 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Detailed introduction to the use tutorial of Django open source framework
Detailed introduction to the use tutorial of Django open source framework
Detailed introduction to the use tutorial of Django open source framework
There are many different web frameworks under Python. Django is the most representative of the heavyweight players. Many successful websites and apps are based on Django. Django is an open source web application framework written in Python. Let’s learn it step by step
This article is aimed at: Beginners who have a python foundation and are new to web frameworks.
Environment: windows7 python3.5.1 pycharm professional version Django 1.10 version pip3
1. DjangoIntroduction
Baidu Encyclopedia: An open source web application framework written in Python...
Focus: A large and comprehensive framework that has everything considered for you.
1. Introduction to web framework
Before introducing Django in detail, concepts such as WEB framework must be introduced first.
Web framework: A web website template has been set by others. You learn its rules, and then "fill in the blanks" or "modify" it to what you need.
The architecture of a general web framework is like this:
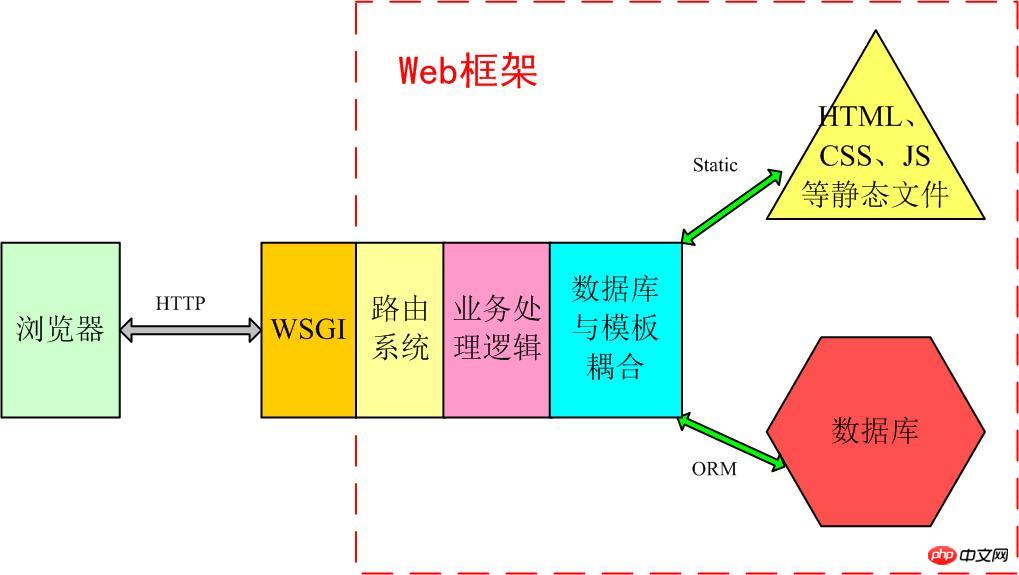
Model View Controller, is model(model )-View(view)-Abbreviation of controller(controller), a software design model that uses a method to separate business logic, data, and interface display to organize code and The business logic is gathered into a component, and there is no need to rewrite the business logic while improving and personalizing the interface and user interaction.
Popular explanation: a form of organization and management of files! Don't be scared by the abbreviation, this is actually a way to put different types of files in different directories, and then give them a fancy name. Of course, it brings many benefits, such as front-end and back-end separation, loose coupling, etc., so I won’t go into details. Model (model): Defines database-related content, usually placed in the models.py file. View: Define HTML and otherstatic web page file related things, that is, those front-end things such as html, css, js.
Controller: defines business logic, which is your main code. MTV: Some WEB frameworks think the literal meaning of MVC is awkward, so they change it. View is no longer related to HTML, but the main business logic, which is equivalent to a controller. HTML was placed in Templates, called templates, so MVC became MTV. This is actually a word game. It is essentially the same as MVC. It just has a different name and method. It does not change the medicine. 3.Django’s MTV model organization If the directories are separated, there must be a mechanism to couple them inside. In Django, urls, orm, static, settings, etc. play an important role. A typical business process is as shown in the figure below: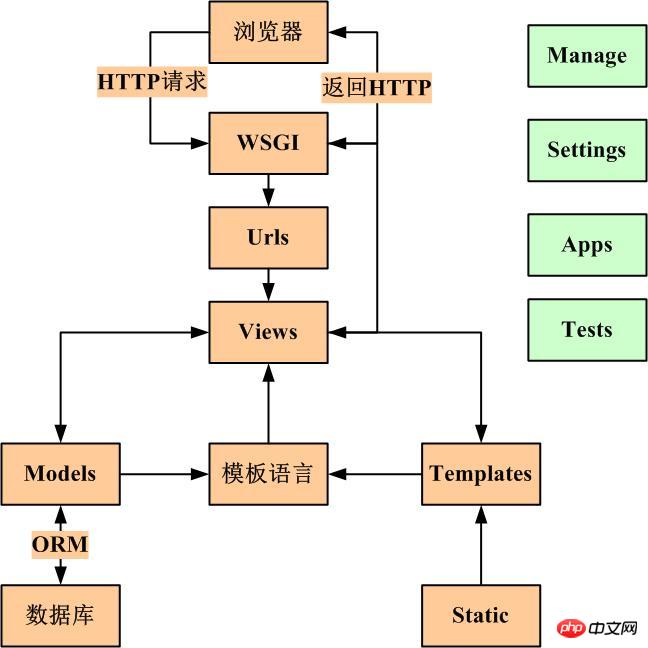
Directory structureSpecification
2. urlsroutingmethod
3. settings configuration 4.ORM operation5. 6. Others2. Django project example
1. Program Python3.5, pip3 and pycharm professional version are installed by yourself. (1) Install Django: Here we only introduce the simpler pip3 command installation method. Win+r, bring up cmd, run the command: pip3 install django, automatically install the latest version provided by Pypi.
After successfully installing Django, you can find the django-admin.exe file in the path in the figure below and add it to the operating system environment variables. This will make future calls more convenient.
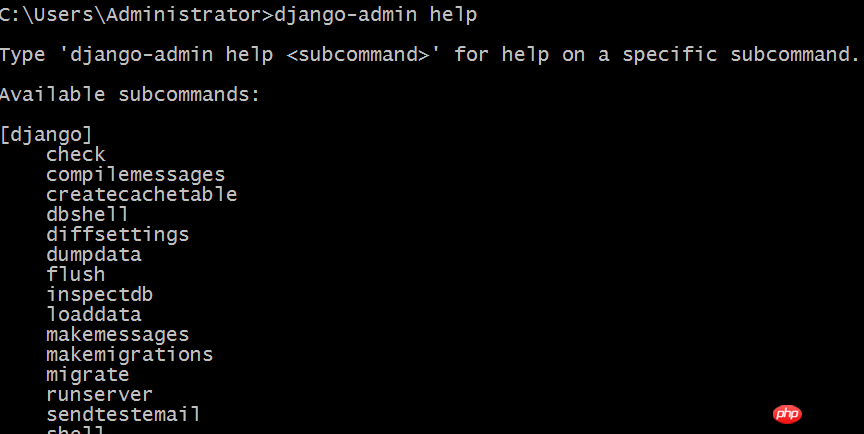
Run: django-admin help. If you see the following content, it means OK.
2. Create a django project
Under command line interfaces such as Linux, project development can also be carried out using the commands and vim provided by django. However, it is recommended to use pycharm, the best Python development IDE
at present. It has powerful functions and friendly interface. (All the following operations are performed in pycharm.)
Click: file-->new project, and the following dialog box appears.
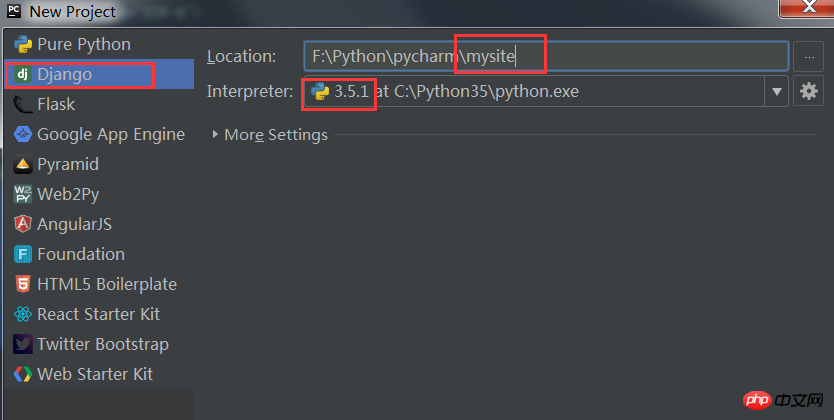
Select the Django column and enter the project name. The international practice of mysite is used here. Select the python interpreter version and click create.
