 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Detailed example of organizational structure adjustment (python)
Detailed example of organizational structure adjustment (python)
Detailed example of organizational structure adjustment (python)
The birth of a web application based on flask is the seventh article. This article mainly introduces the adjustment of the organizational structure and has a certain reference value. Interested friends can refer to
All Py now The codes are all written in the default.py file. Obviously, under this method, once the program becomes responsible, it will cause many problems for both development and maintenance.
The Flask framework does not force projects to use a specific organizational structure, so the organizational structure used here is not necessarily the same as in other projects.
According to the code in default.py, it can be roughly divided into three categories: form model, data model, and view method, so models are also distinguished by this category. Therefore, according to the experience gained from other languages (java), each class is a py file and placed in the corresponding folder
In a single file, all configurations They are all written in a single file. After performing multi-file reconstruction, it is obviously inappropriate to do this, so it is necessary to create an independent config file:
class Config: SECRET_KEY="Niu_blog String" SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI='mysql://root:1234@localhost/cblog' SQLALCHEMY_COMMIT_ON_TEARDOWN=True LOGIN_PROTECTION="strong" LOGIN_VIEW="login"
Then the initialization file ( app/__init__.py):
from flask import Flask from flask_bootstrap import Bootstrap from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy from flask_login import LoginManager import pymysql pymysql.install_as_MySQLdb() from config import Config bootstrap = Bootstrap() db = SQLAlchemy() login_manager=LoginManager(); def create_app(): app = Flask(__name__) app.config.from_object(Config) bootstrap.init_app(app) login_manager.init_app(app) login_manager.session_protection=Config.LOGIN_PROTECTION login_manager.login_view=Config.LOGIN_VIEW db.init_app(app) return app
Further modularization requires the use of blueprints. The functions of blueprints are somewhat similar to areas in asp.net mvc, integrating the view methods of different modules and distinguishing them through URLs. , first the entrance, that is, the index page is defined as the main blueprint. The method is as follows:
Create the main folder
Create a new blueprint initialization file in the folder_ _init__.py
Create the view method file view.py
Create the error page view method errors.py
## in the main blueprint
from flask import Blueprint
main=Blueprint("main",__name__) # 创建蓝本
from . import errors,viewsfrom flask import render_template
from . import main
@main.route("/")
def index():
return render_template("index.html",site_name='myblog')from flask import Blueprint
auth=Blueprint("auth",__name__)
from . import viewsfrom . import auth
from .. import db,login_manager
from ..forms.LoginForm import LoginForm(*)
from ..models.User import User (*)
from flask_login import login_user,logout_user
from flask import render_template,flash,redirect,url_for
@auth.route("/login",methods=["GET","POST"])
def login():
form = LoginForm()
print(url_for("main.index"))
if form.validate_on_submit():
username = form.username.data
password = form.password.data
print(User)
user = User.query.filter_by(username=username, password=password).first()
if user is not None:
login_user(user, form.remember_me.data)
print(url_for("main.index"))
return redirect(url_for("main.index"))
else:
flash("您输入的用户名或密码错误")
return render_template("/auth/login.html", form=form) # 返回的仍为登录页
return redirect(url_for("main.index"))
return render_template("/auth/login.html",form=form)
@auth.route("/logout",methods=["GET","POST"])
def logout():
logout_user()
return redirect(url_for("main.index"))
@login_manager.user_loader
def load_user(user_id):
return User.query.get(int(user_id))from flask_wtf import FlaskForm
from wtforms import StringField,PasswordField,SubmitField,BooleanField
from wtforms.validators import DataRequired
class LoginForm(FlaskForm):
username=StringField("请输入用户名",validators=[DataRequired()])
password=PasswordField("请输入密码")
remember_me=BooleanField("记住我")
submit=SubmitField("登录")from flask_login import UserMixin
from .. import db
class User(UserMixin,db.Model):
__tablename__="users"
id=db.Column(db.Integer,primary_key=True)
username=db.Column(db.String(50),unique=True,index=True)
password=db.Column(db.String(50))
nickname=db.Column(db.String(50))
email=db.Column(db.String(100))
birthday=db.Column(db.DateTime)
gender=db.Column(db.Integer)
remark=db.Column(db.String(200))
role_id=db.Column(db.Integer,db.ForeignKey("roles.id"))def create_app(): app = Flask(__name__) app.config.from_object(Config) bootstrap.init_app(app) login_manager.init_app(app) login_manager.session_protection=Config.LOGIN_PROTECTION login_manager.login_view=Config.LOGIN_VIEW db.init_app(app) from .main import main as main_blueprint from .auth import auth as auth_blueprint app.register_blueprint(main_blueprint) #无url前缀 app.register_blueprint(auth_blueprint,url_prefix="/auth") #url前缀为/auth return app
from app import create_app, db
from flask_script import Manager,Shell
from flask_migrate import Migrate,MigrateCommand
from app.models.User import User
from app.models.Role import Role
import pymysql
pymysql.install_as_MySQLdb()
app=create_app()
manager=Manager(app);
migrate = Migrate(app, db)
def make_shell_context():
return dict(app=app,db=db,User=User,Role=Role) #注册shell命令
manager.add_command("db", MigrateCommand) #新增db命令用于数据库迁移
manager.add_command("shell" ,Shell(make_context=make_shell_context()))
if __name__ =='__main__':
manager.run()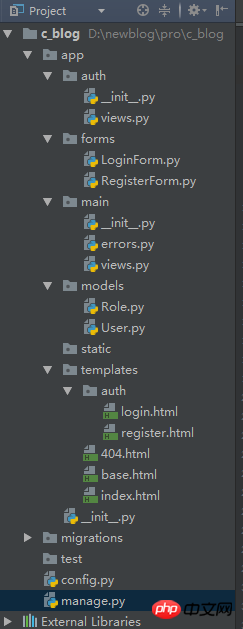
