Detailed explanation of java exception handling examples
This article mainly introduces the detailed introduction and examples of java exception handling. This article summarizes the knowledge level of java exceptions. Friends in need can refer to the
Java exception hierarchy
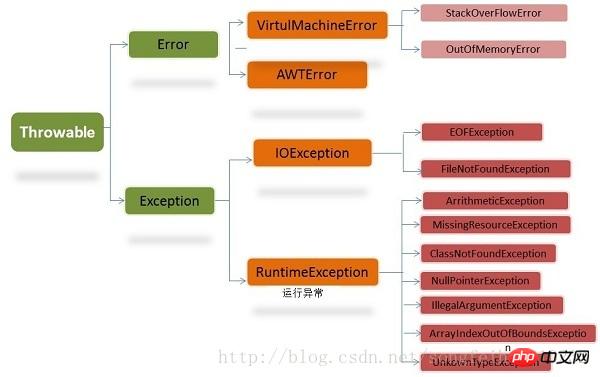
Exception exception
The difference between RuntimeException and non-RuntimeException exception:
非RuntimeException(检查异常):在程序中必须使用try…catch进行处理,否则程序无法编译。 RuntimeException:可以不使用try…catch进行处理,但是如果有异常产生,则异常将由JVM进行处理。 比如:我们从来没有人去处理过NullPointerException异常,它就是运行时异常,并且这种异常还是最常见的异常之一。 出现运行时异常后,系统会把异常一直往上层抛,一直遇到处理代码。如果没有处理块,到最上层, 如果是多线程就由Thread.run()抛出,如果是单线程就被main()抛出。抛出之后,如果是线程,这个线程也就退出了。 如果是主程序抛出的异常,那么这整个程序也就退出了。
The parent classes of the Error class and the Exception class are both throwable classes. The difference between them is:
Error类一般是指与虚拟机相关的问题,如系统崩溃,虚拟机错误,内存空间不足,方法调用栈溢等。 对于这类错误的导致的应用程序中断,仅靠程序本身无法恢复和和预防,遇到这样的错误,建议让程序终止。 Exception类表示程序可以处理的异常,可以捕获且可能恢复。遇到这类异常,应该尽可能处理异常, 使程序恢复运行,而不应该随意终止异常。
RuntimeException
NullPointException
Generally, Java.lang.NullPointerException is reported for the following reasons:
1. The string variable is not initialized;
2. The object is not initialized with a specific class;
The NullPointException code is as follows:
package TestNullPointException;
public class TestNullPointException {
public static void main (String[] args) {
String str = null;
try {
if (str.equals(null)) {
System.out.println("true");
} else {
System.out.println("false");
}
} catch (NullPointException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Output:
java.lang.NullPointerException at TestNullPointException.TestNullPointException.main(TestNullPointException.java:6)
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException exception
Array subscript out-of-bounds exception, when the referenced index value exceeds the length of the array, This exception will occur.
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException code is as follows:
package TestArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public class TestArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException {
public static void main (String[] args) {
Integer[] array = new Integer[10];
try {
Integer temp = array[10];
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Output:
java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 10 at TestArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException.TestArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException.main(TestArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException.java:6)
ArithmeticException
ArithmeticException is thrown when an abnormal operation condition occurs this exception.
ArithmeticException code is as follows:
/**
* ArithmeticException
*/
packet TestArithmeticException;
public class TestArithmeticException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer temp = 1;
try {
System.out.println(temp/0);
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Output:
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero at TestArithmeticException.TestArithmeticException.main(TestArithmeticException.java:6)
ArrayStoreException
When you try to store an object of the wrong type into a Exception thrown when array of objects.
ArrayStoreException code is as follows:
/**
* ArrayStoreException
*/
packet TestArrayStoreException;
public class TestArrayStoreException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object array = new Integer[10];
try {
array[0] = "123";
} catch (ArrayStoreException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Output:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayStoreException: java.lang.String at TestArrayStoreException.TestArrayStoreException.main(TestArrayStoreException.java:6)
NumberFormatException
Inherits IllegalArgumentException and occurs when a string is converted to a number.
NumberFormatException code is as follows:
/**
* NumberFormatException
*/
package test;
public class ExceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "q12";
Integer i = Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}Output:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "q12" at java.lang.NumberFormatException.forInputString(NumberFormatException.java:65) at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:580) at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:615) at test.ExceptionTest.main(ExceptionTest.java:8)
ClassCastException
Type conversion error, usually when performing forced type conversion error.
ClassCastException code is as follows:
/**
* ClassCastException 父类赋值给子类,向下转型
*/
package test;
public class ExceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object obj=new Object();
Integer s=(Integer)obj;
}
}Output:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ClassCastException: java.lang.Object cannot be cast to java.lang.Integer at test.ExceptionTest.main(ExceptionTest.java:5)
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of java exception handling examples. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 How do you handle exceptions effectively in PHP (try, catch, finally, throw)?
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:03 AM
How do you handle exceptions effectively in PHP (try, catch, finally, throw)?
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:03 AM
In PHP, exception handling is achieved through the try, catch, finally, and throw keywords. 1) The try block surrounds the code that may throw exceptions; 2) The catch block handles exceptions; 3) Finally block ensures that the code is always executed; 4) throw is used to manually throw exceptions. These mechanisms help improve the robustness and maintainability of your code.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4