Django will automatically generate the following directory structure:
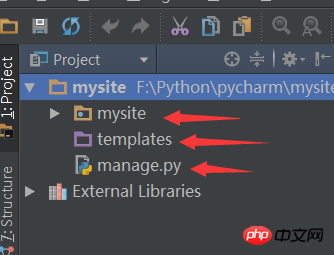
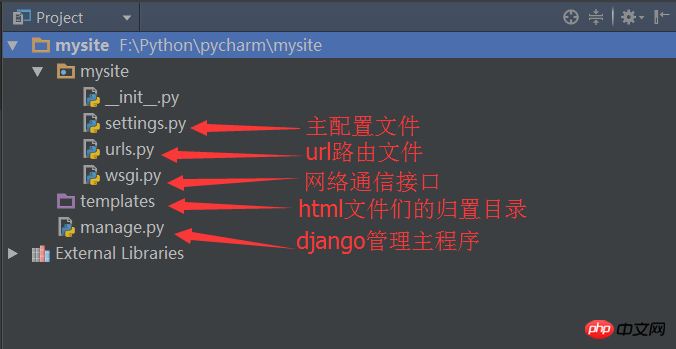
The directory with the same name as the project is the configuration file, and the templates directory is html File storage is the T in MTV. manage.py is the django project management file.
3. Create APP
Each Django project can contain multiple APPs, which are equivalent to subsystems, submodules, Functional components, etc., are relatively independent of each other, but they are also related.
All APPs share project resources.
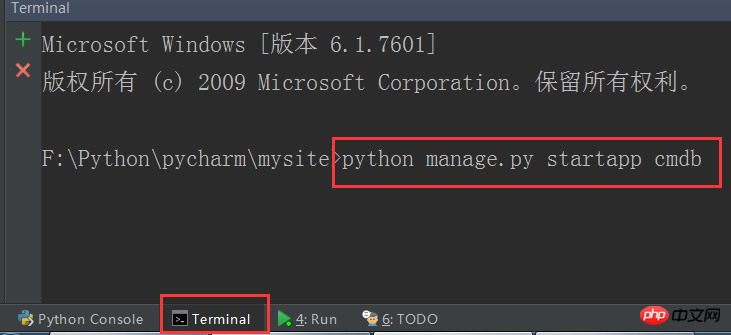
Enter the command in the terminal below pycharm:
python manage.py startapp cmdb
This creates an APP called cmdb, and django automatically generates "cmdb" folder.
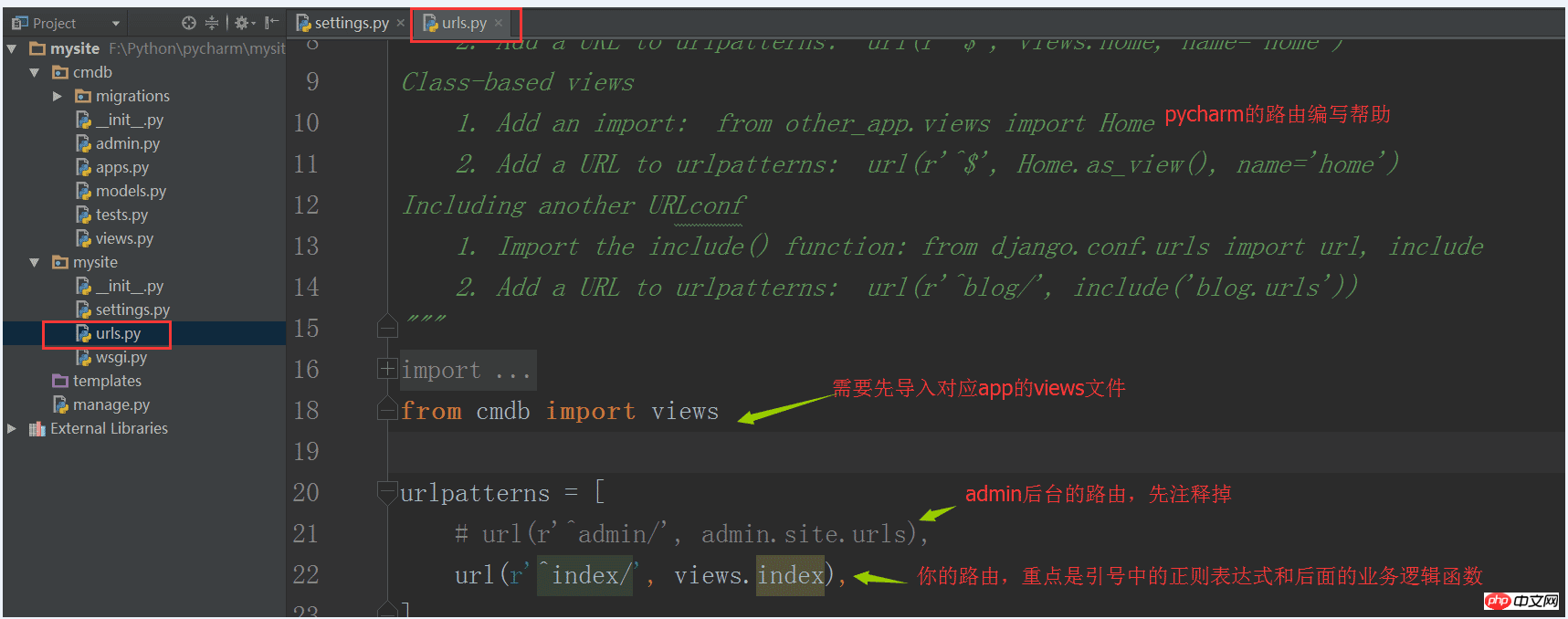
4. Write routes
Routes are all in the urls file, which maps the URL input by the browser to the corresponding business processing logic.
The simple method of writing urls is as follows:
5. Write business processing logic
The business processing logic is all in the views.py file inside.
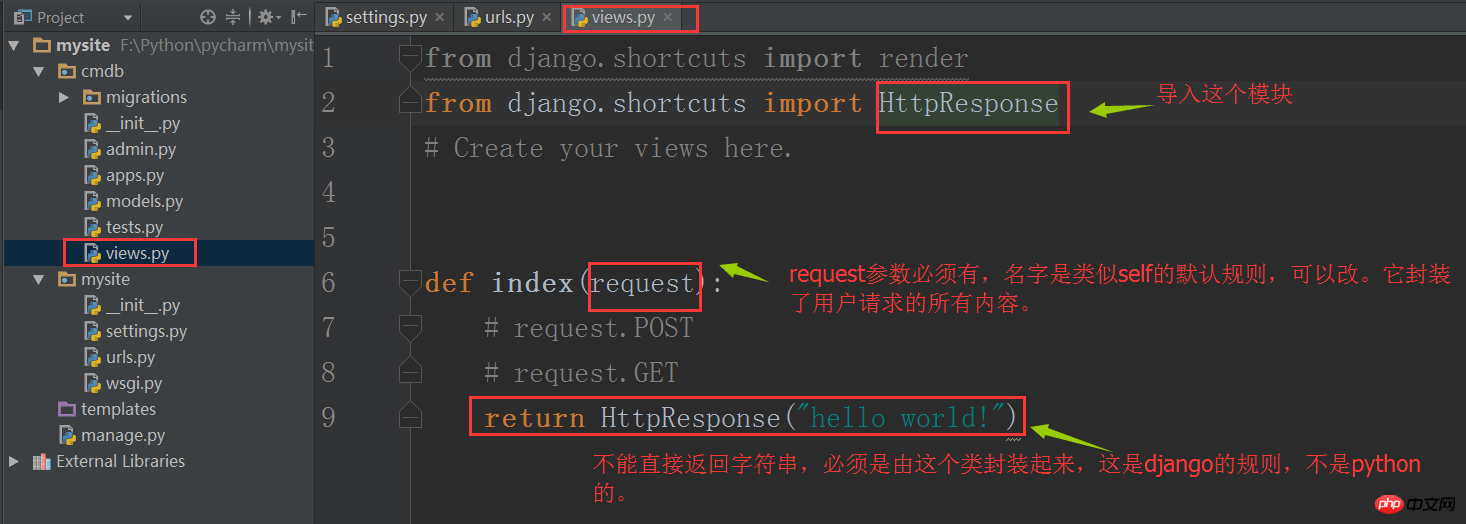
Through the above two steps, we point the index url to the index()function in views, which receives the user request and returns a "hello world"String.
