 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 Detailed introduction on how to implement C++ operation of Mysql database under Linux
Detailed introduction on how to implement C++ operation of Mysql database under Linux
Detailed introduction on how to implement C++ operation of Mysql database under Linux
Due to work, I need to take a week to study C/C++ methods of accessing various databases, and plan to encapsulate a set of database operation classes. Now I will present the simplest part: Access MySQL database under Linux.
If you want to write a project in C++, a database is a must, so in the past two days, I have learned how to operate the MySQL database in C++. There are no tutorials, just the knowledge I searched online. Here is a summary.
There are two ways to connect to the MySQL database: the first is to use ADO connection, but this is only suitable for Windows platforms; the second is touse MySQLyour own C APIFunctionConnect to database. I develop under the Linux platform, so I use the second method. There are many API functions, but only a few are commonly used, and I only use a few of them.
API function
1.mysql_real_connect()
Connect a mysql server
MYSQL *mysql_real_connect (MYSQL *mysql, const char *host, const char *user, const char *passwd, const char *db, unsigned int port, const char *unix_socket, unsigned long client_flag)
If the connection is successful, return the MYSQL* connection handle. If the connection fails, NULL is returned. For a successful connection, the return value is the same as the value of the first parameter
2.mysql_query()
Execute the specified "NULL-terminated string "'s SQL query
returns a result table. Assuming the query is successful, you can call mysql_num_rows() to see how many rows are returned corresponding to the SELECT statement. Or call mysql_affected_rows() to see how many rows are affected by the statement corresponding to DELETE, INSERT, REPLACE or UPDATE.
3.mysql_store_result()
MYSQL_RES *mysql_store_result(MYSQL *mysql)
Retrieve the complete result set to the client. The most common way for clients to process result sets is by calling mysql_store_result(), which retrieves the entire result set at once. This function gets all the rows returned by the query from the server and saves them on the client. For every query (SELECT, SHOW, DESCRIBE, EXPLAIN, CHECK TABLE, etc.) that successfully retrieves data, mysql_store_result() or mysql_use_result() must be called. For other queries, there is no need to call mysql_store_result() or mysql_use_result(), but if mysql_store_result() is called in any case, it will not cause any harm or performance degradation.
4.mysql_num_rows()
Returns the number of rows in the result set.
5.mysql_num_fields()
Returns the number of fields in the result set, or false if failed.
MYSQL_FIELD* mysql_fetch_field(MYSQL_RES *result);
Get the type of the next table field and return NULL at the end.
7.mysql_fetch_row()
MYSQL_ROW mysql_fetch_row(MYSQL_RES *result);
Get the next row from the result set and successfully return an array with a value greater than 0.
8.mysql_fetch_field_direct()
MYSQL_FIELD* mysql_fetch_field_direct(MYSQL_RES *result, int i);
Given the field number, return the type of the table field, and return NULL at the end.
Simple student information management code
I can’t remember it just by looking at it, so I used these functions to write a student information management interface. Alas, this time last yearC Language course design, I didn’t know how to use a database at that time, and it was all written in files. I regretted it when I found out too late. . . . The following is the code:
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: student.cpp
> Author: Tanswer_
> Mail: 98duxm@gmail.com
> Created Time: 2017年05月28日 星期日 16时50分34秒
************************************************************************/
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
#include <algorithm>
#include <sstream>
#include <mysql/mysql.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
MYSQL mysql;
MYSQL_ROW row;
MYSQL_FIELD* field = NULL;
MYSQL_RES* result;
string IntToStr(int num)
{
stringstream ss;
ss.clear();
ss << num;
return ss.str();
}
void Add()
{
string fname,fsex,ftel,faddr;
int fage;
char choice;
do
{
┊ cout << "请依次输入以下信息:" << endl;
┊ cout << "\nName: ";cin >> fname;
┊ cout << "\nSex: ";cin >> fsex;
┊ cout << "\nAge: "; cin >> fage;
┊ cout << "\nTel: "; cin >> ftel;
┊ cout << "\nAddr: "; cin >> faddr;
