Detailed explanation of decorators in Python
I remember when I first learned Python several years ago, when I looked at decorators, I felt that I couldn’t understand the strange words in Jiuyin Manual. Indeed, decorators are a very difficult concept to understand. I believe many beginners must There is also such confusion, so this article mainly introduces relevant information about decorators in Python. Friends in need can refer to it.
This article will lead you to take a closer look at what this decorator is. After reading this article, decorators are no longer difficult.
1. What is a decorator?
Some people on the Internet commented on decorators like this. I think the writing is very interesting and the metaphor is very vivid
The underwear that everyone has is mainly used to cover our shame, but in winter it cannot protect us from wind and cold, what can we do?
One way we thought of was to transform the underwear to make it thicker and longer. In this way, it not only has the function of covering shame, but also provides warmth. However, there is a The problem is, after we transformed this underwear into trousers, although it still has a shame-covering function, it is essentially no longer a real pair of underwear. So smart people invented trousers
and put the trousers directly on the outside of the underwear without affecting the underwear. In this way, the underwear is still underwear. After having trousers, it no longer needs to be worn. It's cold
The decorator is like the trousers we are talking about here. It provides warmth to our bodies without affecting the function of underwear
2. The prequel 4 steps of decorators
Why should I talk about decorators at the end of the introductory chapter? Because this article is too difficult and there are many The prerequisite must be understood. I believe everyone understands Python’s functions, but do you know that functions are also objects and can be passed like parameters? Let’s look at the following example:
1) Functions are also objects
def message(word='hello'): return word.upper()+'!' print message() >> HELLO! my_message=message print my_message >> <function message at 0x000000000288E198> print my_message() >> HELLO!
That is to say, message can be assigned to another variable
2) Functions can be nested and defined inside another function
def show(): print 'Run in show()' def message(word='hello'): return word print message() show() >> Run in show() hello
message It can be nested in the show function. When calling show, the message function will also run.
3) The function returns as a parameter
A function can also be used as The return value of another function, if you don’t believe it, look at the following example

>> <function lower at 0x00000000027DAD68> hello...
4) The function is passed in as a parameter
We first create a getName function, and then pass this function as a parameter to the foo function
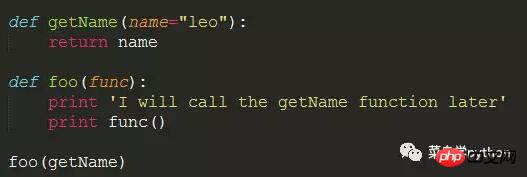
>> I will call the getName function later leo
3. The true face of decorators
1). After the previous steps, everyone should understand that functions can be passed in as parameters, can also be returned as parameters, and can also be nested
Decorations In fact, the function is repackaged. It can increase the function of the function without changing the function. It can execute a piece of code before or after the function is executed.
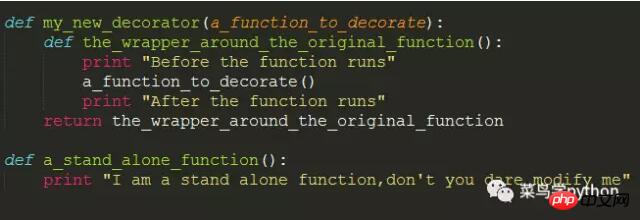
a_stand_alone_function() >> I am a stand alone function,don't you dare modify me a_stand_alone_function_decorated=my_new_decorator(a_stand_alone_function) a_stand_alone_function_decorated() >> Before the function runs I am a stand alone function,don't you dare modify me After the function runs
2). Use a decorator
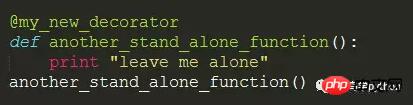
Look it’s so simple. The decorator has a syntactic sugar @, just @my_new_decorator just put it above A bunch of code is easily resolved. This is Pythonic code, simple and efficient
is actually equivalent to:
another_stand_alone_function=my_new_decorator(another_stand_alone_function)
4. Why use decorators
Decorators provide several advantages related to code maintainability and aesthetics. And as structuring tools, decorators naturally facilitate code encapsulation, which reduces redundancy and makes future maintenance and extension easier.