6. Run the web service
Now we can run the web service.
The command line method is: python manage.py runserver 127.0.0.1:8000
But in pycharm, you can do this:
Found in the upper toolbar icon shown below.
Click the drop-down arrow
Click edit configurations
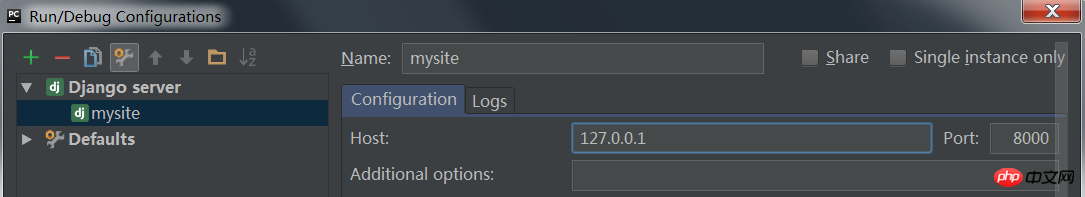
Fill in host: 127.0.0.1 Fill in port: 8000
After OK, click the green triangle, and the web service will start.
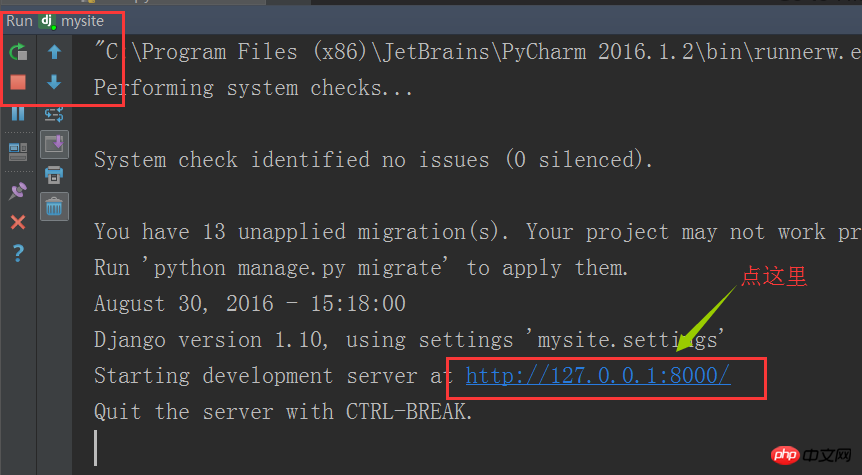
As shown in the picture, it will automatically jump to the browser program interface. What is displayed is the 404 page shown below:
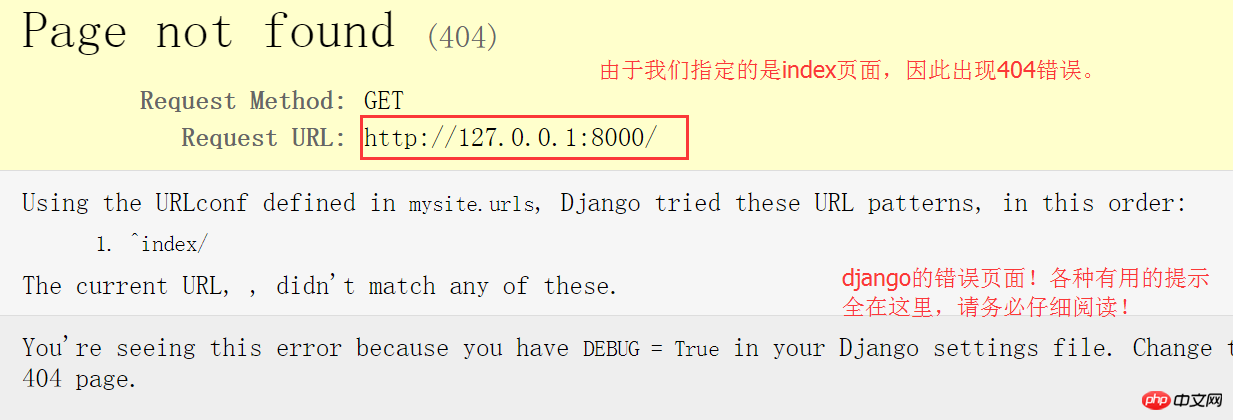
Modify the url, add "/index", and everything is ok!
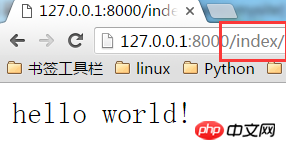
At this point, the simplest web service written in Django has been started successfully.
7. Return HTML file
What did we return to the user’s browser above? A string! In fact, this is definitely not possible. Usually we return the html file to the user.
Next, we write an index.html file like this:
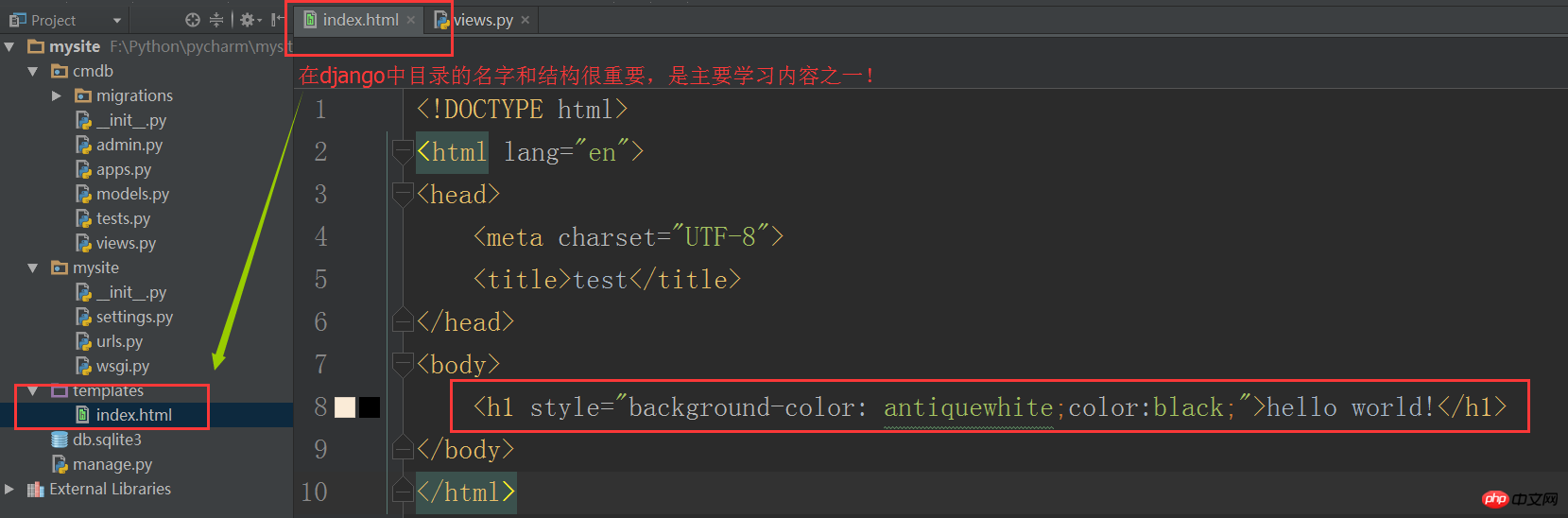
