Code example of Python implementing Hill sorting
This article mainly introduces the implementation of Hill sorting in Python. The programmed Hill sorting has certain reference value. Interested friends can refer to it
Observe "insertion sort" : In fact, it is not difficult to find that she has a shortcoming:
If the data is "5, 4, 3, 2, 1", at this time we will insert the records in the "unordered block" into the "with" "Sequence block", it is estimated that we will crash, and the position will be moved every time we insert. At this time, the efficiency of insertion sort can be imagined.
Based on this weakness, the shell has improved the algorithm and incorporated an idea called "reducing incremental sorting method". It is actually quite simple, but something to note is:
Increment It's not random, but there are rules to follow.
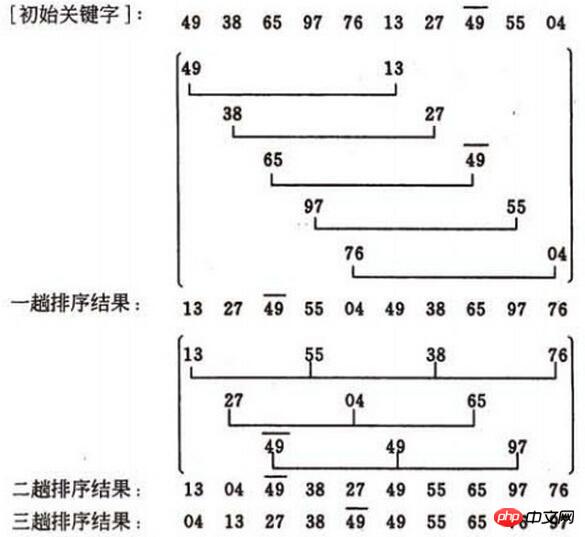
Timeliness analysis of Hill sorting is difficult. The number of comparisons of key codes and the number of record moves depend on the selection of the increment factor sequence d, in certain circumstances The following can accurately estimate the number of key code comparisons and the number of recorded moves. No one has yet given a method for selecting the best incremental factor sequence. The sequence of incremental factors can be taken in various ways, including odd numbers and prime numbers. However, it should be noted that there are no common factors among the incremental factors except 1, and the last incremental factor must be 1. . Hill sorting method is an unstable sorting method. First of all, we need to clarify the method of increment (the pictures here are copied from other people's blogs, the increment is an odd number, and my programming below uses an even number):
The first increment The method of selecting is: d=count/2;
The method of selecting the second increment is: d=(count/2)/2;
Finally, it goes to: d=1;
Okay, pay attention to the picture. The increment d1=5 in the first pass divides the 10 records to be sorted into 5 subsequences,
performs direct insertion sorting respectively, the result is (13, 27, 49, 55, 04, 49, 38, 65, 97, 76)The increment of the second pass is d2=3, and the 10 to-be-queued records are divided into 3 subsequences, and direct insertion is performed respectively. Sorting, the result is (13, 04, 49, 38, 27, 49, 55, 65, 97, 76)
The increment of the third pass is d3=1, direct insertion sorting is performed on the entire sequence,
The final result is (04, 13, 27, 38, 49, 49, 55, 65, 76, 97)Here comes the key point. When the increment decreases to 1, the sequence is basically in order.
The last pass of Hill sorting is direct insertion sortingwhich is close to the best situation. The "macro" adjustments in the previous passes can be regarded as the preprocessing of the last pass, which is more efficient than doing only one direct insertion sort. I am learning python, and today I used python to implement Hill sorting.
def ShellInsetSort(array, len_array, dk): # 直接插入排序
for i in range(dk, len_array): # 从下标为dk的数进行插入排序
position = i
current_val = array[position] # 要插入的数
index = i
j = int(index / dk) # index与dk的商
index = index - j * dk
# while True: # 找到第一个的下标,在增量为dk中,第一个的下标index必然 0<=index<dk
# index = index - dk
# if 0<=index and index <dk:
# break
# position>index,要插入的数的下标必须得大于第一个下标
while position > index and current_val < array[position-dk]:
array[position] = array[position-dk] # 往后移动
position = position-dk
else:
array[position] = current_val
def ShellSort(array, len_array): # 希尔排序
dk = int(len_array/2) # 增量
while(dk >= 1):
ShellInsetSort(array, len_array, dk)
print(">>:",array)
dk = int(dk/2)
if __name__ == "__main__":
array = [49, 38, 65, 97, 76, 13, 27, 49, 55, 4]
print(">:", array)
ShellSort(array, len(array))Output:
>: [49, 38, 65, 97, 76, 13, 27, 49, 55, 4] >>: [13, 27, 49, 55, 4, 49, 38, 65, 97, 76] >>: [4, 27, 13, 49, 38, 55, 49, 65, 97, 76] >>: [4, 13, 27, 38, 49, 49, 55, 65, 76, 97]
First of all, you must know insertion sorting, otherwise you will definitely not understand it.