If you have studied Django and Flask, you will know that a large number of decorators are used in web frameworks to encapsulate code. Let’s look at a simple example below:
We have a theme functionword() outputs a string. We have a function that makes the string bold and another that makes it italic. With decorators, we can combine them very flexibly to extend the functions of the function:
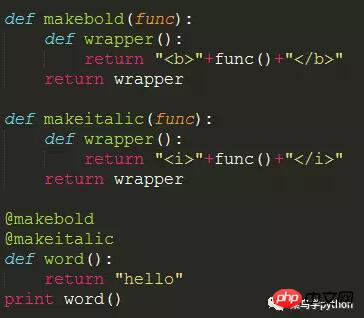
>> <b><i>hello</i></b>
One thing to note is that if the order of the decorators changes, the result will be different. Same.
@makeitalic @makebold def word(): return "hello" print word() >> <i><b>hello</b></i>
That’s it for getting started with decorators. If you don’t understand anything, you can leave a message with me to discuss and communicate. In fact, there are many advanced uses of decorators, such as passing parameters through decorators, class decorators, etc. We will explain them later.
Summarize
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of decorators in Python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
The speed of mobile XML to PDF depends on the following factors: the complexity of XML structure. Mobile hardware configuration conversion method (library, algorithm) code quality optimization methods (select efficient libraries, optimize algorithms, cache data, and utilize multi-threading). Overall, there is no absolute answer and it needs to be optimized according to the specific situation.
 Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
An application that converts XML directly to PDF cannot be found because they are two fundamentally different formats. XML is used to store data, while PDF is used to display documents. To complete the transformation, you can use programming languages and libraries such as Python and ReportLab to parse XML data and generate PDF documents.
 How to control the size of XML converted to images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
How to control the size of XML converted to images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
To generate images through XML, you need to use graph libraries (such as Pillow and JFreeChart) as bridges to generate images based on metadata (size, color) in XML. The key to controlling the size of the image is to adjust the values of the <width> and <height> tags in XML. However, in practical applications, the complexity of XML structure, the fineness of graph drawing, the speed of image generation and memory consumption, and the selection of image formats all have an impact on the generated image size. Therefore, it is necessary to have a deep understanding of XML structure, proficient in the graphics library, and consider factors such as optimization algorithms and image format selection.
 How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
It is impossible to complete XML to PDF conversion directly on your phone with a single application. It is necessary to use cloud services, which can be achieved through two steps: 1. Convert XML to PDF in the cloud, 2. Access or download the converted PDF file on the mobile phone.
 What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
There is no built-in sum function in C language, so it needs to be written by yourself. Sum can be achieved by traversing the array and accumulating elements: Loop version: Sum is calculated using for loop and array length. Pointer version: Use pointers to point to array elements, and efficient summing is achieved through self-increment pointers. Dynamically allocate array version: Dynamically allocate arrays and manage memory yourself, ensuring that allocated memory is freed to prevent memory leaks.
 How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
Use most text editors to open XML files; if you need a more intuitive tree display, you can use an XML editor, such as Oxygen XML Editor or XMLSpy; if you process XML data in a program, you need to use a programming language (such as Python) and XML libraries (such as xml.etree.ElementTree) to parse.
 What is the process of converting XML into images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
What is the process of converting XML into images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
To convert XML images, you need to determine the XML data structure first, then select a suitable graphical library (such as Python's matplotlib) and method, select a visualization strategy based on the data structure, consider the data volume and image format, perform batch processing or use efficient libraries, and finally save it as PNG, JPEG, or SVG according to the needs.
 Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
XML formatting tools can type code according to rules to improve readability and understanding. When selecting a tool, pay attention to customization capabilities, handling of special circumstances, performance and ease of use. Commonly used tool types include online tools, IDE plug-ins, and command-line tools.