The above is the detailed content of Detailed example of organizational structure adjustment (python). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to build simple and easy-to-use web applications with React and Flask
Sep 27, 2023 am 11:09 AM
How to build simple and easy-to-use web applications with React and Flask
Sep 27, 2023 am 11:09 AM
How to use React and Flask to build simple and easy-to-use web applications Introduction: With the development of the Internet, the needs of web applications are becoming more and more diverse and complex. In order to meet user requirements for ease of use and performance, it is becoming increasingly important to use modern technology stacks to build network applications. React and Flask are two very popular frameworks for front-end and back-end development, and they work well together to build simple and easy-to-use web applications. This article will detail how to leverage React and Flask
 Django vs. Flask: A comparative analysis of Python web frameworks
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:36 AM
Django vs. Flask: A comparative analysis of Python web frameworks
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:36 AM
Django and Flask are both leaders in Python Web frameworks, and they both have their own advantages and applicable scenarios. This article will conduct a comparative analysis of these two frameworks and provide specific code examples. Development Introduction Django is a full-featured Web framework, its main purpose is to quickly develop complex Web applications. Django provides many built-in functions, such as ORM (Object Relational Mapping), forms, authentication, management backend, etc. These features allow Django to handle large
 Start from scratch and guide you step by step to install Flask and quickly establish a personal blog
Feb 19, 2024 pm 04:01 PM
Start from scratch and guide you step by step to install Flask and quickly establish a personal blog
Feb 19, 2024 pm 04:01 PM
Starting from scratch, I will teach you step by step how to install Flask and quickly build a personal blog. As a person who likes writing, it is very important to have a personal blog. As a lightweight Python Web framework, Flask can help us quickly build a simple and fully functional personal blog. In this article, I will start from scratch and teach you step by step how to install Flask and quickly build a personal blog. Step 1: Install Python and pip Before starting, we need to install Python and pi first
 Guide to installing the Flask framework: Detailed steps to help you install Flask correctly
Feb 18, 2024 pm 10:51 PM
Guide to installing the Flask framework: Detailed steps to help you install Flask correctly
Feb 18, 2024 pm 10:51 PM
Flask framework installation tutorial: Teach you step by step how to correctly install the Flask framework. Specific code examples are required. Introduction: Flask is a simple and flexible Python Web development framework. It's easy to learn, easy to use, and packed with powerful features. This article will lead you step by step to correctly install the Flask framework and provide detailed code examples for reference. Step 1: Install Python Before installing the Flask framework, you first need to make sure that Python is installed on your computer. You can start from P
 Flask and Intellij IDEA integration: Python web application development tips (Part 2)
Jun 17, 2023 pm 01:58 PM
Flask and Intellij IDEA integration: Python web application development tips (Part 2)
Jun 17, 2023 pm 01:58 PM
The first part introduces basic Flask and Intellij IDEA integration, project and virtual environment settings, dependency installation, etc. Next we will continue to explore more Python web application development tips to build a more efficient working environment: Using FlaskBlueprintsFlaskBlueprints allows you to organize your application code for easier management and maintenance. Blueprint is a Python module that packages
 Flask vs FastAPI: The best choice for efficient Web API development
Sep 27, 2023 pm 09:01 PM
Flask vs FastAPI: The best choice for efficient Web API development
Sep 27, 2023 pm 09:01 PM
FlaskvsFastAPI: The best choice for efficient development of WebAPI Introduction: In modern software development, WebAPI has become an indispensable part. They provide data and services that enable communication and interoperability between different applications. When choosing a framework for developing WebAPI, Flask and FastAPI are two choices that have attracted much attention. Both frameworks are very popular and each has its own advantages. In this article, we will look at Fl
 Comparing the performance of Gunicorn and uWSGI for Flask application deployment
Jan 17, 2024 am 08:52 AM
Comparing the performance of Gunicorn and uWSGI for Flask application deployment
Jan 17, 2024 am 08:52 AM
Flask application deployment: Comparison of Gunicorn vs suWSGI Introduction: Flask, as a lightweight Python Web framework, is loved by many developers. When deploying a Flask application to a production environment, choosing the appropriate Server Gateway Interface (SGI) is a crucial decision. Gunicorn and uWSGI are two common SGI servers. This article will describe them in detail.
 Build interactive data visualization web applications using Flask and D3.js
Jun 17, 2023 pm 09:00 PM
Build interactive data visualization web applications using Flask and D3.js
Jun 17, 2023 pm 09:00 PM
In recent years, data analysis and data visualization have become indispensable skills in many industries and fields. It is very important for data analysts and researchers to present large amounts of data in front of users and allow users to understand the meaning and characteristics of the data through visualization. To meet this need, it has become a trend to use D3.js to build interactive data visualizations in web applications. In this article, we'll cover how to build interactive data visualizations for the web using Flask and D3.js



