 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Introducing various types of sorting when Django queries the database
Introducing various types of sorting when Django queries the database
Introducing various types of sorting when Django queries the database
Querying data according to entry_date from small to large can be written as:
Content.objects.order_by('entry_date')
Sort from large to small:
Content.objects.order_by('-entry_date')
The following introduces other types of sorting
Random sorting:
Content.objects.order_by('?')
But the order_by(?) method may be expensive and slow, depending on the backend database.
Sort by fields of the relational table
class Category(Base):
code = models.CharField(primary_key=True,max_length=100)
title = models.CharField(max_length = 255)
class Content(Base):
title = models.CharField(max_length=255)
description = models.TextField()
category = models.ForeignKey(Category, on_delete=models.CASCADE)# 按照Category的字段code,对Content进行排序,只需要外键后加双下划线 Content.objects.order_by('category__title') # 如果只是按照外键来排序,会默认按照关联的表的主键排序 Content.objects.order_by('category') # 上面等价于 Content.objects.order_by('category__code') # 双下划线返回的是join后的结果集,而单下划线返回的是单个表的集合 Content.objects.order_by('category_title')
Note: Whether it is a single underscore or a double underscore, we can use {{ content.category.title }} to obtain the data of the relational table on the front end.
【Related Tutorial Recommendations】
1. "Python Free Video Tutorial"
2. Basic Introduction to Python Tutorial
3. Application of Python in Data Science
The above is the detailed content of Introducing various types of sorting when Django queries the database. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
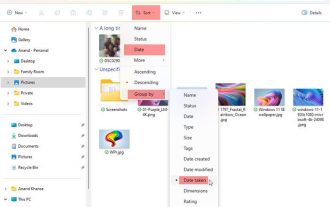 How to sort photos by date taken in Windows 11/10
Feb 19, 2024 pm 08:45 PM
How to sort photos by date taken in Windows 11/10
Feb 19, 2024 pm 08:45 PM
This article will introduce how to sort pictures according to shooting date in Windows 11/10, and also discuss what to do if Windows does not sort pictures by date. In Windows systems, organizing photos properly is crucial to making it easy to find image files. Users can manage folders containing photos based on different sorting methods such as date, size, and name. In addition, you can set ascending or descending order as needed to organize files more flexibly. How to Sort Photos by Date Taken in Windows 11/10 To sort photos by date taken in Windows, follow these steps: Open Pictures, Desktop, or any folder where you place photos In the Ribbon menu, click
 How to check django version
Dec 01, 2023 pm 02:25 PM
How to check django version
Dec 01, 2023 pm 02:25 PM
Steps to check the Django version: 1. Open a terminal or command prompt window; 2. Make sure Django has been installed. If Django is not installed, you can use the package management tool to install it and enter the pip install django command; 3. After the installation is complete , you can use python -m django --version to check the Django version.
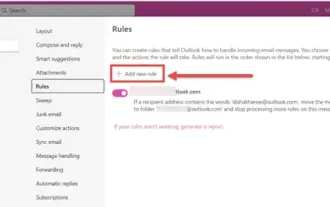 How to sort emails by sender, subject, date, category, size in Outlook
Feb 19, 2024 am 10:48 AM
How to sort emails by sender, subject, date, category, size in Outlook
Feb 19, 2024 am 10:48 AM
Outlook offers many settings and features to help you manage your work more efficiently. One of them is the sorting option that allows you to categorize your emails according to your needs. In this tutorial, we will learn how to use Outlook's sorting feature to organize emails based on criteria such as sender, subject, date, category, or size. This will make it easier for you to process and find important information, making you more productive. Microsoft Outlook is a powerful application that makes it easy to centrally manage your email and calendar schedules. You can easily send, receive, and organize email, while built-in calendar functionality makes it easy to keep track of your upcoming events and appointments. How to be in Outloo
 Django Framework Pros and Cons: Everything You Need to Know
Jan 19, 2024 am 09:09 AM
Django Framework Pros and Cons: Everything You Need to Know
Jan 19, 2024 am 09:09 AM
Django is a complete development framework that covers all aspects of the web development life cycle. Currently, this framework is one of the most popular web frameworks worldwide. If you plan to use Django to build your own web applications, then you need to understand the advantages and disadvantages of the Django framework. Here's everything you need to know, including specific code examples. Django advantages: 1. Rapid development-Djang can quickly develop web applications. It provides a rich library and internal
 Django vs. Flask: A comparative analysis of Python web frameworks
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:36 AM
Django vs. Flask: A comparative analysis of Python web frameworks
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:36 AM
Django and Flask are both leaders in Python Web frameworks, and they both have their own advantages and applicable scenarios. This article will conduct a comparative analysis of these two frameworks and provide specific code examples. Development Introduction Django is a full-featured Web framework, its main purpose is to quickly develop complex Web applications. Django provides many built-in functions, such as ORM (Object Relational Mapping), forms, authentication, management backend, etc. These features allow Django to handle large
 How to check django version
Nov 30, 2023 pm 03:08 PM
How to check django version
Nov 30, 2023 pm 03:08 PM
How to check the django version: 1. To check through the command line, enter the "python -m django --version" command in the terminal or command line window; 2. To check in the Python interactive environment, enter "import django print(django. get_version())" code; 3. Check the settings file of the Django project and find a list named INSTALLED_APPS, which contains installed application information.
 What is the difference between django versions?
Nov 20, 2023 pm 04:33 PM
What is the difference between django versions?
Nov 20, 2023 pm 04:33 PM
The differences are: 1. Django 1.x series: This is an early version of Django, including versions 1.0, 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.6, 1.7, 1.8 and 1.9. These versions mainly provide basic web development functions; 2. Django 2.x series: This is the mid-term version of Django, including 2.0, 2.1, 2.2 and other versions; 3. Django 3.x series: This is the latest version series of Django. Including versions 3.0, 3, etc.
 How to upgrade Django version: steps and considerations
Jan 19, 2024 am 10:16 AM
How to upgrade Django version: steps and considerations
Jan 19, 2024 am 10:16 AM
How to upgrade Django version: steps and considerations, specific code examples required Introduction: Django is a powerful Python Web framework that is continuously updated and upgraded to provide better performance and more features. However, for developers using older versions of Django, upgrading Django may face some challenges. This article will introduce the steps and precautions on how to upgrade the Django version, and provide specific code examples. 1. Back up project files before upgrading Djan