┊ string sql = "INSERT INTO Infor (name,sex,tel,addr,age) values('"+fname+"','"+fsex+"','"+ftel+"','"+faddr+"', "+IntToStr(fage)+");";
┊ //string sql = "INSERT INTO Infor (name,sex,age,tel,addr) values('小红','女',18,'13333333333', '陕西省西安市雁塔区');";
┊ mysql_query(&mysql,sql.c_str());
┊ ┊
┊ cout << "是否继续添加(y/n)?: ";
┊ cin >> choice;
}while(choice == 'y');
}
void Select()
{
int id;
cout << "请输入要查询学生的学号: ";
cin >> id;
string sql = "SELECT * FROM Infor WHERE id = "+IntToStr(id)+";";
mysql_query(&mysql,sql.c_str());
result = mysql_store_result(&mysql);
if(result == NULL)
┊ cout << "fail\n";
for(int i=0; i<mysql_num_fields(result); i++)
{
┊ field = mysql_fetch_field_direct(result,i);
┊ cout << field->name << "\t\t";
}
cout << endl;
row = mysql_fetch_row(result);
while(row != NULL)
{
┊ for(int i=0; i<mysql_num_fields(result); i++)
┊ {
┊ ┊ cout << row[i] << "\t\t";
┊ }
┊ cout << endl;
┊ row = mysql_fetch_row(result);
}
}
void Update()
{
int id;
char choice;
string newaddr;
┊ cout << "请输入要修改同学的学号: ";
┊ cin >> id;
┊ cout << endl << "请输入修改后的地址: ";
┊ cin >> newaddr;
┊ string sql = "UPDATE Infor SET addr = '"+newaddr+"'WHERE id= "+IntToStr(id)+"; ";
┊ mysql_query(&mysql,sql.c_str());
┊
}
int main()
{
char choice[5];
mysql_init(&mysql);
/*连接数据库*/
if(!mysql_real_connect(&mysql,"localhost","root","dxm242012","Student",0,NULL,0))
{
┊ cout << "connect fial\n";
┊ return -1;
}
while(atoi(choice) != 'q')
{
┊ sleep(4);
┊ system("clear");
┊ cout << "1.添加学生信息" << endl;
┊ cout << "2.查询学生信息" << endl;
┊ cout << "3.修改学生信息" << endl;
┊ cin >> choice;
┊ cout << choice << endl;
┊ switch(atoi(choice))
┊ {
┊ ┊ case 1:
┊ ┊ ┊ Add();
┊ ┊ ┊ break;
┊ ┊ case 2:
┊ ┊ ┊ Select();
┊ ┊ ┊ break;
┊ ┊ case 3:
┊ ┊ ┊ Update();
┊ ┊ ┊ break;
┊ ┊ default:
┊ ┊ ┊ break;
┊ }
}
mysql_close(&mysql);
return 0;
}C++ encapsulation of MyDB class
Later, these functions were simply encapsulated for easy use in the future.
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: myDB.h
> Author: Tanswer_
> Mail: 98duxm@gmail.com
> Created Time: 2017年05月28日 星期日 22时26分22秒
************************************************************************/
#ifndef _MYDB_H
#define _MYDB_H
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <mysql/mysql.h>
using namespace std;
class MyDB
{
public:
MyDB();
~MyDB();
bool InitDB(string host,string user,string pwd,string dbname);
bool ExeSQL(string sql);
private:
MYSQL* mysql;
MYSQL* mysql;
MYSQL_ROW row;
MYSQL_RES* result;
MYSQL_FIELD* field;
};
#endif
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: myDB.cpp
> Author: Tanswer_
> Mail: 98duxm@gmail.com
> Created Time: 2017年05月28日 星期日 22时27分18秒
************************************************************************/
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
#include <algorithm>
#include <mysql/mysql.h>
#include "myDB.h"
using namespace std;
MyDB::MyDB()
{
mysql = mysql_init(NULL);
if(mysql == NULL)
{
┊ cout << "Error: " << mysql_error(mysql);
┊ exit(-1);
}
}
MyDB::~MyDB()
{
if(!mysql)
{
┊ mysql_close(mysql);
}
}
bool MyDB::InitDB(string host,string user,string pwd,string dbname)
{
/*连接数据库*/
if(!mysql_real_connect(mysql,host.c_str(),user.c_str(),pwd.c_str(),dbname.c_str(),0,NULL,0))
{
┊ cout << "connect fial: " << mysql_error(mysql);
┊ exit(-1);
}
return true;
}
bool MyDB::ExeSQL(string sql)
{
/*执行失败*/
if(mysql_query(mysql,sql.c_str()))
{
┊ cout << "query fail: " << mysql_error(mysql);
┊ exit(1);
}
else
{
┊ /*获取结果集*/
┊ result = mysql_store_result(mysql);
┊ int fieldnum = mysql_num_fields(result);
┊ for(int i=0; i<fieldnum; i++)
┊ {
┊ ┊ row = mysql_fetch_row(result);
┊ ┊ if(row <= 0)
┊ ┊ ┊ break;
┊ ┊ for(int j=0; j<fieldnum; j++)
┊ ┊ {
┊ ┊ ┊ cout << row[j] << "\t\t";
┊ ┊ }
┊ ┊ cout << endl;
┊ }
┊ mysql_free_result(result);
}
return true;
}
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: main.cpp
> Author: Tanswer_
> Mail: 98duxm@gmail.com
> Created Time: 2017年05月28日 星期日 22时53分43秒
************************************************************************/
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
#include <algorithm>
#include <mysql/mysql.h>
#include "myDB.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
MyDB db;
db.InitDB("localhost","root","xxxxxx","Student");
db.ExeSQL("SELECT * FROM Infor;");
return 0;
}The following are the running results:
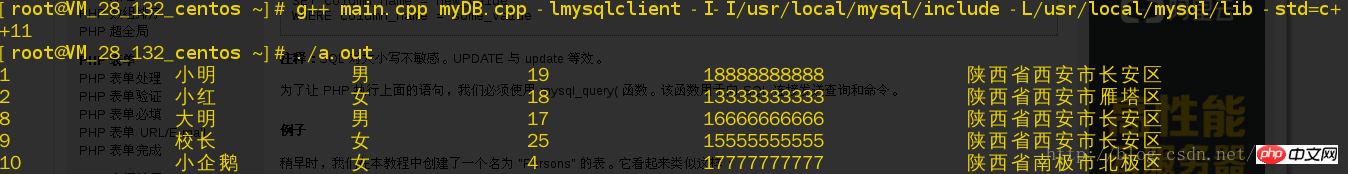
The following are the problems encountered:
1. Error during compilation
There is no such file or directory
#include<mysql/mysql.h> ^
Compilation interrupted.