Modify the views file again:
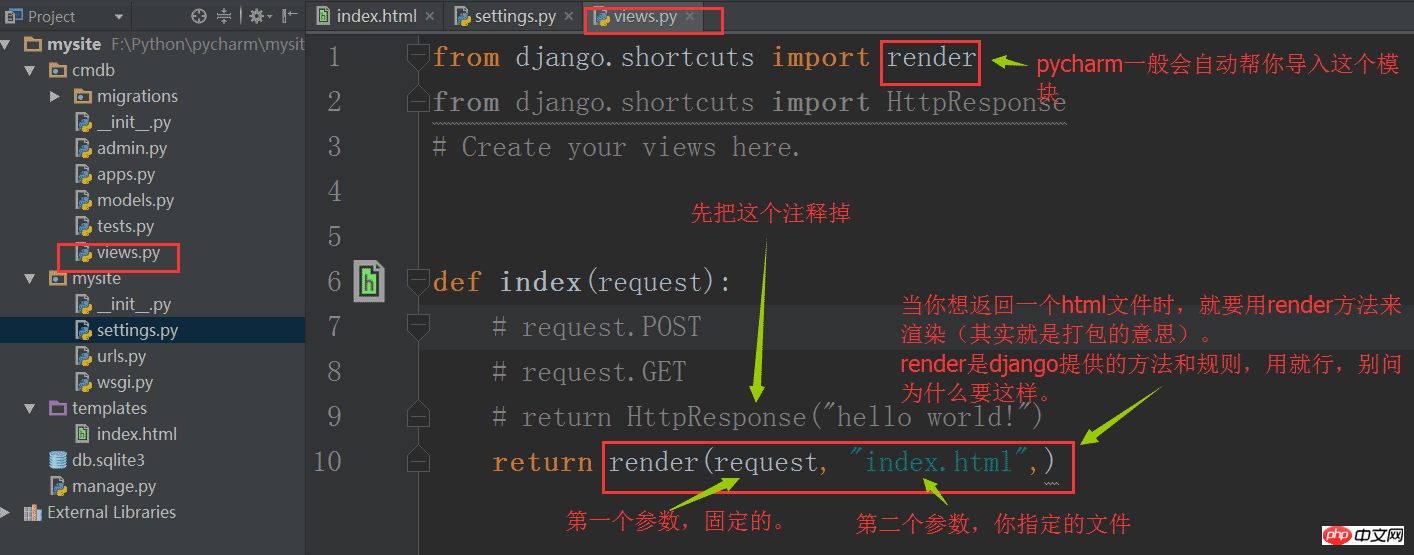
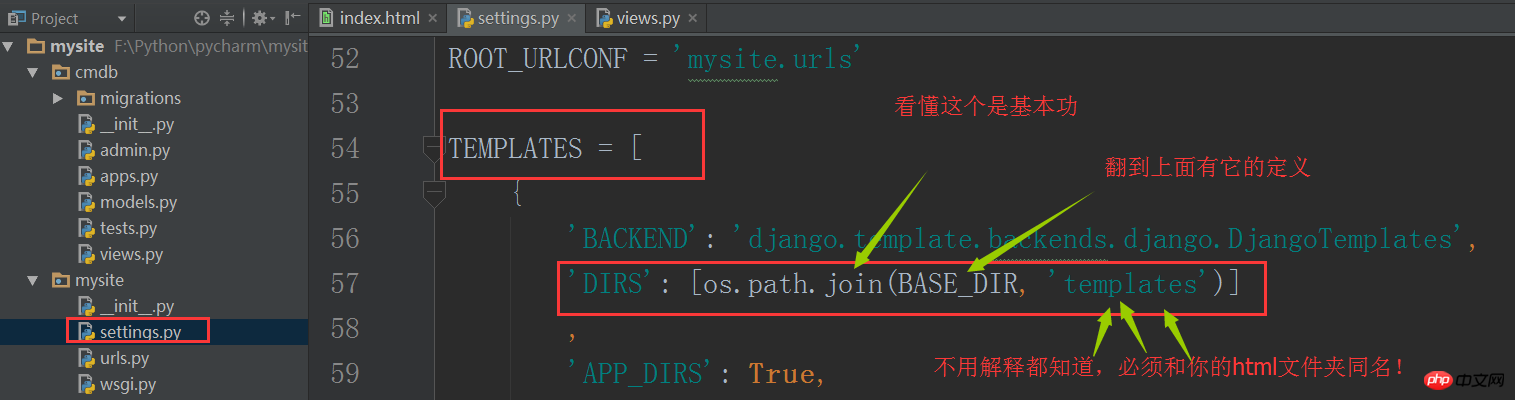
In order to let django know where our html files are, we need to modify the settings file accordingly. content. But by default, it works just fine and you don't need to modify it.
Next, we can restart the web service. Refresh the browser and you will see "hello world" with style.
Note: Here is a little trick. When the service is restarted frequently, the service may not be started due to the port not being released. Just modify the port and it will be OK.
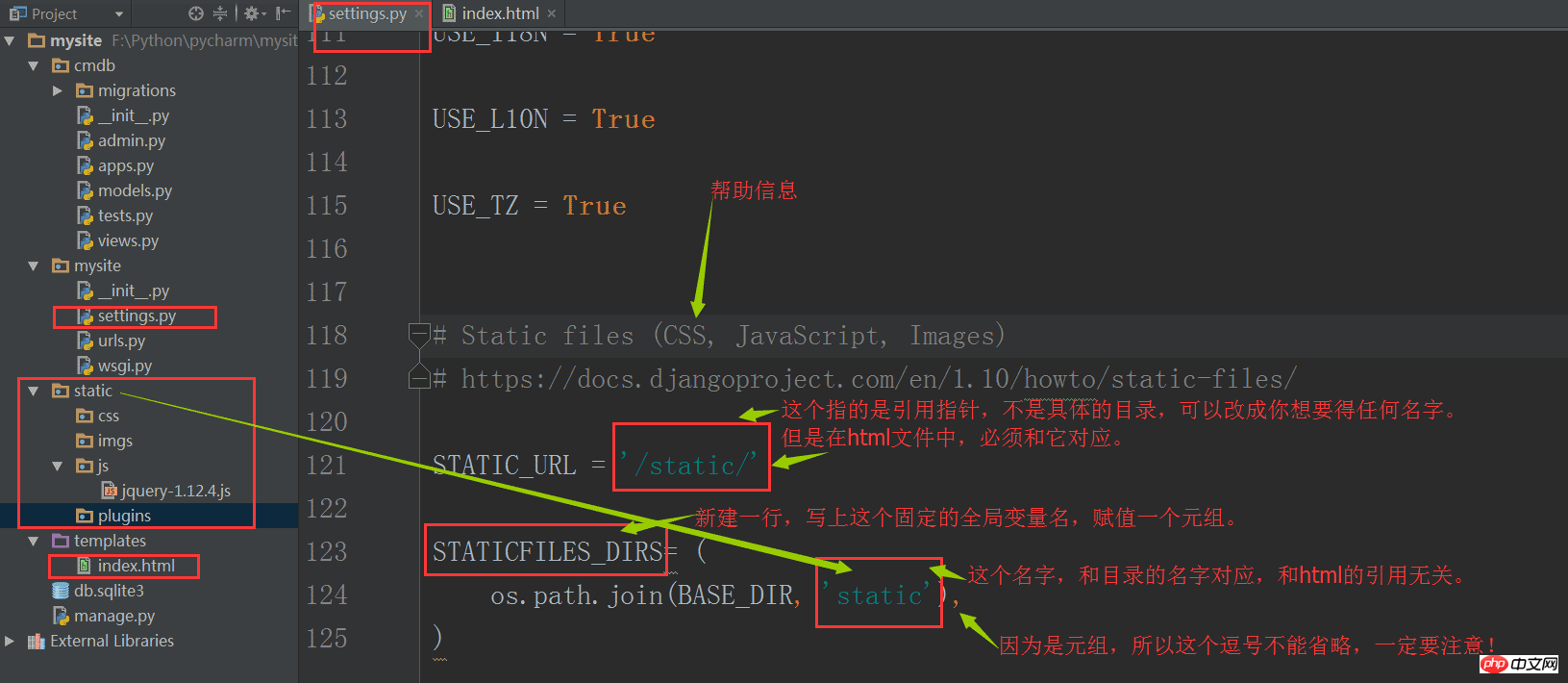
8. Use static files
We can already return html files to users, but it is not enough. The three major parts of the front end are html, css, js and various plug-ins. They are complete. It is a complete
page. In Django, static files are generally placed in the static directory. Next, create a new static directory in mysite.
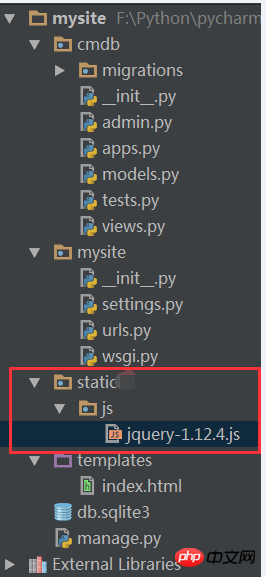
Your CSS, JS and various plug-ins can be placed in this directory.