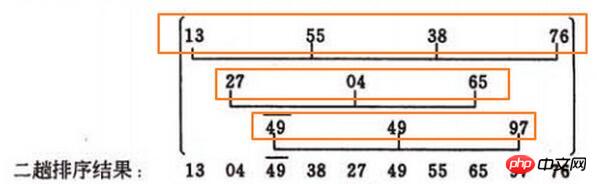 #Insertion sort is to insert and sort the numbers in the three yellow boxes in the picture above. For example: 13, 55, 38, 76
#Insertion sort is to insert and sort the numbers in the three yellow boxes in the picture above. For example: 13, 55, 38, 76
Look directly at 55, 55<13, without moving. Then look at 38, 38<55, then 55 is moved back, and the data becomes [13, 55, 55, 76]. Then compare 13<38, then 38 replaces 55 and becomes [13, 38, 55, 76]. The rest are the same, omitted.
There is a problem here, for example, the second yellow box
[27, 4, 65], 4<27, then 27 moves back, then 4 replaces the first one, and the data becomes [ 4, 27, 65],But how does the computer know that 4 is the first one??My approach is to first
find the first one of [27, 4, 65] The subscript of a number. In this example, the subscript of 27 is 1. When the subscript of the number to be inserted is greater than the first subscript 1, it can be moved backward. The previous number cannot be moved backward. There are two situations, one is If there is data in front and it is smaller than the number to be inserted, you can only insert it after it. Another, very important, when the number to be inserted is smaller than all the previous numbers, the inserted number must be placed first. At this time, the subscript of the number to be inserted = the subscript of the first number. (This passage may not be very understandable to beginners...)In order to find the subscript of the first number, the first thing I thought of was to use a loop, all the way to the front:
while True: # 找到第一个的下标,在增量为dk中,第一个的下标index必然 0<=index<dk index = index - dk if 0<=index and index <dk: break
When debugging, I found that using loops is a waste of time, especially when the increment d=1. In order to insert the last number in the list directly, I have to loop by 1 until the subscript of the first number. Later I learned Be smart, use the following method:
j = int(index / dk) # index与dk的商 index = index - j * dk
Time complexity:
The time complexity of Hill sorting is a function of the increment sequence taken, and it is difficult to analyze accurately. Some literature points out that when the incremental sequence is d[k]=2^(t-k+1), the time complexity of Hill sorting is
O(n^1.5),where t is sorting Number of trips. Stability: Unstable
Hill sorting effect:
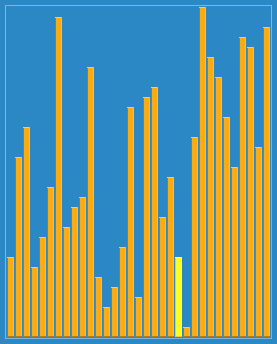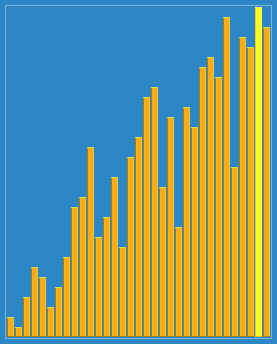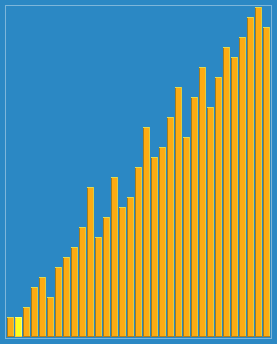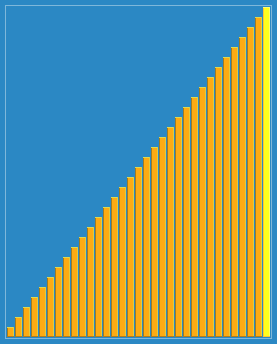
Reference materials: The programming is implemented by myself. It is recommended to Debug and take a look at the running process
Eight sorting algorithms in c++
Visually and intuitively experience several commonly used sorting algorithms
C#Seven classic sorting algorithm series (Part 2)
1. Non-systematic learning is also a waste of time. 2. Be a technical person who can appreciate beauty, understand art, and be good at art
The above is the detailed content of Code example of Python implementing Hill sorting. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Google AI announces Gemini 1.5 Pro and Gemma 2 for developers
Jul 01, 2024 am 07:22 AM
Google AI announces Gemini 1.5 Pro and Gemma 2 for developers
Jul 01, 2024 am 07:22 AM
Google AI has started to provide developers with access to extended context windows and cost-saving features, starting with the Gemini 1.5 Pro large language model (LLM). Previously available through a waitlist, the full 2 million token context windo
 How to download deepseek Xiaomi
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:27 PM
How to download deepseek Xiaomi
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:27 PM
