
1) Need to be in AndroidManifest.xml It is stated in the file that HardwareAccelerate needs to be used, which can be refined to the Activity level. If the View is not needed, it can be declared not to use acceleration, but it needs to be done in the code, as follows:
a. If you want to declare that the entire application must be accelerated:
< application ... android:hardwareAccelerated ="true">
b. If you want to declare it in Activity, then:
<activity
... android:hardwareAccelerated="true" >,
还可以更细化到Window, getWindow.setFlags( WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED);
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED,c. If the application or activity has declared that hardware acceleration is required, but for some reasons (such as power saving?), some Views do not require hardware acceleration,
view. setLayerType(View.LAYER_TYPE_SOFTWARE, null);
2) It can be said that it is quite strange that you need to use
Generally speaking, after the above operations are completed, you can use the video tag to play the video. If you want to support full screen, you need to do a few operations:
1) Give the webview a WebChromeClient object. This WebChromeClient object needs to implement the onShowCustomView and onHideCustomView methods. Here is an implementation example:
@Override
public void onShowCustomView(View
view, CustomViewCallback callback) {
if (myCallback != null)
{
myCallback.onCustomViewHidden();
myCallback = null ;
return;
}
long id
= Thread.currentThread().getId();
WrtLog. v("WidgetChromeClient", "rong
debug in showCustomView Ex: " + id);
ViewGroup parent = (ViewGroup) mWebView.getParent();
String s = parent.getClass().getName();
WrtLog. v("WidgetChromeClient", "rong
debug Ex: " + s);
parent.removeView( mWebView);
parent.addView(view);
myView =
view;
myCallback =
callback;
chromeClient = this ;
}
private View myView = null;
private CustomViewCallback myCallback = null;
public void onHideCustomView()
{
long id
= Thread.currentThread().getId();
WrtLog. v("WidgetChromeClient", "rong
debug in hideCustom Ex: " + id);
if (myView != null)
{
if (myCallback != null)
{
myCallback.onCustomViewHidden();
myCallback = null ;
}
ViewGroup parent = (ViewGroup) myView.getParent();
parent.removeView( myView);
parent.addView( mWebView);
myView = null;
}
} Okay, this way of writing is different from many ways of writing on the Internet. Most of the examples on the Internet are that the view received by the onShowCustomView method is a VideoView object, and here it is a VideoView object that cannot be found HTML5## The VideoSurfaceView subclass of #VideoFullScreen, and this subclass is still a private subclass and cannot be accessed from the outside. There is no HTML5VideoFullScreen class in android.jar. If you want to access this class in the application, you need to add the package
In fact, no matter what version it is, the general meaning of this code is that in the onShowCustomView method, put the obtained view at the top of the current Activity, and in onHideCustomView, hide the previous view OrDelete, put back the originally covered webview, and end the playback, otherwise it will report to MediaPlayer IllegalStatusException, and it is still a Native method, so there is no way to debug it.
You can download it, use eclipse to import the project, and put the samplevideoPut it in the root directory of sdcard, which is /mnt/sdcard from a system perspective.
The effect is as shown:
Before full screen:
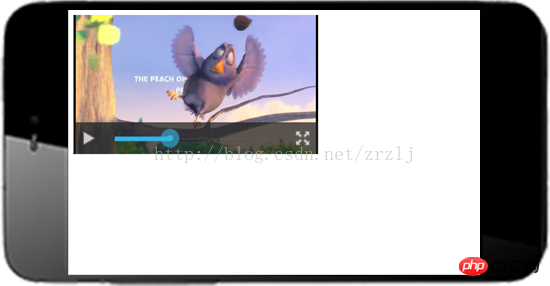
## After full screen:
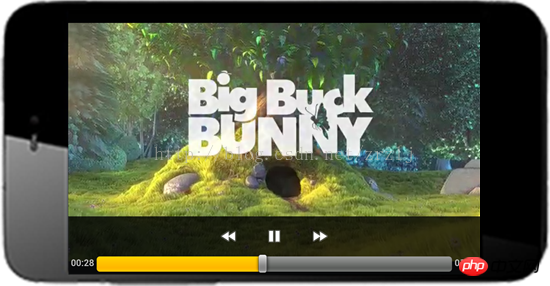
##
The above is the detailed content of How to make Android WebView support full-screen playback of HTML5 Video (picture). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




