
The following is conventional MVC routing
config.Routes.MapHttpRoute(
name: "DefaultApi",
routeTemplate: "api/{controller}/{id}",
defaults: new { id = RouteParameter.Optional },
);If we want to achieve routing with effects similar to the following, it is more troublesome to use conventional convention routing.
order/Miles/三只松鼠干果/2袋 order/2017/1/13
It would be simpler if you use attribute routing.
If you create a new WEB API project, open the WebApiConfig.cs file in the App_Start directory and add the following code to enable attribute routing configuration.
config.MapHttpAttributeRoutes();
Attribute routing can also be mixed with convention routing, as follows:
public static void Register(HttpConfiguration config)
{
// Web API 配置和服务
// Web API 路由
config.MapHttpAttributeRoutes();
config.Routes.MapHttpRoute(
name: "DefaultApi",
routeTemplate: "api/{controller}/{id}",
defaults: new { id = RouteParameter.Optional },
constraints: new { id=@"\d+"}
);
}Mark the attribute on the method to use attribute routing, as follows:
[Route("order/{UserNickName}/{ProductName}/{count}")]Test results ( The URL is encoded, otherwise a 400 error will be reported)
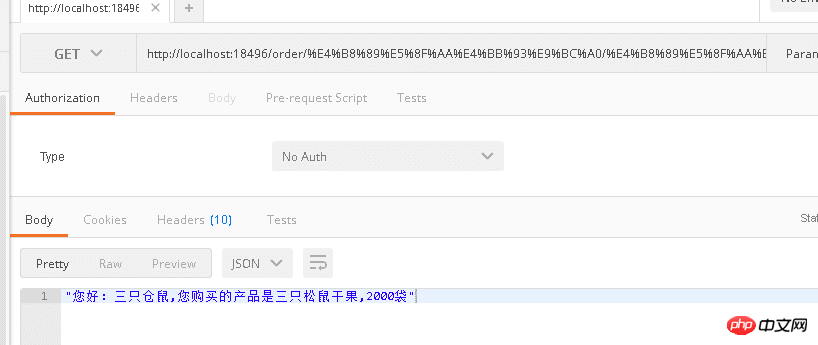
[Route("api/books")]
[Route("api/books/{id:int}")]
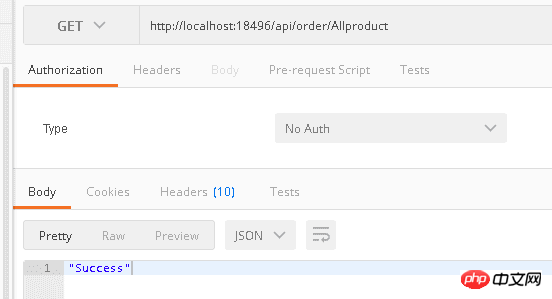
[Route("api/books")]This is obviously more troublesome. So we use the [RoutePrefix] attribute to set a public prefix
 Test result
Test result
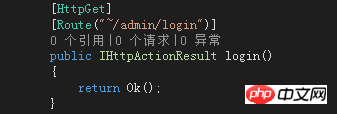
 If [RoutePrefix is used ], for some special APIs, we can use wavy lines to rewrite the routing prefix, as follows:
If [RoutePrefix is used ], for some special APIs, we can use wavy lines to rewrite the routing prefix, as follows:
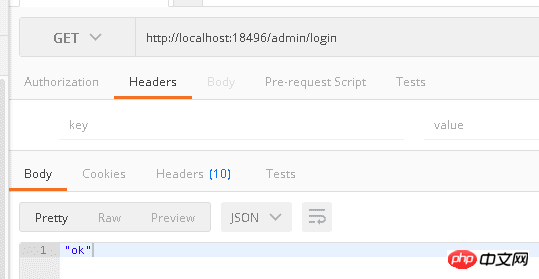
 Test results (under the same class)
Test results (under the same class)
 The route prefix can also contain parameters, as follows
The route prefix can also contain parameters, as follows
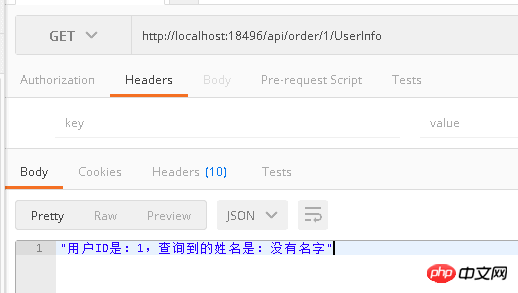
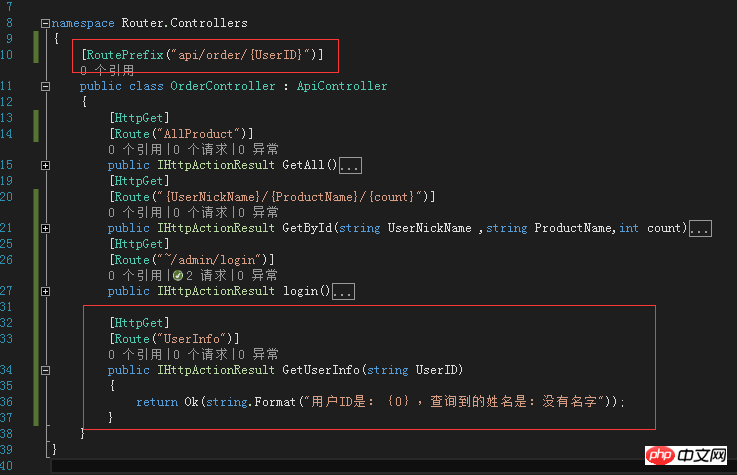 Test results
Test results
 ##You can add parameter constraints in the route, as follows
##You can add parameter constraints in the route, as follows
Test result
If the parameter is not Int type, the route will not be matched 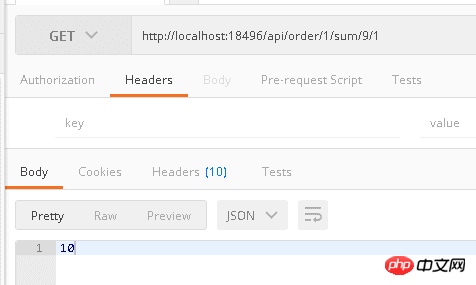
The following are some constraints that will be supported
You can use multiple constraints, but Use colons to separate 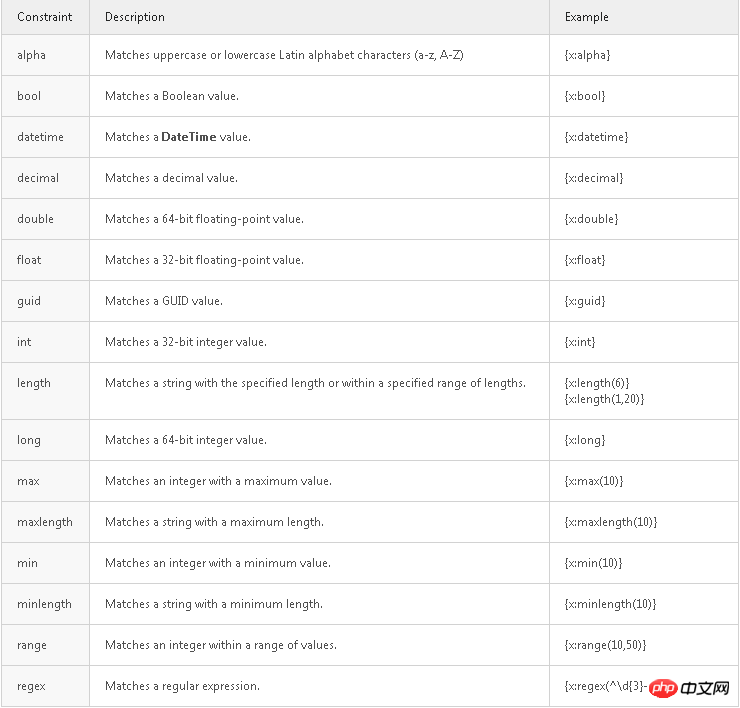
[Route("users/{id:int:length(1,3)}")]
public User GetUserById(int id) { ... }If it is not within the range, it will not match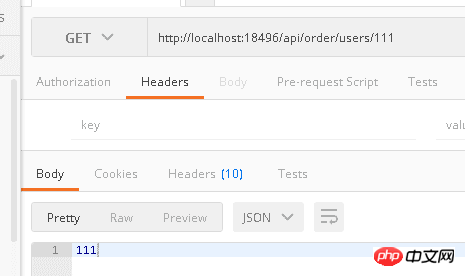
Custom routing constraints need to implement the IHttpRouteConstraint interface. For details, check the official 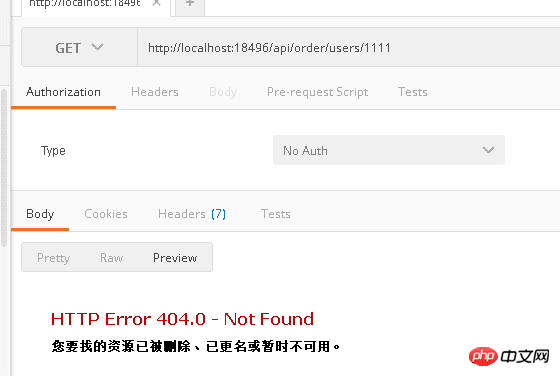
public class NonZeroConstraint : IHttpRouteConstraint
{
public bool Match(HttpRequestMessage request, IHttpRoute route, string parameterName,
IDictionary<string, object> values, HttpRouteDirection routeDirection)
{
object value;
if (values.TryGetValue(parameterName, out value) && value != null)
{
long longValue;
if (value is long)
{
longValue = (long)value;
return longValue != 0;
}
string valueString = Convert.ToString(value, CultureInfo.InvariantCulture);
if (Int64.TryParse(valueString, NumberStyles.Integer,
CultureInfo.InvariantCulture, out longValue))
{
return longValue != 0;
}
}
return false;
}
}public static class WebApiConfig
{