How to download DeepSeek Xiaomi? Search for "DeepSeek" in the Xiaomi App Store. If it is not found, continue to step 2. Identify your needs (search files, data analysis), and find the corresponding tools (such as file managers, data analysis software) that include DeepSeek functions.
 How do you ask him deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 04:42 PM
How do you ask him deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 04:42 PM
The key to using DeepSeek effectively is to ask questions clearly: express the questions directly and specifically. Provide specific details and background information. For complex inquiries, multiple angles and refute opinions are included. Focus on specific aspects, such as performance bottlenecks in code. Keep a critical thinking about the answers you get and make judgments based on your expertise.
 How to search deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:18 PM
How to search deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:18 PM
Just use the search function that comes with DeepSeek. Its powerful semantic analysis algorithm can accurately understand the search intention and provide relevant information. However, for searches that are unpopular, latest information or problems that need to be considered, it is necessary to adjust keywords or use more specific descriptions, combine them with other real-time information sources, and understand that DeepSeek is just a tool that requires active, clear and refined search strategies.
 How to program deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
How to program deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
DeepSeek is not a programming language, but a deep search concept. Implementing DeepSeek requires selection based on existing languages. For different application scenarios, it is necessary to choose the appropriate language and algorithms, and combine machine learning technology. Code quality, maintainability, and testing are crucial. Only by choosing the right programming language, algorithms and tools according to your needs and writing high-quality code can DeepSeek be successfully implemented.
 How to use deepseek to settle accounts
Feb 19, 2025 pm 04:36 PM
How to use deepseek to settle accounts
Feb 19, 2025 pm 04:36 PM
Question: Is DeepSeek available for accounting? Answer: No, it is a data mining and analysis tool that can be used to analyze financial data, but it does not have the accounting record and report generation functions of accounting software. Using DeepSeek to analyze financial data requires writing code to process data with knowledge of data structures, algorithms, and DeepSeek APIs to consider potential problems (e.g. programming knowledge, learning curves, data quality)
 The Key to Coding: Unlocking the Power of Python for Beginners
Oct 11, 2024 pm 12:17 PM
The Key to Coding: Unlocking the Power of Python for Beginners
Oct 11, 2024 pm 12:17 PM
Python is an ideal programming introduction language for beginners through its ease of learning and powerful features. Its basics include: Variables: used to store data (numbers, strings, lists, etc.). Data type: Defines the type of data in the variable (integer, floating point, etc.). Operators: used for mathematical operations and comparisons. Control flow: Control the flow of code execution (conditional statements, loops).
 Problem-Solving with Python: Unlock Powerful Solutions as a Beginner Coder
Oct 11, 2024 pm 08:58 PM
Problem-Solving with Python: Unlock Powerful Solutions as a Beginner Coder
Oct 11, 2024 pm 08:58 PM
Pythonempowersbeginnersinproblem-solving.Itsuser-friendlysyntax,extensivelibrary,andfeaturessuchasvariables,conditionalstatements,andloopsenableefficientcodedevelopment.Frommanagingdatatocontrollingprogramflowandperformingrepetitivetasks,Pythonprovid






