
This article mainly introduces the query cache of the mybatis tutorial (first-level cache, second-level cache and integrated ehcache), which has certain reference value. Interested friends can refer to it
1 The meaning of cache
Put the data frequently queried by users in the cache (memory). Users do not need to query the data from the disk (relational database data file), but from the cache query, thereby improving query efficiency and solving the performance problem of high-concurrency systems.

2 mybatis persistence layer cache
mybatis provides first-level cache and second-level cache
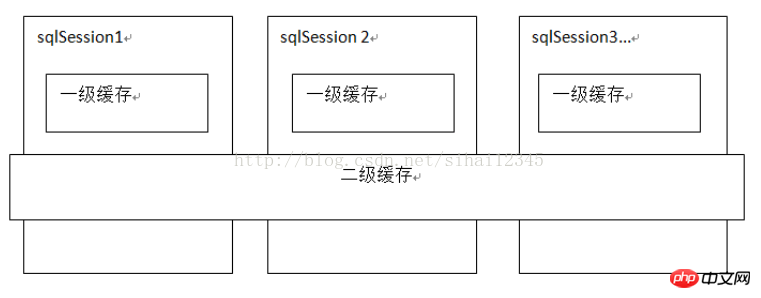
Mybatis first-level cache is a SqlSession level. sqlsession can only access the data of its own first-level cache. The second-level cache is across sqlSession and is a mapper-level cache. For The mapper level cache can be shared by different sqlsession.
3 Level 1 cache
3.1 Principle
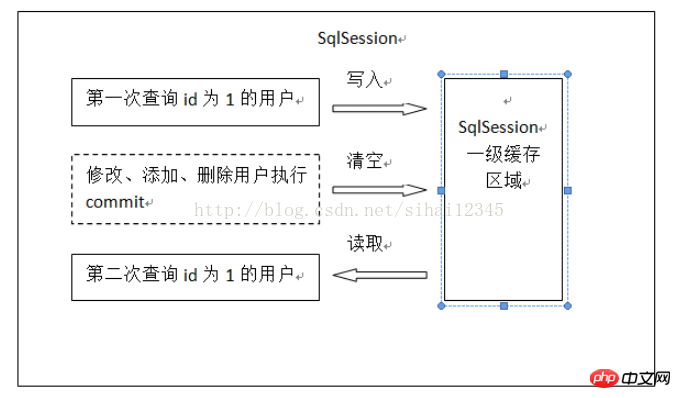
The first time a query sql is issued, the sql query results are written into the first-level cache of sqlsession. The data structure used in the cache is a map
key: hashcode+ sql+sql input parameter + output parameter (the unique identifier of sql)
value: user information
If the same sqlsession issues the same sql again, it will be fetched from the cache Don't use the database. If there is a commit operation (modify, add, delete) between two times, all the first-level cache area in this sqlsession will be cleared, and the next time you go to the cache to query it, you will not be able to query it, so you have to query it from the database, query it from the database to the cache again.
Every query is first queried from the cache:

If the query is found in the cache, the cache dataReturn directly.
If the query cannot be found in the cache, query it from the database:

3.2 Level 1 cache configuration
Mybatis supports first-level cache by default and does not require configuration.
Note: Mapper agent development is carried out after the integration of mybatis and spring. First-level cache is not supported. Mybatis and spring are integrated. Spring generates the mapper agent according to the mapper template. Object, template Close the sqlsession uniformly at the end.
3.3 Level 1 cache test
//一级缓存
@Test
public void testCache1() throws Exception {
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
//第一次查询用户id为1的用户
User user = userMapper.findUserById(1);
System.out.println(user);
//中间修改用户要清空缓存,目的防止查询出脏数据
/*user.setUsername("测试用户2");
userMapper.updateUser(user);
sqlSession.commit();*/
//第二次查询用户id为1的用户
User user2 = userMapper.findUserById(1);
System.out.println(user2);
sqlSession.close();
}4 Level 2 cache
4.1 Principle
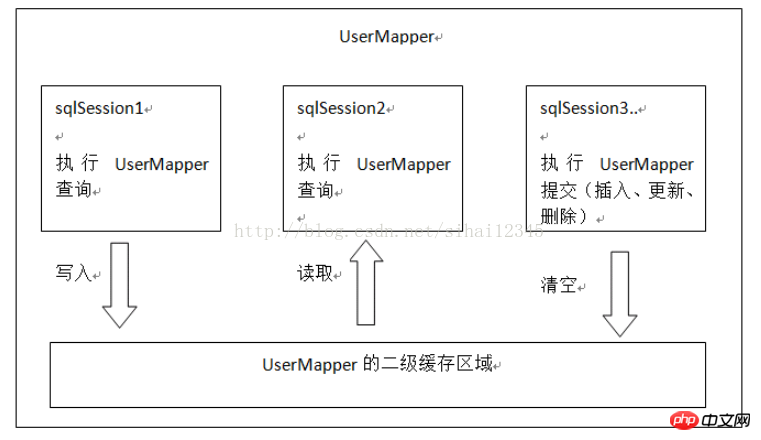
The scope of the second-level cache is the mapper level (the mapper is named with the same Space), mapper creates a cache data structure in namespace units, and the structure is map
Every time you query, first check whether the second-level cache is enabled. If it is enabled to fetch cached data from the data structure of the second-level cache,

