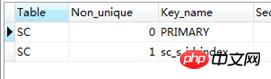
在执行连接查询
时间: 1.076s,竟然时间还变长了,什么原因?查看执行计划:
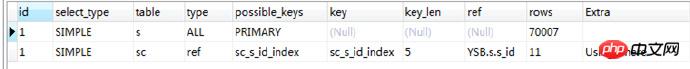
优化后的查询语句为:
SELECT `YSB`.`s`.`s_id` AS `s_id`, `YSB`.`s`.`name` AS `name` FROM `YSB`.`Student` `s` JOIN `YSB`.`SC` `sc` WHERE ( ( `YSB`.`sc`.`s_id` = `YSB`.`s`.`s_id` ) AND (`YSB`.`sc`.`score` = 100) AND (`YSB`.`sc`.`c_id` = 0) )
貌似是先做的连接查询,再进行的where条件过滤
回到前面的执行计划:
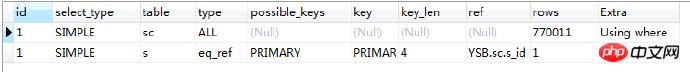
这里是先做的where条件过滤,再做连表,执行计划还不是固定的,那么我们先看下标准的sql执行顺序:
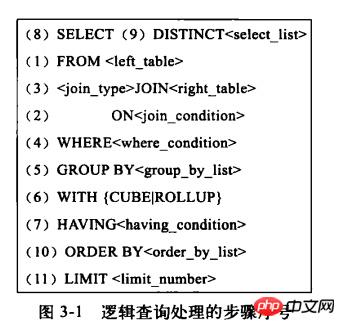
正常情况下是先join再where过滤,但是我们这里的情况,如果先join,将会有70w条数据发送join做操,因此先执行where
过滤是明智方案,现在为了排除mysql的查询优化,我自己写一条优化后的sql
SELECT s.* FROM ( SELECT * FROM SC sc WHERE sc.c_id = 0 AND sc.score = 100 ) t INNER JOIN Student s ON t.s_id = s.s_id
即先执行sc表的过滤,再进行表连接,执行时间为:0.054s
和之前没有建s_id索引的时间差不多
查看执行计划:
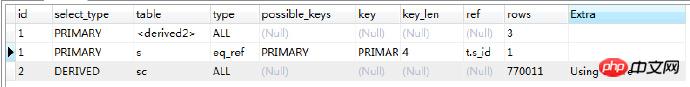
先提取sc再连表,这样效率就高多了,现在的问题是提取sc的时候出现了扫描表,那么现在可以明确需要建立相关索引
CREATE index sc_c_id_index on SC(c_id); CREATE index sc_score_index on SC(score);
再执行查询:
SELECT s.* FROM ( SELECT * FROM SC sc WHERE sc.c_id = 0 AND sc.score = 100 ) t INNER JOIN Student s ON t.s_id = s.s_id
执行时间为:0.001s,这个时间相当靠谱,快了50倍
执行计划:
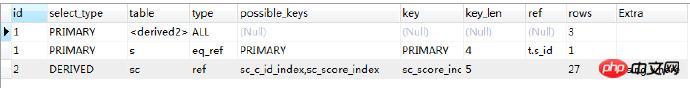
我们会看到,先提取sc,再连表,都用到了索引。
那么再来执行下sql
SELECT s.* from Student s INNER JOIN SC sc on sc.s_id = s.s_id where sc.c_id=0 and sc.score=100
执行时间0.001s
执行计划:

这里是mysql进行了查询语句优化,先执行了where过滤,再执行连接操作,且都用到了索引。
总结:
1.mysql嵌套子查询效率确实比较低
2.可以将其优化成连接查询
3.连接表时,可以先用where条件对表进行过滤,然后做表连接
(虽然mysql会对连表语句做优化)
4.建立合适的索引
5.学会分析sql执行计划,mysql会对sql进行优化,所以分析执行计划很重要
索引优化
上面讲到子查询的优化,以及如何建立索引,而且在多个字段索引时,分别对字段建立了单个索引
后面发现其实建立联合索引效率会更高,尤其是在数据量较大,单个列区分度不高的情况下。
单列索引
查询语句如下:
select * from user_test_copy where sex = 2 and type = 2 and age = 10
索引:
CREATE index user_test_index_sex on user_test_copy(sex); CREATE index user_test_index_type on user_test_copy(type); CREATE index user_test_index_age on user_test_copy(age);
分别对sex,type,age字段做了索引,数据量为300w,查询时间:0.415s
执行计划:

发现type=index_merge
这是mysql对多个单列索引的优化,对结果集采用intersect并集操作
多列索引
我们可以在这3个列上建立多列索引,将表copy一份以便做测试
create index user_test_index_sex_type_age on user_test(sex,type,age);
查询语句:
select * from user_test where sex = 2 and type = 2 and age = 10
执行时间:0.032s,快了10多倍,且多列索引的区分度越高,提高的速度也越多
执行计划:

最左前缀
多列索引还有最左前缀的特性:
执行一下语句:
select * from user_test where sex = 2 select * from user_test where sex = 2 and type = 2 select * from user_test where sex = 2 and age = 10
都会使用到索引,即索引的第一个字段sex要出现在where条件中
索引覆盖
就是查询的列都建立了索引,这样在获取结果集的时候不用再去磁盘获取其它列的数据,直接返回索引数据即可
如:
select sex,type,age from user_test where sex = 2 and type = 2 and age = 10
执行时间:0.003s
要比取所有字段快的多
排序
select * from user_test where sex = 2 and type = 2 ORDER BY user_name
时间:0.139s
在排序字段上建立索引会提高排序的效率
create index user_name_index on user_test(user_name)
最后附上一些sql调优的总结,以后有时间再深入研究
1. 列类型尽量定义成数值类型,且长度尽可能短,如主键和外键,类型字段等等
2. 建立单列索引
3. 根据需要建立多列联合索引
当单个列过滤之后还有很多数据,那么索引的效率将会比较低,即列的区分度较低,
那么如果在多个列上建立索引,那么多个列的区分度就大多了,将会有显著的效率提高。
4. Create a covering index based on the business scenario
Only query the fields required by the business. If these fields are covered by the index, the query efficiency will be greatly improved
5. Multi-table connection Indexes need to be established on fields
This can greatly improve the efficiency of table connections
6. Indexes need to be established on where condition fields
7. Indexes need to be established on sorting fields
8. An index needs to be created on the grouping field
9. Do not use arithmetic functions on the Where condition to avoid index failure
The above is the detailed content of Share a SQL statement optimization experience. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
You can open phpMyAdmin through the following steps: 1. Log in to the website control panel; 2. Find and click the phpMyAdmin icon; 3. Enter MySQL credentials; 4. Click "Login".
 MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system, mainly used to store and retrieve data quickly and reliably. Its working principle includes client requests, query resolution, execution of queries and return results. Examples of usage include creating tables, inserting and querying data, and advanced features such as JOIN operations. Common errors involve SQL syntax, data types, and permissions, and optimization suggestions include the use of indexes, optimized queries, and partitioning of tables.
 Why Use MySQL? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Why Use MySQL? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
MySQL is chosen for its performance, reliability, ease of use, and community support. 1.MySQL provides efficient data storage and retrieval functions, supporting multiple data types and advanced query operations. 2. Adopt client-server architecture and multiple storage engines to support transaction and query optimization. 3. Easy to use, supports a variety of operating systems and programming languages. 4. Have strong community support and provide rich resources and solutions.
 How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Redis uses a single threaded architecture to provide high performance, simplicity, and consistency. It utilizes I/O multiplexing, event loops, non-blocking I/O, and shared memory to improve concurrency, but with limitations of concurrency limitations, single point of failure, and unsuitable for write-intensive workloads.
 How to remotely connect to oracle database
Apr 11, 2025 pm 02:27 PM
How to remotely connect to oracle database
Apr 11, 2025 pm 02:27 PM
Remotely connecting to Oracle requires a listener, service name and network configuration. 1. The client request is forwarded to the database instance through the listener; 2. The instance verifies the identity and establishes a session; 3. The user name/password, host name, port number and service name must be specified to ensure that the client can access the server and the configuration is consistent. When the connection fails, check the network connection, firewall, listener and username and password. If the ORA-12154 error, check the listener and network configuration. Efficient connections require connection pooling, optimization of SQL statements and selection of appropriate network environments.
 MySQL's Place: Databases and Programming
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL's Place: Databases and Programming
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL's position in databases and programming is very important. It is an open source relational database management system that is widely used in various application scenarios. 1) MySQL provides efficient data storage, organization and retrieval functions, supporting Web, mobile and enterprise-level systems. 2) It uses a client-server architecture, supports multiple storage engines and index optimization. 3) Basic usages include creating tables and inserting data, and advanced usages involve multi-table JOINs and complex queries. 4) Frequently asked questions such as SQL syntax errors and performance issues can be debugged through the EXPLAIN command and slow query log. 5) Performance optimization methods include rational use of indexes, optimized query and use of caches. Best practices include using transactions and PreparedStatemen
 How to create an oracle database How to create an oracle database
Apr 11, 2025 pm 02:33 PM
How to create an oracle database How to create an oracle database
Apr 11, 2025 pm 02:33 PM
Creating an Oracle database is not easy, you need to understand the underlying mechanism. 1. You need to understand the concepts of database and Oracle DBMS; 2. Master the core concepts such as SID, CDB (container database), PDB (pluggable database); 3. Use SQL*Plus to create CDB, and then create PDB, you need to specify parameters such as size, number of data files, and paths; 4. Advanced applications need to adjust the character set, memory and other parameters, and perform performance tuning; 5. Pay attention to disk space, permissions and parameter settings, and continuously monitor and optimize database performance. Only by mastering it skillfully requires continuous practice can you truly understand the creation and management of Oracle databases.
 How to write oracle database statements
Apr 11, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
How to write oracle database statements
Apr 11, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
The core of Oracle SQL statements is SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE, as well as the flexible application of various clauses. It is crucial to understand the execution mechanism behind the statement, such as index optimization. Advanced usages include subqueries, connection queries, analysis functions, and PL/SQL. Common errors include syntax errors, performance issues, and data consistency issues. Performance optimization best practices involve using appropriate indexes, avoiding SELECT *, optimizing WHERE clauses, and using bound variables. Mastering Oracle SQL requires practice, including code writing, debugging, thinking and understanding the underlying mechanisms.




