
Three ways to execute SQL statements in PDO
In PDO, we can use three ways to execute SQL statements, namely exec() method, query method, and prepared statement prepare() and execute() methods~
In the previous article "Using the PDO constructor to connect to the database and DSN detailed explanation", we introduced Now that we have a detailed explanation of how to use constructors to connect databases and DSNs, this article will introduce to you three ways to execute SQL statements in PDO. We will introduce them one by one below!
First method: exec() method
#The exec() method returns the number of rows affected after executing the SQL statement, its syntax The format is as follows:
int PDO::exec(string statement)
The parameter satatement is the SQL statement to be executed. This method returns the number of rows affected when executing the SQL statement. It is usually used in INSERT, DELETE and UPDATE statements. Let's explain it with specific code. The code is as follows:
<?php
header("Content-Type:text/html; charset=utf-8"); //设置页面的编码格式
$dbms = "mysql"; // 数据库的类型
$dbName ="php_cn"; //使用的数据库名称
$user = "root"; //使用的数据库用户名
$pwd = "root"; //使用的数据库密码
$host = "localhost"; //使用的主机名称
$dsn = "$dbms:host=$host;dbName=$dbName ";
try{ //捕获异常
$pdo = new PDO($dsn,$user,$pwd); //实例化对象
$query="insert into user(username,password) values('php','523')";//需要执行的sql语句
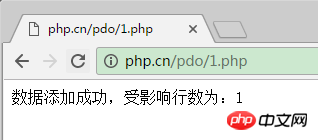
$res=$pdo->exec($query);//执行添加语句并返回受影响行数
echo "数据添加成功,受影响行数为: ".$res;
}catch(Exception $e){
die("Error!:".$e->getMessage().'<br>');
}
?>The output result is:
Second method: query() Method
query() method is used to return the result set after executing the query. The syntax format of this function is as follows:
PDOStatement PDO::query(string statement)
The parameter satatement is the SQL statement to be executed , it returns a PODStatement object! Please see the sample code below for details:
<?php
header("Content-Type:text/html; charset=utf-8"); //设置页面的编码格式
$dbms = "mysql"; // 数据库的类型
$dbName ="php_cn"; //使用的数据库名称
$user = "root"; //使用的数据库用户名
$pwd = "root"; //使用的数据库密码
$host = "localhost"; //使用的主机名称
$dsn = "$dbms:host=$host;dbName=$dbName ";
try{
$pdo=new PDO($dsn,$user,$pwd);
$query="select * from user";
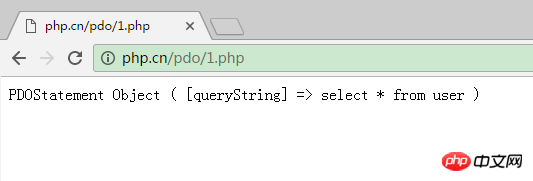
$res=$pdo->query($query);
print_r($res);
}catch(Exception $e){
die("Error!:".$e->getMessage().'<br>');
}
?>The output result is:
##Note:
1. Both query and exec can execute all sql statements, but the return values are different.
2. Query can realize all exec functions.
3. When applying the select statement to exec, it always returns 0
4. If you want to see the specific results of the query, you can Complete the loop output through the foreach statement
The third method: prepared statements: prepare() statement and execute() Statement
Preprocessing statements include two methods: prepare() and execute(). First, prepare the query through the prepare() method, and then execute the query through the execute() method. You can also bind parameters to the execute() method through the bindParam() method. The syntax is as follows:
PDOStatement PDO::prepare(string statement[,array driver_options]) bool PDOStatement::execute([array input_parameters])
<?php
header("Content-Type:text/html; charset=utf-8"); //设置页面的编码格式
$dbms = "mysql"; // 数据库的类型
$dbName ="php_cn"; //使用的数据库名称
$user = "root"; //使用的数据库用户名
$pwd = "root"; //使用的数据库密码
$host = "localhost"; //使用的主机名称
$dsn = "$dbms:host=$host;dbname=$dbName";
try{
$pdo=new PDO($dsn,$user,$pwd);//初始化一个PDO对象,就是创建了数据库连接对象$pdo
$query="select * from user";//需要执行的sql语句
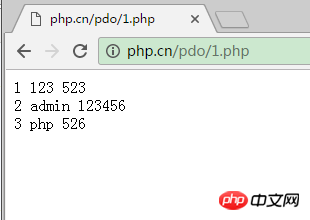
$res=$pdo->prepare($query);//准备查询语句
$res->execute();
while($result=$res->fetch(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC)){
echo $result['id']." ".$result['username']." ".$result['password'].'<br>';
}
}catch(Exception $e){
die("Error!:".$e->getMessage().'<br>');
}
Detailed Explanation of the fetch() Method of Obtaining the Result Set in PDO"!
The above is the detailed content of Three ways to execute SQL statements in PDO. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




