Two solutions for Ajax to retain browser history
I always download something from github. The entire interface of github is well made and the experience is very good. I like the special effect of the source code sliding the most. At first I thought this was just an ordinary ajax request effect, but I found that this special effect can lead to browsing. The address bar of the server will follow the changes, and you can slide the code back and out after clicking the forward and back buttons~~ So let’s study it~
1. Implementation through anchor point Hash:
In fact, this aspect has been done in China for a long time, such as Taobao Illustrated, which is achieved by adding # anchor point after the address bar. The browser can identify the historical records in units of anchor points. But it does not mean that the page itself has this anchor point. The Hash of the anchor point only serves to guide the browser to push this record to the top of the history stack.
Let’s make a small demo:
<style type="text/css">
#tab1_header,#tab2_header{
cursor:pointer;
border:1px solid;
width:50px;
}
#tab1,#tab2{
width:90%;
height:200px;
border:1px solid;
}
</style>
<p id="tab_header">
<span id="tab1_header">Tab1</span>
<span id="tab2_header">Tab2</span>
</p>
<p id="tab1">1</p>
<p id="tab2">2</p>A very simple Tab switch, if it is direct under normal circumstances:
$("#tab1_header").click(function() {
$("#tab2").hide();
$("#tab1").show();
});
$("#tab2_header").click(function() {
$("#tab1").hide();
$("#tab2").show();
});But if you want to use the back button to return to tab1 when you click tab2, it will not work. If you refresh, the behavior of the browser is not at all based on the user's ideas. In this case, we can add # anchor to simulate a new page. Why do we say For simulation, if you change window.location directly through js, the browser will reload the page, but adding # will not reload it and can be saved in the history. JS uses window.location.hash to control the anchor point # behind the URL.
We change the code to this:
$(function(){
showTab();
$(window).bind('hashchange', function(e){
showTab();
});
$("#tab1_header").click(showTab1);
$("#tab2_header").click(showTab2);
});
function showTab() {
if (window.location.hash == "#tab2"){
showTab2();
} else {
showTab1();
}
}
function showTab1() {
$("#tab2").hide();
$("#tab1").show();
window.location.hash = "#tab1";
};
function showTab2() {
$("#tab1").hide();
$("#tab2").show();
window.location.hash = "#tab2";
};Just add window.location.hash = "#tab1". After clicking tab, #tab1 will be added after the address bar. After clicking tab2, it will be changed to #tab2. When the browser detects the url change When the hashchange event is triggered, the event that the user can get when clicking back can be judged through window.location.hash and perform ajax operations. However, the haschange event is not available in every browser. Only modern advanced browsers have it, so polling is needed in low-level browsers to detect whether the URL is changing. This will not be discussed in detail here.
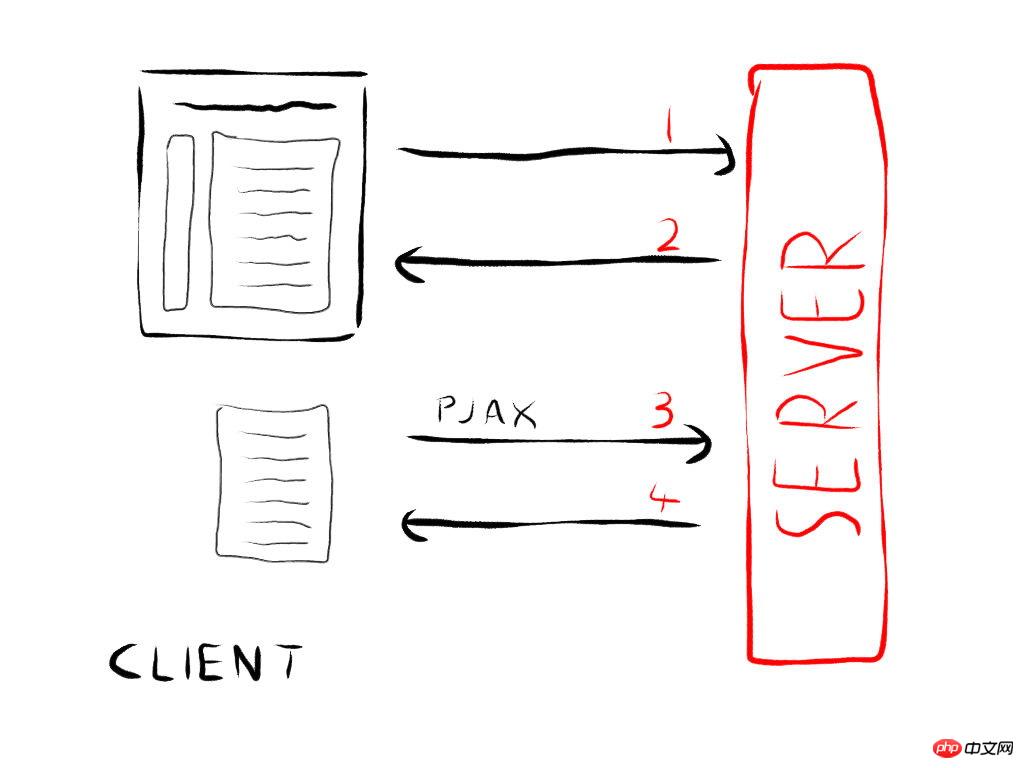
2. Implementation through HTML5 enhanced History object (like Pjax)
You can update the browser address bar without refreshing through the window.history.pushState method. This method pushes the address into the history stack while updating the address bar. To remove the top page of the stack, you can use the popstate event to capture it. ~
Let’s simulate the github environment. Each url in github corresponds to a complete actual page, so when requesting the page with ajax, you need to asynchronously obtain the content in the specified id container in the target page:
For example, there are two pages like this:
index.html
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gbk">
<title>index</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>document.write(new Date());</script>
<p id="cn">
<a href="second.html">加载前</a>
</p>
</body>