In order for django to find this directory, settings still need to be configured:
Similarly, in the index.html file, the js file can be introduced:
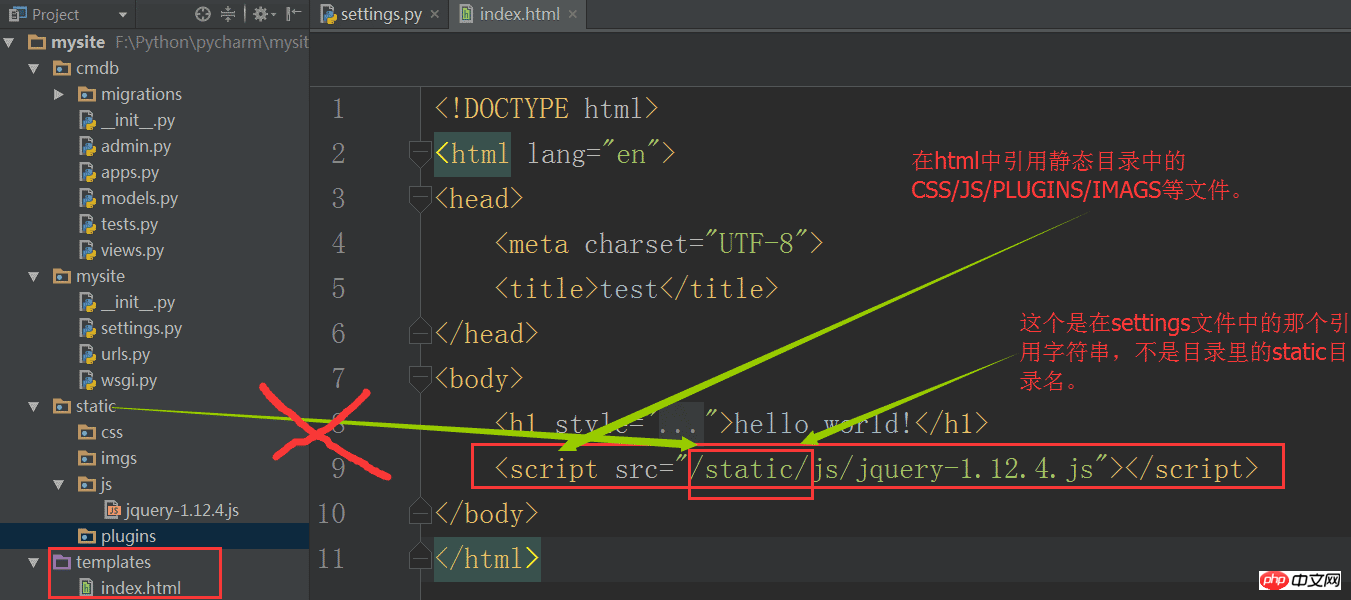
Restart the web service, refresh the browser, and view the results.
9. Receive data sent by the user
Above, we returned an html file with complete elements to the user's browser. But this is not enough because there is no dynamic interaction between the web server and the user.
Next we design a form to allow users to enter their username and password and submit it to the index URL, and the server will receive this data.
First modify the index.html file

and then modify the views.py file
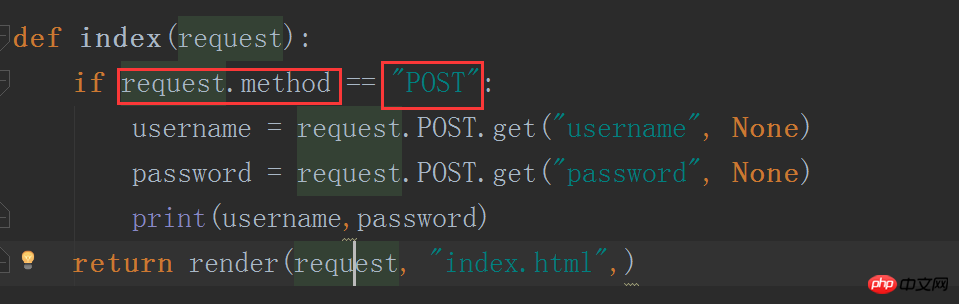
At this time , an error will occur when restarting the web service, because Django has a cross-site request protection mechanism, and we turn it off in the settings file.
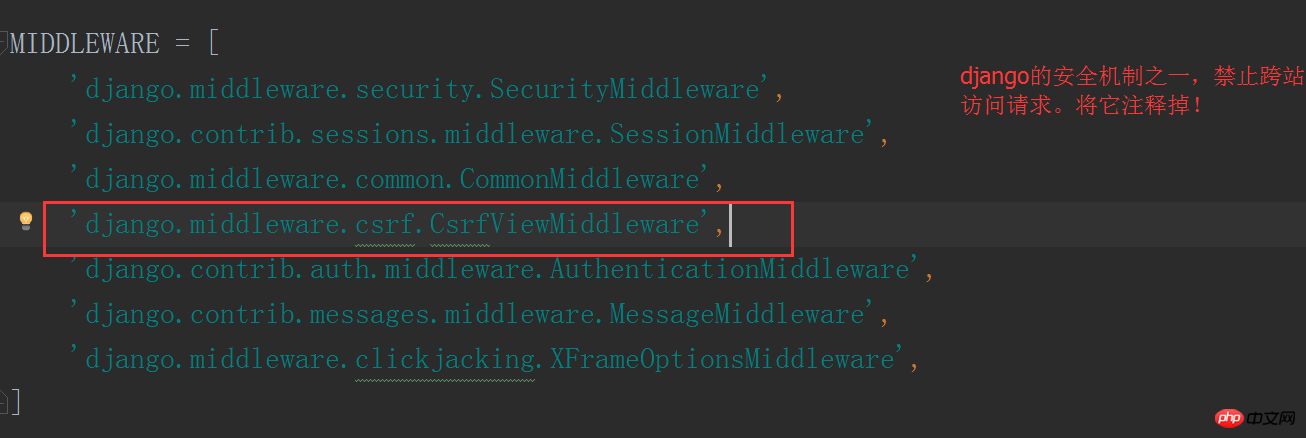
Enter the browser again and refresh the page:
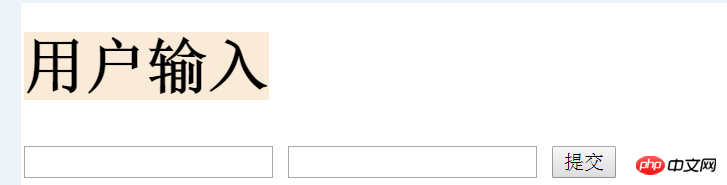
Enter something, and then we can see it in pycharm corresponding data.
10. Return to the dynamic page
We have received the user's data, but what is returned to the user is still a static page. Usually we will process it based on the user's data and then return it to the user.
At this time, django uses its own template language, similar to jinja2, and replaces the corresponding parts of the html based on the provided data. After getting started with the detailed syntax, learn more about it.
