PHP: Detailed explanation of object data type instances
What is an object?
Objects are data types that store data and information about how to process the data. It is an entity used to describe objective things in the system. It is a basic unit that constitutes the system. An object consists of a set of properties and a set of services that operate on the set of properties.
Syntax
In PHP, objects must be declared explicitly.
First we must declare the class of the object. We use the keyword class to declare a class, followed by the name of the class, and the body is enclosed in {} symbols. Think of it like this
class class_name{
......
}The class contains attributes and methods.
Attributes
By using the keyword var in the class definition to declare variables, the attributes of the class are created, also called member attributes of the class.
Grammar:
class class_name{
var $var_name;
}For example, if you define a human class, then the person’s name, age, gender, etc. can be regarded as the human class. Attributes.
Method
By declaring a function in the class definition, a method of the class is created.
Grammar:
class class_name{
function function_name(arg1,arg2,……)
{
函数功能代码
}
}Application of classes
A class that defines properties and methods is a complete class, and a complete processing logic can be included in a class . Use the new keyword to instantiate an object in order to apply logic within the class. Multiple objects can be instantiated simultaneously.
Syntax:
object = new class_name();
After instantiating an object, use the -> operator to access the object's member properties and methods.
Syntax:
object->var_name; object->function_name;
If you want to access the properties or methods of members in the defined class, you can use the pseudo variable $this. $this is used to represent the current object or the object itself.
Example:
<?php
header("content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8");
class Person {
//人的成员属性
var $name; //人的名字
var $age; //人的年龄
//人的成员 say() 方法
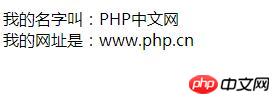
function say() {
echo "我的名字叫:".$this->name."<br />";
echo "我的网址是:".$this->age;
}
} //类定义结束
//实例化一个对象
$p1 = new Person();
//给 $p1 对象属性赋值
$p1->name = "PHP中文网";
$p1->age = 'www.php.cn';
//调用对象中的 say()方法
$p1->say();
?>Run this example, output:
The above is a simple example of our composite data type "object", about For more knowledge about objects, please visit our Object Topics, In the next section, we will explain the "Resources"# among the two special data types in PHP ##
The above is the detailed content of PHP: Detailed explanation of object data type instances. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 What data type should be used for gender field in MySQL database?
Mar 14, 2024 pm 01:21 PM
What data type should be used for gender field in MySQL database?
Mar 14, 2024 pm 01:21 PM
In a MySQL database, gender fields can usually be stored using the ENUM type. ENUM is an enumeration type that allows us to select one as the value of a field from a set of predefined values. ENUM is a good choice when representing a fixed and limited option like gender. Let's look at a specific code example: Suppose we have a table called "users" that contains user information, including gender. Now we want to create a field for gender, we can design the table structure like this: CRE
 What is the best data type for gender fields in MySQL?
Mar 15, 2024 am 10:24 AM
What is the best data type for gender fields in MySQL?
Mar 15, 2024 am 10:24 AM
In MySQL, the most suitable data type for gender fields is the ENUM enumeration type. The ENUM enumeration type is a data type that allows the definition of a set of possible values. The gender field is suitable for using the ENUM type because gender usually only has two values, namely male and female. Next, I will use specific code examples to show how to create a gender field in MySQL and use the ENUM enumeration type to store gender information. The following are the steps: First, create a table named users in MySQL, including
 How to convert MySQL query result array to object?
Apr 29, 2024 pm 01:09 PM
How to convert MySQL query result array to object?
Apr 29, 2024 pm 01:09 PM
Here's how to convert a MySQL query result array into an object: Create an empty object array. Loop through the resulting array and create a new object for each row. Use a foreach loop to assign the key-value pairs of each row to the corresponding properties of the new object. Adds a new object to the object array. Close the database connection.
 Mind map of Python syntax: in-depth understanding of code structure
Feb 21, 2024 am 09:00 AM
Mind map of Python syntax: in-depth understanding of code structure
Feb 21, 2024 am 09:00 AM
Python is widely used in a wide range of fields with its simple and easy-to-read syntax. It is crucial to master the basic structure of Python syntax, both to improve programming efficiency and to gain a deep understanding of how the code works. To this end, this article provides a comprehensive mind map detailing various aspects of Python syntax. Variables and Data Types Variables are containers used to store data in Python. The mind map shows common Python data types, including integers, floating point numbers, strings, Boolean values, and lists. Each data type has its own characteristics and operation methods. Operators Operators are used to perform various operations on data types. The mind map covers the different operator types in Python, such as arithmetic operators, ratio
 What is the difference between arrays and objects in PHP?
Apr 29, 2024 pm 02:39 PM
What is the difference between arrays and objects in PHP?
Apr 29, 2024 pm 02:39 PM
In PHP, an array is an ordered sequence, and elements are accessed by index; an object is an entity with properties and methods, created through the new keyword. Array access is via index, object access is via properties/methods. Array values are passed and object references are passed.
 What is the best data type choice for gender field in MySQL?
Mar 14, 2024 pm 01:24 PM
What is the best data type choice for gender field in MySQL?
Mar 14, 2024 pm 01:24 PM
When designing database tables, choosing the appropriate data type is very important for performance optimization and data storage efficiency. In the MySQL database, there is really no so-called best choice for the data type to store the gender field, because the gender field generally only has two values: male or female. But for efficiency and space saving, we can choose a suitable data type to store the gender field. In MySQL, the most commonly used data type to store gender fields is the enumeration type. An enumeration type is a data type that can limit the value of a field to a limited set.
 How do PHP functions return objects?
Apr 10, 2024 pm 03:18 PM
How do PHP functions return objects?
Apr 10, 2024 pm 03:18 PM
PHP functions can encapsulate data into a custom structure by returning an object using a return statement followed by an object instance. Syntax: functionget_object():object{}. This allows creating objects with custom properties and methods and processing data in the form of objects.
 What should I pay attention to when a C++ function returns an object?
Apr 19, 2024 pm 12:15 PM
What should I pay attention to when a C++ function returns an object?
Apr 19, 2024 pm 12:15 PM
In C++, there are three points to note when a function returns an object: The life cycle of the object is managed by the caller to prevent memory leaks. Avoid dangling pointers and ensure the object remains valid after the function returns by dynamically allocating memory or returning the object itself. The compiler may optimize copy generation of the returned object to improve performance, but if the object is passed by value semantics, no copy generation is required.