</html>second.html
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gbk">
<title>second</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>document.write(new Date());</script>
<p id="cn">
<a href="index.html">加载后</a>
</p>
</body>
</html>If it is opened with a synchronous http request, it will be two pages. If the two pages have many similarities, we can use this method to implement the ajax request to change the DOM. I added <script>document.write(new The Date());</script> statement can be used to know whether it is taken from two http requests through its changes. Bureau
The external ajax request will not change the time display.
$(function() {
var state = {
title: "index",
url: "index.html"
};
$("#cn").click(function() {
window.history.pushState(state, "index", "second.html");
var $self = $(this);
$.ajax({
url: "second.html",
dataType: "html",
complete: function(jqXHR, status, responseText) {
responseText = jqXHR.responseText;
if (jqXHR.isResolved()) {
jqXHR.done(function(r) {
responseText = r;
});
$self.html($("<p>").append(responseText.replace(/<script\b[^<]*(?:(?!<\/script>)<[^<]*)*<\/script>/gi, "")).find("#cn"));
}
}
});
document.title = "second";
return false;
});
$(window).bind('popstate', function(e) {
var st = e.state;
//$("#cn").load(st.url + " #cn");
$.ajax({
url: "index.html",
dataType: "html",
complete: function(jqXHR, status, responseText) {
responseText = jqXHR.responseText;
if (jqXHR.isResolved()) {
jqXHR.done(function(r) {
responseText = r;
});
$("#cn").html($("<p>").append(responseText.replace(/<script\b[^<]*(?:(?!<\/script>)<[^<]*)*<\/script>/gi, "")).find("#cn"));
}
}
});
document.title = e.state.title;
});
});In the above statement, when the #cn element is clicked, the state is pushed into the history stack through the pushState method, and in the third parameter, the browser URL box points to the second page, and the second page is loaded asynchronously through ajax, and the corresponding part is added to the container, thus realizing asynchronous loading and changing the address bar URL. Similarly, when the user clicks back, popstate is triggered. The first parameter state in the pushState method just now is the state in the formal parameter e passed in here. Attributes are taken out through var st = e.state for development use. At the same time, the corresponding content in the index page is loaded. Due to limited time, this js has not been reconstructed, so I wrote $.ajax directly. In fact, if you do not need any special effects and simply load asynchronously in jQ, you can directly use $("#cn").load(st.url + " #cn ");Put the #cn corresponding to the requested HTML into the #cn container of this page. However, if you want to add more dazzling special effects, you must directly operate the data returned by ajax.
$("#cn").html($("<p>").append(responseText.replace(/<script\b[^<]*(?:(?!<\/script>)<[^<]*)*<\/script>/gi, "")).find("#cn"));First create a p container, then load the script-filtered code into this container. Use the find method to find the corresponding selector container and insert it into your own page. You don’t need to fill it with html here. You can use slideUp according to your own project needs. Show what special effects to display the content~~
In addition, I would like to recommend a jQuery component called pjax (https://github.com/defunkt/jquery-pjax). It is a relatively cool component. The asynchronous part loads into another page corresponding to the content in the container. The implementation mechanism and Same as my second option above. pushState + ajax = pjax I feel like this application will become popular.
To sum up, the two solutions are actually not very good at supporting lower-level browsers such as IE6 or FF3.6. The former needs to use polling to monitor the browser address bar behavior if it is to be compatible with low-end browsers, while the latter is A complete HTML5 application can only make judgment jumps for non-HTML5 browsers.