Solution: In addition to mysql-client and mysql-server, installed mysql-devel, and then the problem was solved.
2. Customized variablesA problem occurs when passing in the sql statement
在网上查找到这样一种格式,
string sql = "INSERT INTO Infor (name,sex,tel,addr,age) values('"+fname+"','"+fsex+"','"+ftel+"','"+faddr+"', "+IntToStr(fage)+");";
然后string类型的可以成功,整型的变量还是不行,我又写了个函数把int转为string。
string IntToStr(int num)
{
stringstream ss;
ss.clear();
ss << num;
return ss.str();
}The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction on how to implement C++ operation of Mysql database under Linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Why Use MySQL? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Why Use MySQL? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
MySQL is chosen for its performance, reliability, ease of use, and community support. 1.MySQL provides efficient data storage and retrieval functions, supporting multiple data types and advanced query operations. 2. Adopt client-server architecture and multiple storage engines to support transaction and query optimization. 3. Easy to use, supports a variety of operating systems and programming languages. 4. Have strong community support and provide rich resources and solutions.
 MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system, mainly used to store and retrieve data quickly and reliably. Its working principle includes client requests, query resolution, execution of queries and return results. Examples of usage include creating tables, inserting and querying data, and advanced features such as JOIN operations. Common errors involve SQL syntax, data types, and permissions, and optimization suggestions include the use of indexes, optimized queries, and partitioning of tables.
 Python vs. C : Applications and Use Cases Compared
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python vs. C : Applications and Use Cases Compared
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python is suitable for data science, web development and automation tasks, while C is suitable for system programming, game development and embedded systems. Python is known for its simplicity and powerful ecosystem, while C is known for its high performance and underlying control capabilities.
 How to view instance name of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
How to view instance name of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
There are three ways to view instance names in Oracle: use the "sqlplus" and "select instance_name from v$instance;" commands on the command line. Use the "show instance_name;" command in SQL*Plus. Check environment variables (ORACLE_SID on Linux) through the operating system's Task Manager, Oracle Enterprise Manager, or through the operating system.
 What is Linux actually good for?
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:20 AM
What is Linux actually good for?
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Linux is suitable for servers, development environments, and embedded systems. 1. As a server operating system, Linux is stable and efficient, and is often used to deploy high-concurrency applications. 2. As a development environment, Linux provides efficient command line tools and package management systems to improve development efficiency. 3. In embedded systems, Linux is lightweight and customizable, suitable for environments with limited resources.
 How to add, modify and delete MySQL data table field operation guide
Apr 11, 2025 pm 05:42 PM
How to add, modify and delete MySQL data table field operation guide
Apr 11, 2025 pm 05:42 PM
Field operation guide in MySQL: Add, modify, and delete fields. Add field: ALTER TABLE table_name ADD column_name data_type [NOT NULL] [DEFAULT default_value] [PRIMARY KEY] [AUTO_INCREMENT] Modify field: ALTER TABLE table_name MODIFY column_name data_type [NOT NULL] [DEFAULT default_value] [PRIMARY KEY]
 Solution to MySQL encounters 'Access denied for user' problem
Apr 11, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
Solution to MySQL encounters 'Access denied for user' problem
Apr 11, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
How to solve the MySQL "Access denied for user" error: 1. Check the user's permission to connect to the database; 2. Reset the password; 3. Allow remote connections; 4. Refresh permissions; 5. Check the database server configuration (bind-address, skip-grant-tables); 6. Check the firewall rules; 7. Restart the MySQL service. Tip: Make changes after backing up the database.
 MySQL's Place: Databases and Programming
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL's Place: Databases and Programming
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL's position in databases and programming is very important. It is an open source relational database management system that is widely used in various application scenarios. 1) MySQL provides efficient data storage, organization and retrieval functions, supporting Web, mobile and enterprise-level systems. 2) It uses a client-server architecture, supports multiple storage engines and index optimization. 3) Basic usages include creating tables and inserting data, and advanced usages involve multi-table JOINs and complex queries. 4) Frequently asked questions such as SQL syntax errors and performance issues can be debugged through the EXPLAIN command and slow query log. 5) Performance optimization methods include rational use of indexes, optimized query and use of caches. Best practices include using transactions and PreparedStatemen