public static void Register(HttpConfiguration config)
{
var constraintResolver = new DefaultInlineConstraintResolver();
constraintResolver.ConstraintMap.Add("nonzero", typeof(NonZeroConstraint));
config.MapHttpAttributeRoutes(constraintResolver);
}
}[Route("{id:nonzero}")]
public HttpResponseMessage GetNonZero(int id) { ... }
You can make a route parameter an optional URI parameter by adding a question mark to mark it. If a route parameter is optional, you must define a default value for the method parameter.
public class BooksController : ApiController
{
[Route("api/books/locale/{lcid:int?}")]
public IEnumerable<Book> GetBooksByLocale(int lcid = 1033) { ... }
}public class BooksController : ApiController
{
[Route("api/books/locale/{lcid=1033}")]
public IEnumerable<Book> GetBooksByLocale(int lcid) { ... }
}The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of ASP.NET attribute routing examples of WEB API. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 What are the asp development tools?
What are the asp development tools?
 How to use a few thousand to make hundreds of thousands in the currency circle
How to use a few thousand to make hundreds of thousands in the currency circle
 What are the five types of aggregate functions?
What are the five types of aggregate functions?
 How to use the Print() function in Python
How to use the Print() function in Python
 How to close app resource library
How to close app resource library
 Website dead link detection method
Website dead link detection method
 What to do if the documents folder pops up when the computer is turned on
What to do if the documents folder pops up when the computer is turned on
 word to ppt
word to ppt