If it is not obtained from the second-level cache, search it from the first-level cache. If it is not found in the first-level cache, query it from the database.
4.2 mybatis second-level cache configuration
Add ## to the core configuration file
SqlMapConfig.xml
#
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>

4.3 Query result mapping pojo serialization
interface for the query result mapping pojo , if not implemented, throws an exception :
4.4 二级缓存禁用
对于变化频率较高的sql,需要禁用二级缓存:
在statement中设置useCache=false可以禁用当前select语句的二级缓存,即每次查询都会发出sql去查询,默认情况是true,即该sql使用二级缓存。
<select id="findOrderListResultMap" resultMap="ordersUserMap" useCache="false">
4.5 刷新缓存
如果sqlsession操作commit操作,对二级缓存进行刷新(全局清空)。
设置statement的flushCache是否刷新缓存,默认值是true。
4.6 测试代码
//二级缓存的测试
@Test
public void testCache2() throws Exception {
SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
SqlSession sqlSession3 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper userMapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
UserMapper userMapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
UserMapper userMapper3 = sqlSession3.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
//第一次查询用户id为1的用户
User user = userMapper1.findUserById(1);
System.out.println(user);
sqlSession1.close();
//中间修改用户要清空缓存,目的防止查询出脏数据
/*user.setUsername("测试用户2");
userMapper3.updateUser(user);
sqlSession3.commit();
sqlSession3.close();*/
//第二次查询用户id为1的用户
User user2 = userMapper2.findUserById(1);
System.out.println(user2);
sqlSession2.close();
}4.7 mybatis的cache参数
mybatis的cache参数只适用于mybatis维护缓存。
flushInterval(刷新间隔)可以被设置为任意的正整数,而且它们代表一个合理的毫秒形式的时间段。默认情况是不设置,也就是没有刷新间隔,缓存仅仅调用语句时刷新。
size(引用数目)可以被设置为任意正整数,要记住你缓存的对象数目和你运行环境的可用内存资源数目。默认值是1024。
readOnly(只读)属性可以被设置为true或false。只读的缓存会给所有调用者返回缓存对象的相同实例。因此这些对象不能被修改。这提供了很重要的性能优势。可读写的缓存会返回缓存对象的拷贝(通过序列化)。这会慢一些,但是安全,因此默认是false。
如下例子:
<cache eviction="FIFO" flushInterval="60000" size="512" readOnly="true"/>
这个更高级的配置创建了一个 FIFO 缓存,并每隔 60 秒刷新,存数结果对象或列表的 512 个引用,而且返回的对象被认为是只读的,因此在不同线程中的调用者之间修改它们会导致冲突。可用的收回策略有, 默认的是 LRU:
1. LRU – 最近最少使用的:移除最长时间不被使用的对象。
2. FIFO – 先进先出:按对象进入缓存的顺序来移除它们。
3. SOFT – 软引用:移除基于垃圾回收器状态和软引用规则的对象。
4. WEAK – 弱引用:更积极地移除基于垃圾收集器状态和弱引用规则的对象。
5 mybatis和ehcache缓存框架整合
mybatis二级缓存通过ehcache维护缓存数据。
5.1 分布缓存
将缓存数据数据进行分布式管理。
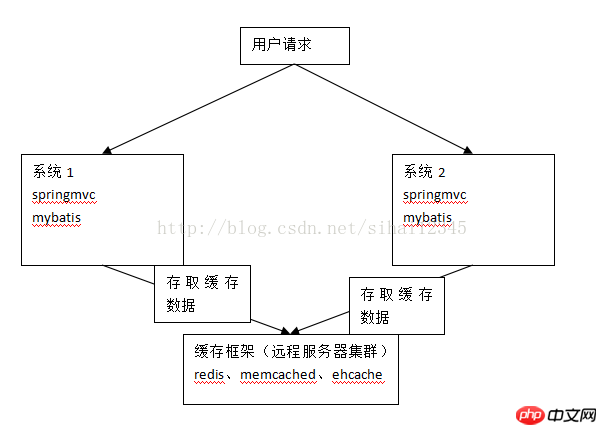
5.2 mybatis和ehcache思路
通过mybatis和ehcache框架进行整合,就可以把缓存数据的管理托管给ehcache。
在mybatis中提供一个cache接口,只要实现cache接口就可以把缓存数据灵活的管理起来。
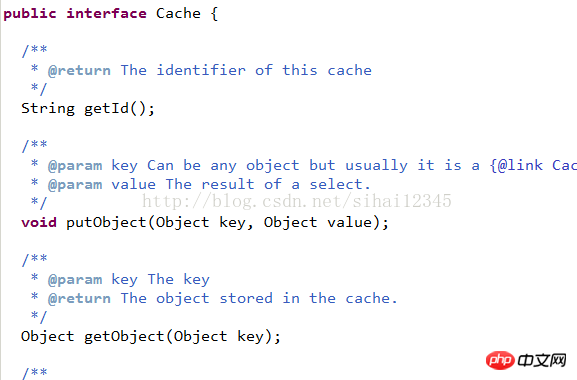
mybatis中默认实现:
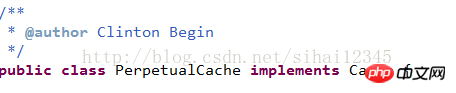
5.3 下载和ehcache整合的jar包