如pjax最后的一段无奈的兼容处理:
$.support.pjax = window.history && window.history.pushState
// Fall back to normalcy for older browsers.
if ( !$.support.pjax ) {
$.pjax = function( options ) {
window.location = $.isFunction(options.url) ? options.url() : options.url
}
$.fn.pjax = function() { return this }
}
The above is the detailed content of Two solutions for Ajax to retain browser history. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1393
1393
 52
52
 1207
1207
 24
24
 How to solve the 403 error encountered by jQuery AJAX request
Feb 20, 2024 am 10:07 AM
How to solve the 403 error encountered by jQuery AJAX request
Feb 20, 2024 am 10:07 AM
Title: Methods and code examples to resolve 403 errors in jQuery AJAX requests. The 403 error refers to a request that the server prohibits access to a resource. This error usually occurs because the request lacks permissions or is rejected by the server. When making jQueryAJAX requests, you sometimes encounter this situation. This article will introduce how to solve this problem and provide code examples. Solution: Check permissions: First ensure that the requested URL address is correct and verify that you have sufficient permissions to access the resource.
 How to solve jQuery AJAX request 403 error
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:55 PM
How to solve jQuery AJAX request 403 error
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:55 PM
jQuery is a popular JavaScript library used to simplify client-side development. AJAX is a technology that sends asynchronous requests and interacts with the server without reloading the entire web page. However, when using jQuery to make AJAX requests, you sometimes encounter 403 errors. 403 errors are usually server-denied access errors, possibly due to security policy or permission issues. In this article, we will discuss how to resolve jQueryAJAX request encountering 403 error
 PHP and Ajax: Building an autocomplete suggestion engine
Jun 02, 2024 pm 08:39 PM
PHP and Ajax: Building an autocomplete suggestion engine
Jun 02, 2024 pm 08:39 PM
Build an autocomplete suggestion engine using PHP and Ajax: Server-side script: handles Ajax requests and returns suggestions (autocomplete.php). Client script: Send Ajax request and display suggestions (autocomplete.js). Practical case: Include script in HTML page and specify search-input element identifier.
 How to solve the problem of jQuery AJAX error 403?
Feb 23, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
How to solve the problem of jQuery AJAX error 403?
Feb 23, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
How to solve the problem of jQueryAJAX error 403? When developing web applications, jQuery is often used to send asynchronous requests. However, sometimes you may encounter error code 403 when using jQueryAJAX, indicating that access is forbidden by the server. This is usually caused by server-side security settings, but there are ways to work around it. This article will introduce how to solve the problem of jQueryAJAX error 403 and provide specific code examples. 1. to make
 How to get variables from PHP method using Ajax?
Mar 09, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
How to get variables from PHP method using Ajax?
Mar 09, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
Using Ajax to obtain variables from PHP methods is a common scenario in web development. Through Ajax, the page can be dynamically obtained without refreshing the data. In this article, we will introduce how to use Ajax to get variables from PHP methods, and provide specific code examples. First, we need to write a PHP file to handle the Ajax request and return the required variables. Here is sample code for a simple PHP file getData.php:
 PHP vs. Ajax: Solutions for creating dynamically loaded content
Jun 06, 2024 pm 01:12 PM
PHP vs. Ajax: Solutions for creating dynamically loaded content
Jun 06, 2024 pm 01:12 PM
Ajax (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) allows adding dynamic content without reloading the page. Using PHP and Ajax, you can dynamically load a product list: HTML creates a page with a container element, and the Ajax request adds the data to that element after loading it. JavaScript uses Ajax to send a request to the server through XMLHttpRequest to obtain product data in JSON format from the server. PHP uses MySQL to query product data from the database and encode it into JSON format. JavaScript parses the JSON data and displays it in the page container. Clicking the button triggers an Ajax request to load the product list.
 PHP and Ajax: Ways to Improve Ajax Security
Jun 01, 2024 am 09:34 AM
PHP and Ajax: Ways to Improve Ajax Security
Jun 01, 2024 am 09:34 AM
In order to improve Ajax security, there are several methods: CSRF protection: generate a token and send it to the client, add it to the server side in the request for verification. XSS protection: Use htmlspecialchars() to filter input to prevent malicious script injection. Content-Security-Policy header: Restrict the loading of malicious resources and specify the sources from which scripts and style sheets are allowed to be loaded. Validate server-side input: Validate input received from Ajax requests to prevent attackers from exploiting input vulnerabilities. Use secure Ajax libraries: Take advantage of automatic CSRF protection modules provided by libraries such as jQuery.
 What are the ajax versions?
Nov 22, 2023 pm 02:00 PM
What are the ajax versions?
Nov 22, 2023 pm 02:00 PM
Ajax is not a specific version, but a technology that uses a collection of technologies to asynchronously load and update web page content. Ajax does not have a specific version number, but there are some variations or extensions of ajax: 1. jQuery AJAX; 2. Axios; 3. Fetch API; 4. JSONP; 5. XMLHttpRequest Level 2; 6. WebSockets; 7. Server-Sent Events; 8, GraphQL, etc.




