
The following editor will bring you a summary and detailed comparison of several methods of Java collection traversal. The editor thinks it’s pretty good, so I’ll share it with you now and give it as a reference. Let’s follow the editor to take a look at the general traversal method of collection classes, using iterators to iterate: Iterator it = list.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
Object obj = it.next();
}Map traversal method: 1. Traverse by getting all keys //Set
1. 10 recommended articles about traversal methods

Introduction: The following editor will bring you a summary and detailed comparison of several methods of java collection traversal. The editor thinks it’s pretty good, so I’ll share it with you now and give it as a reference. Let’s follow the editor to take a look at the general traversal method of collection classes, using iterators to iterate: Iterator it = list.iterator();while(it.hasNext()) { Object obj = ;it.ne...
2. 10 recommended articles about php next() function

Introduction: The user has multiple business cards and needs to switch left and right to view them. Switching down is the menu button. Here we need to slide in two places. We use the sliding component swiper provided by WeChat and use it in a nested manner. The first layer is the up and down sliding of the business card display and the menu button. The second layer is the left and right sliding of the business card display (supports mutual embedding. It can be used as a set, so you can use it with confidence). Vertical Adding it means sliding vertically, removing it means sliding left and right. The overall structure is as follows: The click event is bound to the data switching method because it needs to support multiple click switching. The initialization data is nextSli...
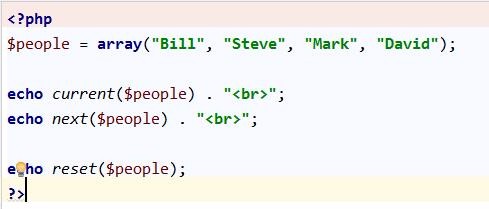
Introduction: The current() function in php returns the current element (unit, which is the first element of the array) in the array, and the next() function returns the internal The pointer points to the next element in the array and outputs the value of the element. The reset() function points the internal pointer to the first element in the array and outputs the value of the element. This article mainly introduces the current and Next and reset function usage, in the form of examples, the specific usage of the functions current, next and reset for array operations in PHP are described in detail. It has certain reference value for in-depth understanding of the usage of arrays. I hope it will be helpful to everyone's understanding of arrays
4. python iterator and itertools module
# #Introduction: In Python, the iterator protocol is to implement the __iter() method and next() method of the object. The former returns the object itself, and the latter returns the next element of the container. The object that implements these two methods is available. Iterable objects. Iterators are lazy and are only generated when used. This provides benefits for processing large amounts of data, unlike writing all data into memory at once. I wrote an iterator below, and you can see how it is used. The for loop can handle iterators written by yourself, objects that implement the iterator protocol, and you can use any iterator tool similar to the for loop. However, look at the output below, the second output is empty, why is this? When we use list, we can output the same message multiple times
##5.Detailed explanation of the use of jQuery's next() function

Introduction: php array: php array php array function sequence next - moves the internal pointer of the array to the position of the next element and returns the element value: next() Definition and usage next() function moves the pointer to the current element to The position of the next element and returns the value of that element. If the internal pointer has passed the last element of the array, the function returns false. Syntax next(array) Parameter Description array Required. Specifies the array to use. Note that next() and current() behave similarly, with one difference: the internal pointer is moved forward one position before returning the value. This means that it returns the value of the next array element and
# Introduction: PHP array function sequence next() - moves the internal pointer of the array to the position of the next element, and returns the element value. next() Definition and Usage The next() function moves the pointer to the current element to the position of the next element and returns the value of that element. If the internal pointer has exceeded the last element of the array
8. php iterator, php proxy_PHP tutorial

Introduction: php iterator, php proxy. php iterator, php implements Iterator, implements Iterator's current();next(); key(); valid();rewind(); 1 ? php 2 /* 3 *First define an array 4 *Define the first Position $position
9. Python Advanced Tutorial Loop Object
Introduction: This article mainly introduces Learn about the loop object of the python advanced tutorial. The loop object is an object that contains a next() method. The purpose of this method is to proceed to the next result. Friends who need it can refer to it
10. Use PHP iterator to implement a Fibonacci sequence
Introduction: Use PHP iterator to implement a Fibonacci sequence The Fibonacci sequence is usually implemented recursively, but of course there are other methods. Here you can learn and sell now. It is almost not difficult to use PHP iterator to implement a Fibonacci sequence. You just need to rewrite the next() method in the class. The comments have been written into the code and are quite easy to understand.
【Related Q&A recommendations】:
java - not to keep references to the objects from this iterator ?
Python3 interactive mode next(file) file.tell() OSError recovery problem?
jsp - The output result of rs.next() in java is inconsistent with the sql query result
javascript - Using the beforeEach hook of vue-router, next('/') error
javascript - Array.keys related issues
The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to next(). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




