Application of MySQL view to create a view
The application of MySQL view to create a view
View is also called a virtual table, including a set of records returned by executing a query . Views can simplify the method of obtaining data and implement abstract queries through aliases.
In order to simplify the query, in the actual project development process, you can usually create a view for a certain table in the database. Only the fields that developers care about are created in the view. Enter the username and password of the logged-in user in the input box respectively. After clicking the "Enter" button, if the user enters an incorrect username or password, an error prompt will be given. Otherwise, if the entered username and password are correct, a successful login will be prompted. .
Recommended related mysql video tutorials: "mysql tutorial"
Technical points
Creating views in MySQL can be achieved through the create view statement. The specific creation format is as follows:
$create [ or deplace] [algorithm={merge | temptable | undefined}] view view_name[( column_list)] as select_statement [with [cascaded | local] check option]algorithm={merge | temptable | undefined} attribute is used to optimize the execution of MySQL views. This attribute has 3 available set up. The following will introduce how to use these 3 settings.
merge: This parameter causes any clauses passed in when MySQL executes the view to be merged into the view's query definition.
temptable: If the data in the table below the view changes, these changes will be reflected immediately on the next pass through the table.
undefined: When the query result and the view result have a one-to-one correspondence, MySQL sets the algorithm to temptable.
view_name: The name of the new view.
select_statement: SQL query statement is used to limit the contents of the virtual table.
mysql view creation process
Since this example uses a view to create a virtual table, it should be created first under the "Command Prompt" view, you can create a view at the command prompt. The code to create the view is as follows:
create view chkadmin as select username, password from user
Create the view in the "Command Prompt" as follows:
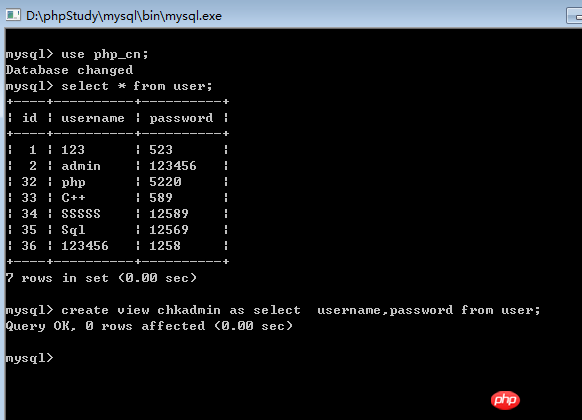
After creating the view chkadmin, the view only contains There are two fields, username and password, which will bring great convenience to the password verification work.
Then we create the user input login interface, connect to the database, and determine whether the user clicked the "Enter" button. If so, verify the user identity through the view chkadmin. The process code is as follows:
<form method="post" action="3.php" name="form1">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username" ><br>
密 码:<input type="password" name="pwd"><br>
<input type="submit" name="Submit" value="进入">
<input type="submit" value="重置">
</form>
<?php
if($_POST['Submit']){
$name = $_POST['username'];
$password = $_POST['pwd'];
header("Content-Type:text/html; charset=utf-8");
$link = mysqli_connect("localhost", "root", "root");
$conn = mysqli_select_db($link, "php_cn");
$sql = ("select * from chkadmin where username='".$name."' and password = '".$password."'");
$result = mysqli_query($link, $sql);
$res = mysqli_fetch_array($result, MYSQLI_ASSOC);
if ($res==false){
echo "<script>alert('用户名或者密码输入错误');history.back();</script>";
exit();
}else{
echo "<br><p align='center'>登录成功!</p>";
}
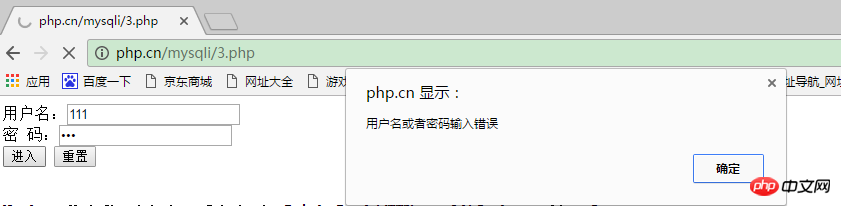
}When we enter wrong information, as shown below:
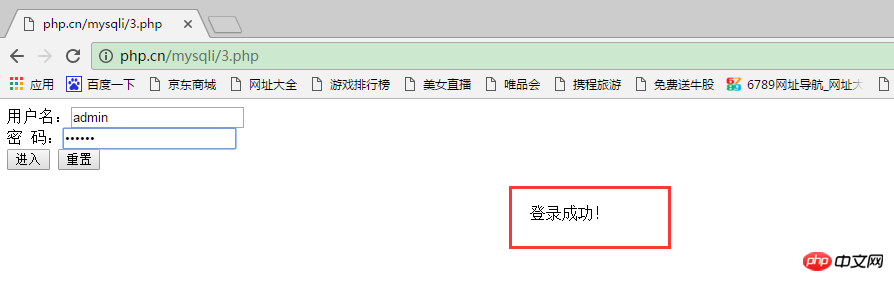
When we enter correct information, as shown below:
Then we will introduce the MySQL creation view here. Have you guys mastered it? If you haven’t mastered it yet, you can read another article carefully. , in the next article we will continue to introduce the application of MySQL views. For details, please read "MySQL View Applications - Modifying Views"!