First transform the views.py file:
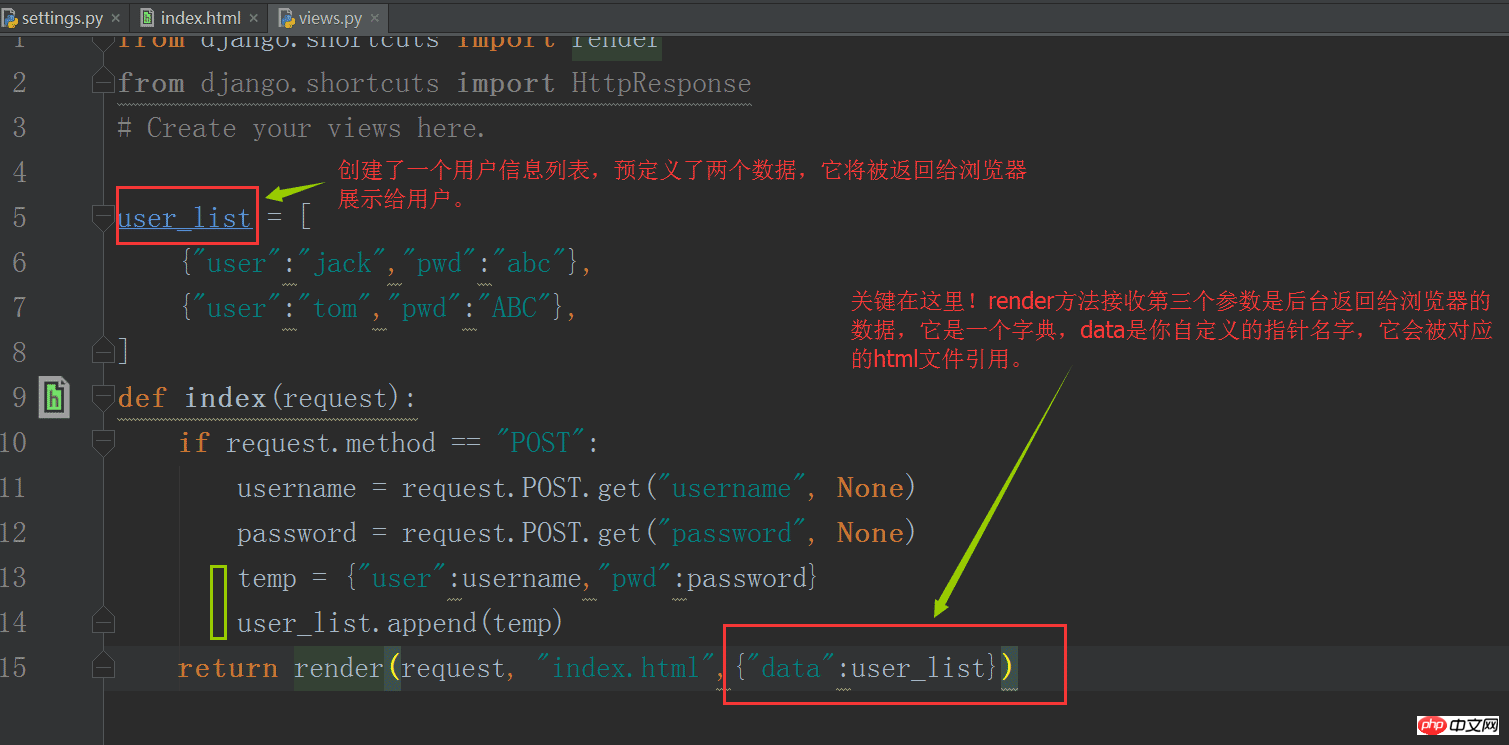
Then transform the index.html file:
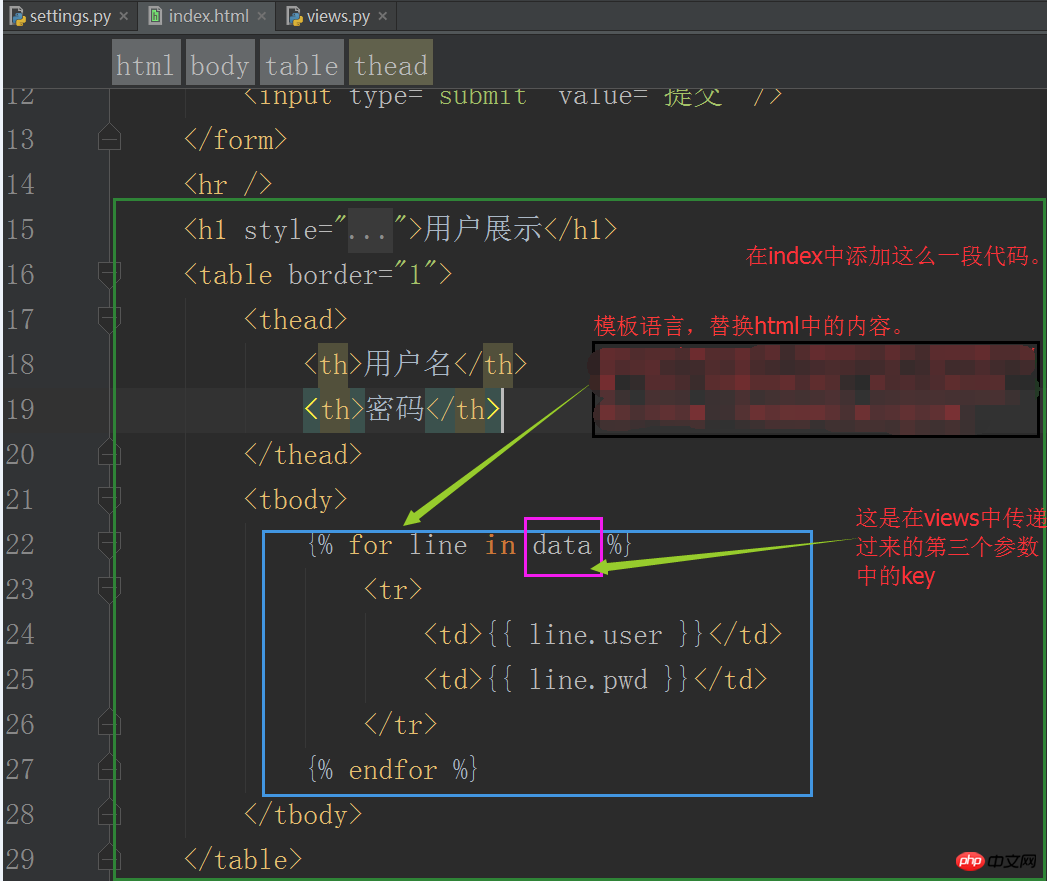
Restart the service and refresh the browser:
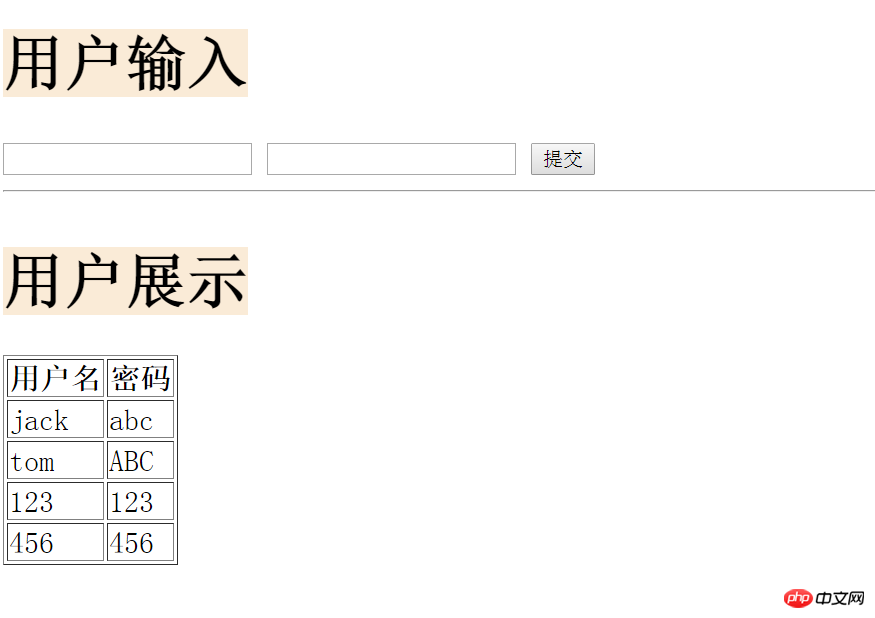
As you can see, we have obtained the data entered by the user in real time and displayed it on the user page in real time. This is good. interactive process.
11. Using the database
At this point in the process, Django’s MTV framework has basically surfaced, leaving only the final database part.
Although we interacted well with the user above, we did not save any data. Once the page is closed or the server is restarted, everything will return to the original state.
There is no doubt about using the database. Django operates the database through its own ORM framework and comes with its own lightweight sqlite3 database. Let’s take a look below:
First, register the app:
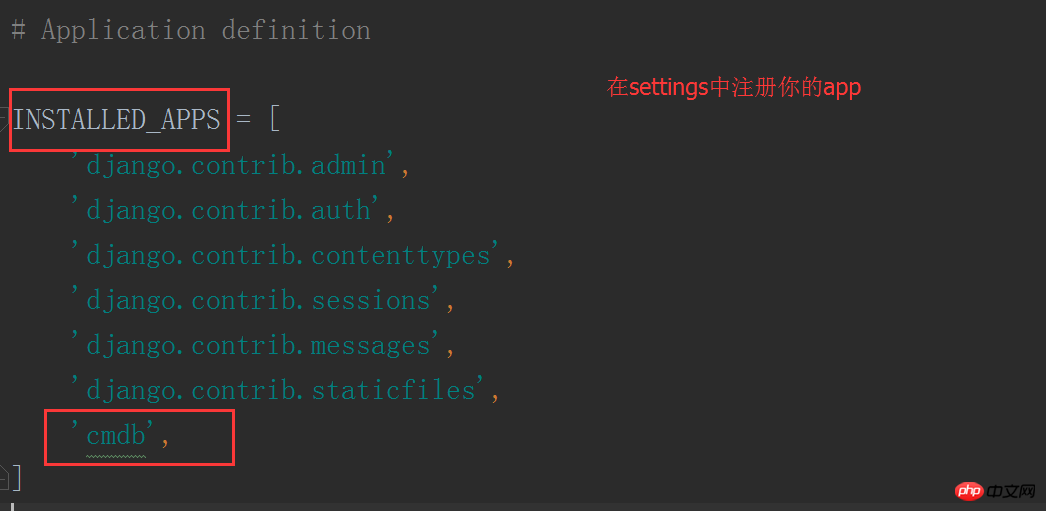
If you don’t register it, your database will not know which app to create a table for.
