Tutorial on using regular expressions to search and match in mysql (3)
匹配特殊字符
正则表达式语言由具有特定含义的特殊字符构成。我们已经看到.、[]、|和-等,还有其他一些字符。请问,如果你需要匹配这些字符,应该怎么办呢?例如,如果要找出包含.字符的值,怎样搜索?请看下面的例子:
输入:
select vend_name from vendors where venr_name regexp '.’ order by vend_name;
输出:

分析:这并不是期望的输出,.匹配任意字符,因此每个行都被检索出来。
为了匹配特殊字符,必须用\\为前导。\\-表示查找-,\\.表示查找.。
\\也用来引用元字符(具有特殊含义的字符),如下表
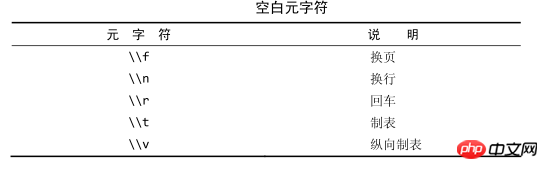
注意:为了匹配反斜杠(\)字符本身,需要使用\\\。
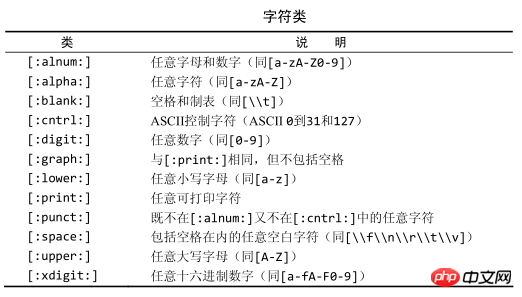
匹配字符类
存在找出你自己经常使用的数字、所有字母符或所有数字字母字符等的匹配。为更方便工作,可以使用预定义的字符集,成为字符类。下表列出字符类以及他们的含义。
匹配多个实例
目前为止使用的所有正则表达式都试图匹配单次出现。如果存在一个匹配,该行被检索出来,如果不存在,检所不出任何行。但是有时需要对匹配的数目进行更强的控制。例如,你可能需要寻找所有的数,不管数中包含多少数字,或者你可能想寻找的一个单词并且还能够适应一个尾随的s(如果存在),等等。
这个可以用下表列出的正则表达式重复元字符来完成。

下面举个例子:
输入:
select prod_name from products where prod_name regexp '\\([0-9] sticks?\\)’ order by prod_name;
输出:

分析:正则表达式\\([0-9] sticks?\\)需要解说下。\\(匹配),[0-9]匹配任意数字(这个例子中为1和5), sticks?匹配 stick和 sticks(s后的?使s可选,因为?匹配它前面的任何字符的0次或1次出现),\\)匹配。没有?,匹配 stick和 sticks会非常困难。
定位符
目前为止的所有例子都是匹配一个串中任意为止的文本。为了匹配特定位置的文本,需要使用下表列出的定位符:

例如,如果你想找出以一个数(包括以小数点开始的数)开始的所有产品,怎么办?简单搜索[0-9\\.](或[[:digit:]\\.])不行,因为它将在文本内任意位置查找匹配。解决办法是^定位符,如下所示:
输入:
select prod_name from products where prod_name regexp '^[0-9\\.]' order by prod_name;
输出:

分析:^匹配串的开始。因此,^[0-9\\.]只在.或任意数字为串中第一个字符时才匹配它们。没有^,则还要多检索出4个别的行。
【相关推荐】
The above is the detailed content of Tutorial on using regular expressions to search and match in mysql (3). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use MySQL backup and restore in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 12:19 PM
How to use MySQL backup and restore in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 12:19 PM
Backing up and restoring a MySQL database in PHP can be achieved by following these steps: Back up the database: Use the mysqldump command to dump the database into a SQL file. Restore database: Use the mysql command to restore the database from SQL files.
 How to optimize MySQL query performance in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
How to optimize MySQL query performance in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
MySQL query performance can be optimized by building indexes that reduce lookup time from linear complexity to logarithmic complexity. Use PreparedStatements to prevent SQL injection and improve query performance. Limit query results and reduce the amount of data processed by the server. Optimize join queries, including using appropriate join types, creating indexes, and considering using subqueries. Analyze queries to identify bottlenecks; use caching to reduce database load; optimize PHP code to minimize overhead.
 How to insert data into a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:26 PM
How to insert data into a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:26 PM
How to insert data into MySQL table? Connect to the database: Use mysqli to establish a connection to the database. Prepare the SQL query: Write an INSERT statement to specify the columns and values to be inserted. Execute query: Use the query() method to execute the insertion query. If successful, a confirmation message will be output.
 How to create a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:57 PM
How to create a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:57 PM
Creating a MySQL table using PHP requires the following steps: Connect to the database. Create the database if it does not exist. Select a database. Create table. Execute the query. Close the connection.
 How to use MySQL stored procedures in PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
How to use MySQL stored procedures in PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
To use MySQL stored procedures in PHP: Use PDO or the MySQLi extension to connect to a MySQL database. Prepare the statement to call the stored procedure. Execute the stored procedure. Process the result set (if the stored procedure returns results). Close the database connection.
 How to validate email address in Golang using regular expression?
May 31, 2024 pm 01:04 PM
How to validate email address in Golang using regular expression?
May 31, 2024 pm 01:04 PM
To validate email addresses in Golang using regular expressions, follow these steps: Use regexp.MustCompile to create a regular expression pattern that matches valid email address formats. Use the MatchString function to check whether a string matches a pattern. This pattern covers most valid email address formats, including: Local usernames can contain letters, numbers, and special characters: !.#$%&'*+/=?^_{|}~-`Domain names must contain at least One letter, followed by letters, numbers, or hyphens. The top-level domain (TLD) cannot be longer than 63 characters.
 How to fix mysql_native_password not loaded errors on MySQL 8.4
Dec 09, 2024 am 11:42 AM
How to fix mysql_native_password not loaded errors on MySQL 8.4
Dec 09, 2024 am 11:42 AM
One of the major changes introduced in MySQL 8.4 (the latest LTS release as of 2024) is that the "MySQL Native Password" plugin is no longer enabled by default. Further, MySQL 9.0 removes this plugin completely. This change affects PHP and other app
 How to match timestamps using regular expressions in Go?
Jun 02, 2024 am 09:00 AM
How to match timestamps using regular expressions in Go?
Jun 02, 2024 am 09:00 AM
In Go, you can use regular expressions to match timestamps: compile a regular expression string, such as the one used to match ISO8601 timestamps: ^\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2}T \d{2}:\d{2}:\d{2}(\.\d+)?(Z|[+-][0-9]{2}:[0-9]{2})$ . Use the regexp.MatchString function to check if a string matches a regular expression.