【Recommended related tutorials】
1.【MYSQL online free video tutorial】
2. Recommended related video courses : "Han Shunping's latest MySQL basic video tutorial in 2016"
The above is the detailed content of Application of MySQL view to create a view. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 The relationship between mysql user and database
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
The relationship between mysql user and database
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
In MySQL database, the relationship between the user and the database is defined by permissions and tables. The user has a username and password to access the database. Permissions are granted through the GRANT command, while the table is created by the CREATE TABLE command. To establish a relationship between a user and a database, you need to create a database, create a user, and then grant permissions.
 MySQL: The Ease of Data Management for Beginners
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
MySQL: The Ease of Data Management for Beginners
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
MySQL is suitable for beginners because it is simple to install, powerful and easy to manage data. 1. Simple installation and configuration, suitable for a variety of operating systems. 2. Support basic operations such as creating databases and tables, inserting, querying, updating and deleting data. 3. Provide advanced functions such as JOIN operations and subqueries. 4. Performance can be improved through indexing, query optimization and table partitioning. 5. Support backup, recovery and security measures to ensure data security and consistency.
 Can I retrieve the database password in Navicat?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:51 PM
Can I retrieve the database password in Navicat?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:51 PM
Navicat itself does not store the database password, and can only retrieve the encrypted password. Solution: 1. Check the password manager; 2. Check Navicat's "Remember Password" function; 3. Reset the database password; 4. Contact the database administrator.
 Query optimization in MySQL is essential for improving database performance, especially when dealing with large data sets
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Query optimization in MySQL is essential for improving database performance, especially when dealing with large data sets
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
1. Use the correct index to speed up data retrieval by reducing the amount of data scanned select*frommployeeswherelast_name='smith'; if you look up a column of a table multiple times, create an index for that column. If you or your app needs data from multiple columns according to the criteria, create a composite index 2. Avoid select * only those required columns, if you select all unwanted columns, this will only consume more server memory and cause the server to slow down at high load or frequency times For example, your table contains columns such as created_at and updated_at and timestamps, and then avoid selecting * because they do not require inefficient query se
 How to create navicat premium
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:09 AM
How to create navicat premium
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:09 AM
Create a database using Navicat Premium: Connect to the database server and enter the connection parameters. Right-click on the server and select Create Database. Enter the name of the new database and the specified character set and collation. Connect to the new database and create the table in the Object Browser. Right-click on the table and select Insert Data to insert the data.
 How to copy tables in mysql
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
How to copy tables in mysql
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Copying a table in MySQL requires creating new tables, inserting data, setting foreign keys, copying indexes, triggers, stored procedures, and functions. The specific steps include: creating a new table with the same structure. Insert data from the original table into a new table. Set the same foreign key constraint (if the original table has one). Create the same index. Create the same trigger (if the original table has one). Create the same stored procedure or function (if the original table is used).
 How to view database password in Navicat for MariaDB?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:18 PM
How to view database password in Navicat for MariaDB?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:18 PM
Navicat for MariaDB cannot view the database password directly because the password is stored in encrypted form. To ensure the database security, there are three ways to reset your password: reset your password through Navicat and set a complex password. View the configuration file (not recommended, high risk). Use system command line tools (not recommended, you need to be proficient in command line tools).
 How to view mysql
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to view mysql
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
View the MySQL database with the following command: Connect to the server: mysql -u Username -p Password Run SHOW DATABASES; Command to get all existing databases Select database: USE database name; View table: SHOW TABLES; View table structure: DESCRIBE table name; View data: SELECT * FROM table name;




