The future direction of CSS
When will plain CSS be good enough to replace Sass, Less, Stylus, and rest?

One of the toughest facts that web developers have to face is that most people still use old, low-performance browsers when browsing websites. Browsers are adding new features all the time, but you usually can't take advantage of them unless you're willing to lose a lot of users who haven't updated their browsers.
This problem does not exist when you use Electron to develop applications. Because the code of the Electron application you wrote runs on a separate Chromium browser. Chromium is the core engine of Google Chrome and is powered by Google. At the same time, it is also open source, which means that a large number of developers in the community are optimizing it every day.
CSS custom properties
Last week, Electron released a new version that supports CSS custom properties. If you've used preprocessing languages like Sass and Less, you're probably already familiar with variables, which allow you to define reusable values for things like color schemes or layouts. Variables keep your stylesheet DRY (Don't Repeat Yourself) and improve maintainability.
Since CSS custom properties are just regular CSS properties, they can be manipulated through JavaScript. This subtle but powerful feature allows developers to dynamically change the visual interface while enjoying CSS hardware acceleration, and can reduce duplication between front-end code and style sheets.
The following is an example of using custom attributes:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
|
View the demo in Google Chrome (requires chrome version higher than 49)
CSS Mixin and Inheritance
Now, we have variables in our CSS. That's great, but it's not enough to write perfect CSS. What we really need is a way to write reusable CSS. These features already exist in Sass, Less and Stylus, but are not available in regular CSS.
Enter the @apply Rule
Someone at Google is developing a new set of specifications:
This specification defines the @apply rule, which allows developers to store a set of properties in a named variable that can then be referenced in other style rules.
The following is an example of using the @apply rule:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
|
At the time of writing this article (April 8, 2016), this feature is still very new and is not supported by Google Chrome or even Chrome Canary, but it is possible in the latest Chromium nightly by enabling the flag.
If you want to try the @apply rule yourself, you can first download the latest Chromium, and then implement @apply by enabling the tag. Here’s how to do it on OS X:
1 |
|
To view all the cool styles combined by the above rules, you can refer to my codepen demo:
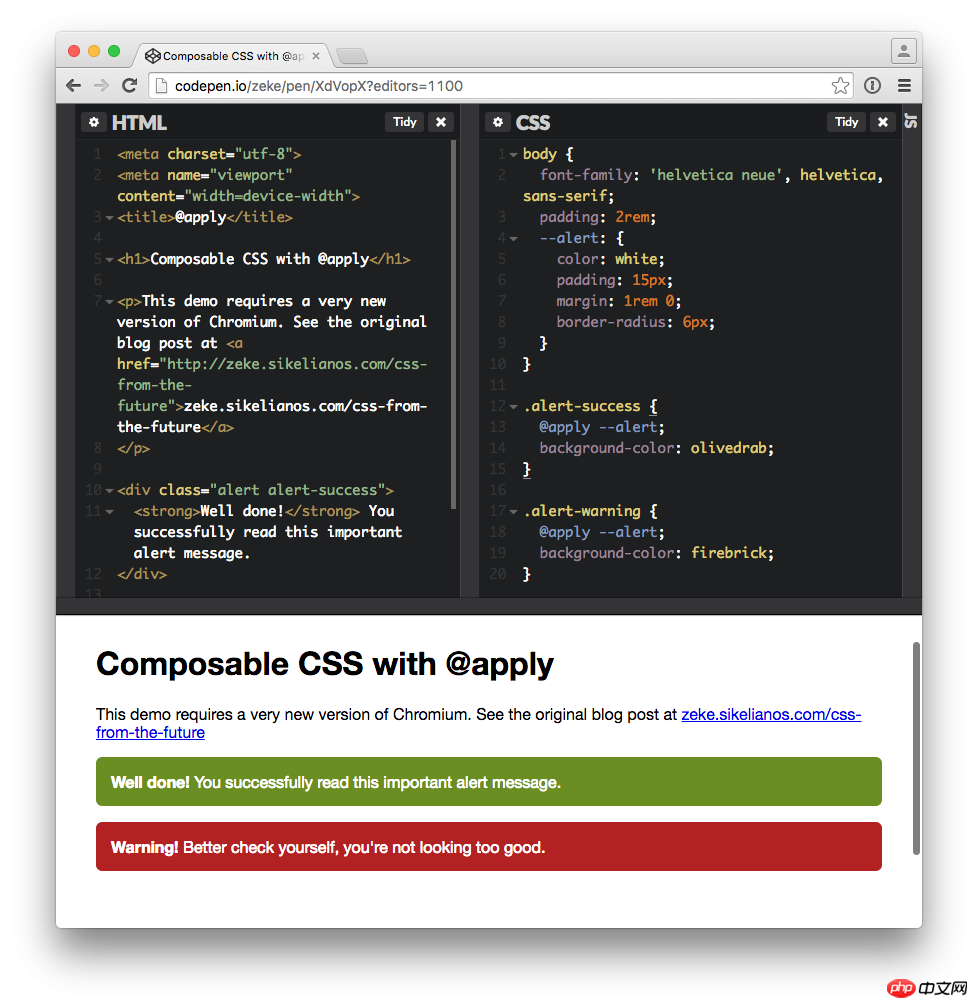
@apply Codepen demo on Chromium browser
Start writing future CSS now
Once @apply is supported by Chromium and Electron, we will be able to write clean and maintainable styles using native CSS. But until that day comes, we still need to continue to learn preprocessors to fill these gaps.
There are at least two projects that allow you to write the CSS of the future: Myth and cssnext. Of the two projects, cssnext is more active and even has a dedicated git issue to promote the implementation of @apply (Translator's Note: The latest version of postcss-cssnext already supports @apply rules).
The above is the future of CSS.
The above is the detailed content of The future direction of CSS. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1389
1389
 52
52
 The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
HTML defines the web structure, CSS is responsible for style and layout, and JavaScript gives dynamic interaction. The three perform their duties in web development and jointly build a colorful website.
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 How to write split lines on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
How to write split lines on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
There are two ways to create a Bootstrap split line: using the tag, which creates a horizontal split line. Use the CSS border property to create custom style split lines.
 Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
WebdevelopmentreliesonHTML,CSS,andJavaScript:1)HTMLstructurescontent,2)CSSstylesit,and3)JavaScriptaddsinteractivity,formingthebasisofmodernwebexperiences.
 How to use bootstrap button
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use bootstrap button
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use the Bootstrap button? Introduce Bootstrap CSS to create button elements and add Bootstrap button class to add button text
 How to resize bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
How to resize bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
To adjust the size of elements in Bootstrap, you can use the dimension class, which includes: adjusting width: .col-, .w-, .mw-adjust height: .h-, .min-h-, .max-h-
 How to set up the framework for bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
How to set up the framework for bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
To set up the Bootstrap framework, you need to follow these steps: 1. Reference the Bootstrap file via CDN; 2. Download and host the file on your own server; 3. Include the Bootstrap file in HTML; 4. Compile Sass/Less as needed; 5. Import a custom file (optional). Once setup is complete, you can use Bootstrap's grid systems, components, and styles to create responsive websites and applications.
 How to insert pictures on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
How to insert pictures on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
There are several ways to insert images in Bootstrap: insert images directly, using the HTML img tag. With the Bootstrap image component, you can provide responsive images and more styles. Set the image size, use the img-fluid class to make the image adaptable. Set the border, using the img-bordered class. Set the rounded corners and use the img-rounded class. Set the shadow, use the shadow class. Resize and position the image, using CSS style. Using the background image, use the background-image CSS property.