ehcache对cache接口的实现类:
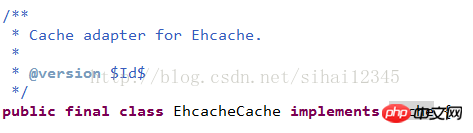
5.4 配置ehcache.xml
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="../config/ehcache.xsd">
<!--diskStore:缓存数据持久化的目录 地址 -->
<diskStore path="F:\develop\ehcache" />
<defaultCache
maxElementsInMemory="1000"
maxElementsOnDisk="10000000"
eternal="false"
overflowToDisk="false"
diskPersistent="true"
timeToIdleSeconds="120"
timeToLiveSeconds="120"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU">
</defaultCache>
</ehcache>5.5 整合测试
在mapper.xml添加ehcache配置:
<!-- 开启二级缓存 -->
<!-- 单位:毫秒 -->
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache">
<property name="timeToIdleSeconds" value="12000"/>
<property name="timeToLiveSeconds" value="3600"/>
<!-- 同ehcache参数maxElementsInMemory -->
<property name="maxEntriesLocalHeap" value="1000"/>
<!-- 同ehcache参数maxElementsOnDisk -->
<property name="maxEntriesLocalDisk" value="10000000"/>
<property name="memoryStoreEvictionPolicy" value="LRU"/>
</cache>6 二级缓存的应用场景
对查询频率高,变化频率低的数据建议使用二级缓存。
对于访问多的查询请求且用户对查询结果实时性要求不高,此时可采用mybatis二级缓存技术降低数据库访问量,提高访问速度,业务场景比如:耗时较高的统计分析sql、电话账单查询sql等。
实现方法如下:通过设置刷新间隔时间,由mybatis每隔一段时间自动清空缓存,根据数据变化频率设置缓存刷新间隔flushInterval,比如设置为30分钟、60分钟、24小时等,根据需求而定。
7 mybatis局限性
mybatis second-level cache is not good at fine-grained data level caching, such as the following requirements: caching product information. Due to the large number of product information query visits, users are required to query the latest product information every time. At this time, if you use the second-level cache of mybatis, it will not be possible to refresh only the cache information of a product when a product changes and not refresh the information of other products, because the second-level cache area of mybaits is divided in units of mappers. , when a product information changes, all cached data of all product information will be cleared. Solving such problems requires targeted caching of data based on needs at the business layer.
【Related Recommendations】
1. Special Recommendation:"php Programmer Toolbox" V0.1 version Download
3. Comprehensive analysis of Java annotations
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of cache examples in mybatis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