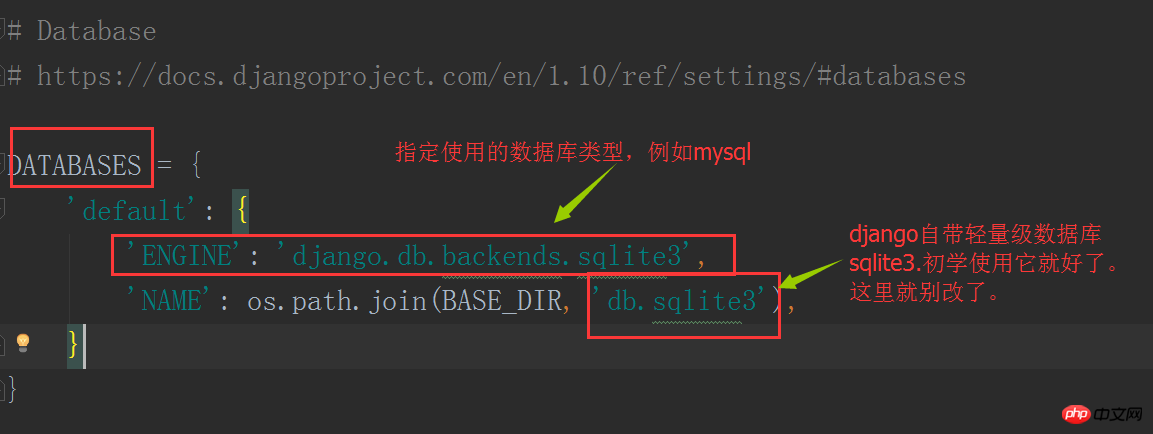
Then we configure the database-related parameters in settings. If you use the built-in sqlite, there is no need to modify it.
Then edit the models.py file, which is the M in MTV.
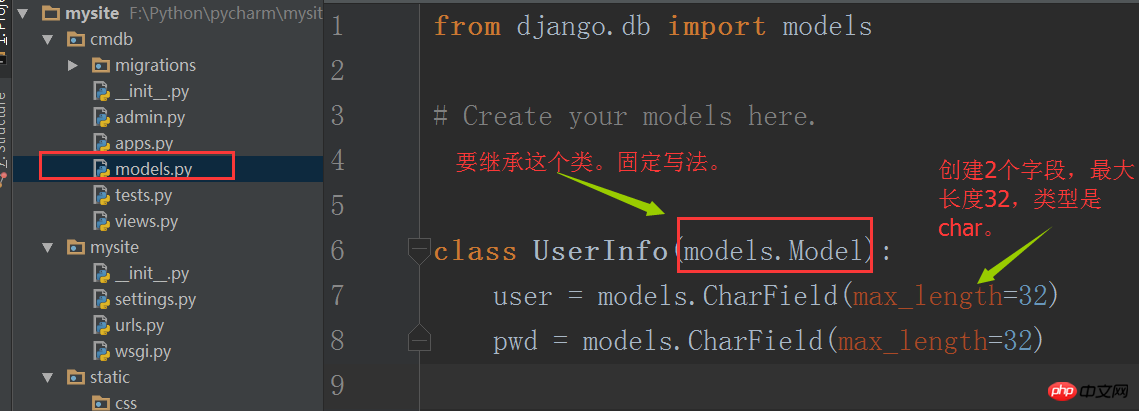
Here we create 2 fields to save the user's name and password respectively.
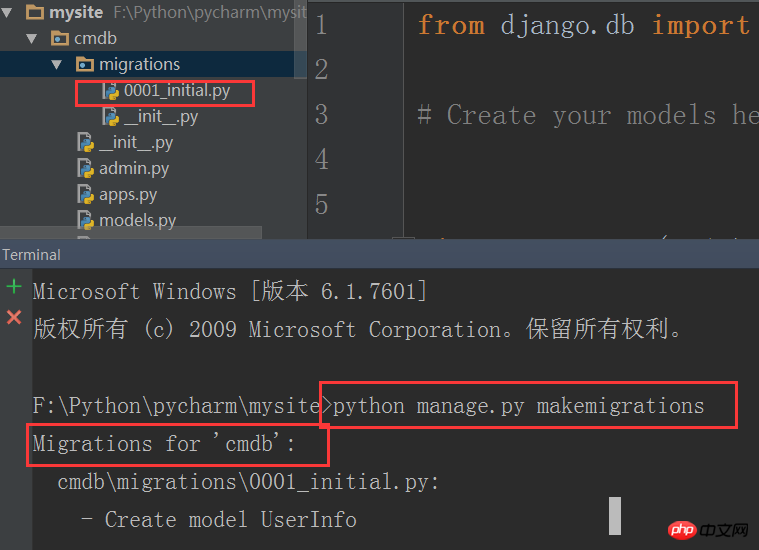
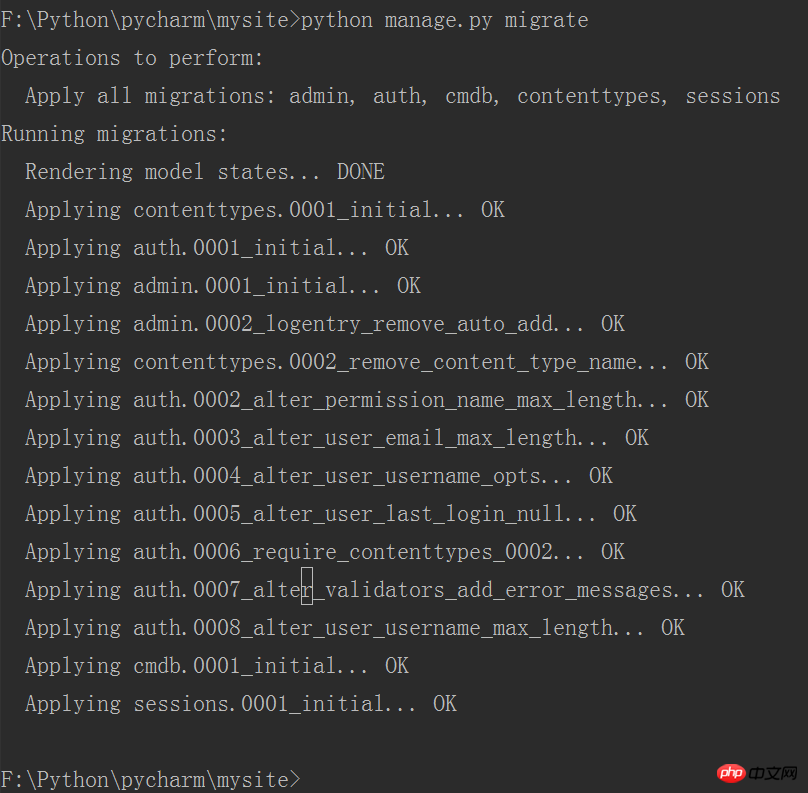
Next, we need to create the table of the database through the command in the terminal of pycharm. There are 2 commands, namely:
python manage.py makemigrations
Then enter the command: python manage.py migrate
Modify the business logic in views.py
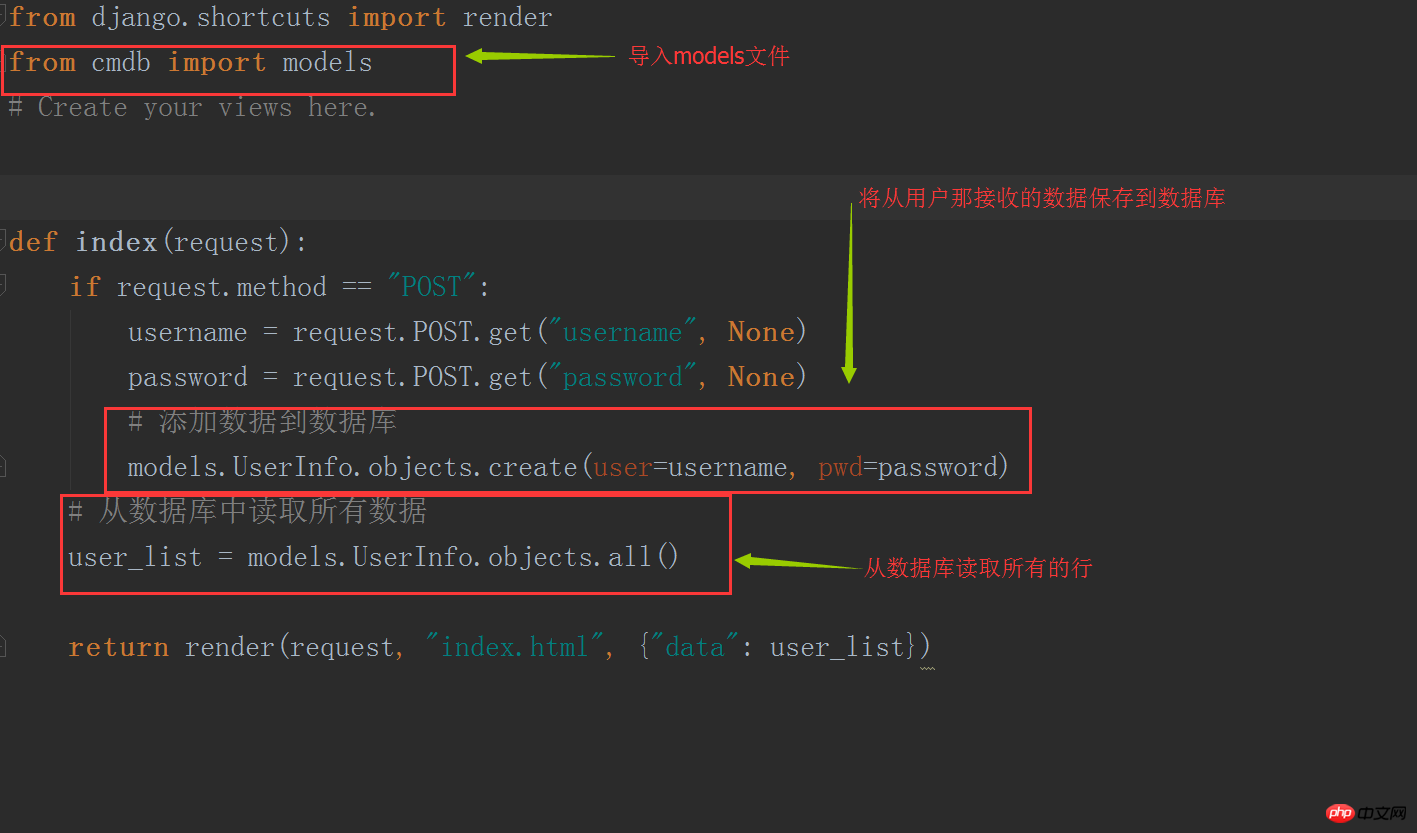
After restarting the web service, refresh the browser page, and the data interacted with the user will be saved. into the database. Data can be read from the database at any time and displayed on the page.
At this point, a Django project with complete elements and a clear main frame display is completed. It is actually very simple, right?
3. Summary of Django
As a necessary web framework for python, Django has powerful functions and comprehensive content, but it also means many restrictions and low flexibility. , poor modifiability, which means you can’t have your cake and eat it too. When we learn Django, we actually learn a software. We need to understand its basic principles, grasp its overall framework, and keep in mind some basic rules. The rest is to continue to delve into the details, and then practice makes perfect, and the amount of experience is a matter of it. There is no such thing as too advanced. Master the technology.
Suggestions on learning methods: When learning anything, don’t dive directly into the details. You should first understand its peripheral knowledge, look at its overall structure, then learn its basic content, and then study in depth. Polish your skills!
The whole article is complete. Please correct me if there are any mistakes. If you think it is good, please give it a like and support.
【Related Recommendations】
1. Special Recommendation: "php Programmer Toolbox" V0.1 version download
3. Video tutorial on the application of Python in data science
The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to the use tutorial of Django open source framework. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1381
1381
 52
52
 PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1.PHP is suitable for rapid development and maintenance of large-scale web applications. 2. Python dominates the field of data science and machine learning.
 How to train PyTorch model on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 03:03 PM
How to train PyTorch model on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 03:03 PM
Efficient training of PyTorch models on CentOS systems requires steps, and this article will provide detailed guides. 1. Environment preparation: Python and dependency installation: CentOS system usually preinstalls Python, but the version may be older. It is recommended to use yum or dnf to install Python 3 and upgrade pip: sudoyumupdatepython3 (or sudodnfupdatepython3), pip3install--upgradepip. CUDA and cuDNN (GPU acceleration): If you use NVIDIAGPU, you need to install CUDATool
 Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Docker uses Linux kernel features to provide an efficient and isolated application running environment. Its working principle is as follows: 1. The mirror is used as a read-only template, which contains everything you need to run the application; 2. The Union File System (UnionFS) stacks multiple file systems, only storing the differences, saving space and speeding up; 3. The daemon manages the mirrors and containers, and the client uses them for interaction; 4. Namespaces and cgroups implement container isolation and resource limitations; 5. Multiple network modes support container interconnection. Only by understanding these core concepts can you better utilize Docker.
 How is the GPU support for PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:48 PM
How is the GPU support for PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:48 PM
Enable PyTorch GPU acceleration on CentOS system requires the installation of CUDA, cuDNN and GPU versions of PyTorch. The following steps will guide you through the process: CUDA and cuDNN installation determine CUDA version compatibility: Use the nvidia-smi command to view the CUDA version supported by your NVIDIA graphics card. For example, your MX450 graphics card may support CUDA11.1 or higher. Download and install CUDAToolkit: Visit the official website of NVIDIACUDAToolkit and download and install the corresponding version according to the highest CUDA version supported by your graphics card. Install cuDNN library:
 Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and Resources
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and Resources
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python and JavaScript have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of community, libraries and resources. 1) The Python community is friendly and suitable for beginners, but the front-end development resources are not as rich as JavaScript. 2) Python is powerful in data science and machine learning libraries, while JavaScript is better in front-end development libraries and frameworks. 3) Both have rich learning resources, but Python is suitable for starting with official documents, while JavaScript is better with MDNWebDocs. The choice should be based on project needs and personal interests.
 How to choose the PyTorch version under CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:51 PM
How to choose the PyTorch version under CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:51 PM
When selecting a PyTorch version under CentOS, the following key factors need to be considered: 1. CUDA version compatibility GPU support: If you have NVIDIA GPU and want to utilize GPU acceleration, you need to choose PyTorch that supports the corresponding CUDA version. You can view the CUDA version supported by running the nvidia-smi command. CPU version: If you don't have a GPU or don't want to use a GPU, you can choose a CPU version of PyTorch. 2. Python version PyTorch
 MiniOpen Centos compatibility
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:45 PM
MiniOpen Centos compatibility
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:45 PM
MinIO Object Storage: High-performance deployment under CentOS system MinIO is a high-performance, distributed object storage system developed based on the Go language, compatible with AmazonS3. It supports a variety of client languages, including Java, Python, JavaScript, and Go. This article will briefly introduce the installation and compatibility of MinIO on CentOS systems. CentOS version compatibility MinIO has been verified on multiple CentOS versions, including but not limited to: CentOS7.9: Provides a complete installation guide covering cluster configuration, environment preparation, configuration file settings, disk partitioning, and MinI
 How to install nginx in centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:06 PM
How to install nginx in centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:06 PM
CentOS Installing Nginx requires following the following steps: Installing dependencies such as development tools, pcre-devel, and openssl-devel. Download the Nginx source code package, unzip it and compile and install it, and specify the installation path as /usr/local/nginx. Create Nginx users and user groups and set permissions. Modify the configuration file nginx.conf, and configure the listening port and domain name/IP address. Start the Nginx service. Common errors need to be paid attention to, such as dependency issues, port conflicts, and configuration file errors. Performance optimization needs to be adjusted according to the specific situation, such as turning on cache and adjusting the number of worker processes.



