 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 Wildcards and regular expressions under linux
Wildcards and regular expressions under linux
Wildcards and regular expressions under linux
Regular expressions match qualified strings in files. This article will introduce wildcards and regular expressions under Linux to you. Friends who need it can refer to it
Wildcard
* Any character , can be repeated multiple times
? Any character, repeated once
[] represents a character
Example: [a,b,c] represents any
wildcard in abc
Regular expression used to match file names
Regular expression is used to match qualified strings in files
ls find cp does not support regular expressions
But grep awk sed supports regular expressions
[root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# touch aa
[ root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# touch aab aabb
[root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# ll
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 May 16 19:47 aa
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 May 16 19:47 aab
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 May 16 19:47 aabb
[root @hadoop-bigdata01 test]# ls aa
aa
[root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# ls aa?
aab
[root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# ls aa*
aa aab aabb
Regular expression special characters
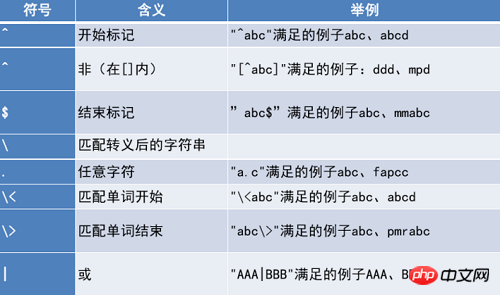
Regular expression matching range
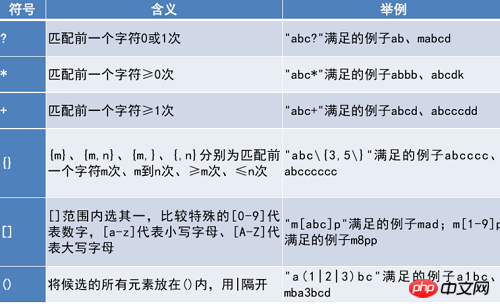
Regular expression Expression standard characters

Use regular expression
grep "1" /etc/passwd
Lines containing keyword 1, grep only needs to contain it , do not want wildcards, want to be completely consistent
##
[root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# grep "1" /etc/passwd bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin uucp:x:10:14:uucp:/var/spool/uucp:/sbin/nologin operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin games:x:12:100:games:/usr/games:/sbin/nologin gopher:x:13:30:gopher:/var/gopher:/sbin/nologin ftp:x:14:50:FTP User:/var/ftp:/sbin/nologin dbus:x:81:81:System message bus:/:/sbin/nologin usbmuxd:x:113:113:usbmuxd user:/:/sbin/nologin avahi-autoipd:x:170:170:Avahi IPv4LL Stack:/var/lib/avahi-autoipd:/sbin/nologin abrt:x:173:173::/etc/abrt:/sbin/nologin wang:x:501:501::/home/wang:/bin/bash grep 'root' /etc/passwd cat /etc/passwd | grep 'root'
##
grep '[0-9]' /etc/passwd
2. Match lines containing three consecutive numbers
grep '[0-9][0-9][0-9]' /etc/passwd 或者 grep ':[0-9][0-9][0-9]:' /etc/passwd
[root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# grep '[0-9][0-9][0-9]' /etc/passwd games:x:12:100:games:/usr/games:/sbin/nologin usbmuxd:x:113:113:usbmuxd user:/:/sbin/nologin rtkit:x:499:497:RealtimeKit:/proc:/sbin/nologin avahi-autoipd:x:170:170:Avahi IPv4LL Stack:/var/lib/avahi-autoipd:/sbin/nologin abrt:x:173:173::/etc/abrt:/sbin/nologin nfsnobody:x:65534:65534:Anonymous NFS User:/var/lib/nfs:/sbin/nologin saslauth:x:498:76:"Saslauthd user":/var/empty/saslauth:/sbin/nologin pulse:x:497:496:PulseAudio System Daemon:/var/run/pulse:/sbin/nologin liucheng:x:500:500::/home/liucheng:/bin/bash wang:x:501:501::/home/wang:/bin/bas
3. Match lines starting with r and ending with n
grep '^r.*n$' /etc/passwd .*代表所有 [root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# grep '^r.*n$' /etc/passwd rpc:x:32:32:Rpcbind Daemon:/var/cache/rpcbind:/sbin/nologin rtkit:x:499:497:RealtimeKit:/proc:/sbin/nologin rpcuser:x:29:29:RPC Service User:/var/lib/nfs:/sbin/nologin
4. Filter ifconfig, Intercept ip
grep -v represents reverse interception, which means to remove the lines with a certain keyword sed means replacement
[root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# ifconfig | grep 'inet addr:'
inet addr:192.168.126.191 Bcast:192.168.126.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
[root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]#
[root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# ifconfig | grep 'inet addr:' | grep -v '127.0.0.1'
inet addr:192.168.126.191 Bcast:192.168.126.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
[root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# ifconfig | grep 'inet addr:' | grep -v '127.0.0.1' | sed 's/inet addr://g'
192.168.126.191 Bcast:192.168.126.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
[root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# ifconfig | grep 'inet addr:' | grep -v '127.0.0.1' | sed 's/inet addr://g' | sed 's/Bcast.*//g'
192.168.126.191MisunderstandingThere is a misunderstanding here. I have thought about it for a long time. It is the difference between regular expressions and wildcards
We know that the wildcard * refers to Any character can be repeated multiple times. The * in the regular expression refers to matching the previous character >= 0 times.
These two are completely different. So how do I know whether the * I use is a wildcard or a regular expression? Formula
At first I fell into a misunderstanding. Look at the following series of commands
[root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# touch ac aac abc abbc [root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# ll total 0 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 May 16 19:55 aac -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 May 16 19:55 abbc -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 May 16 19:55 abc -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 May 16 19:55 ac [root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# ls | grep 'a*c' aac abbc abc ac [root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# ls | grep 'a.*c' aac abbc abc ac [root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# ls | grep '^a.*c' aac abbc abc ac [root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# ls | grep '^a*c' aac ac
Why grep 'a*c' and grep '^a*c$' The results will be different. I thought one was a wildcard and the other was a regular expression, because the four results displayed by a*c happened to be
. Doesn’t it match any number of characters?
is actually not the case.
The wildcard is used to match the file name.
The regular expression is to match the string that meets the conditions in the file.
Use grep after passing it to the pipe character. It's not matching file names, it's an operation on files, so it's completely a regular expression.
grep 'a*c' means matching a>=0, so it's OK as long as it contains c.
And grep '^a*c$' is also a regular pattern, which means it starts with a, and the second character matches a zero or more times, followed by the letter c
So only aac and ac meet the conditions
So look at this example
[root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# ls a aac abb abbc abc ac b bb c cb [root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# ls | grep 'a*b' abb abbc abc b bb cb
Here grep 'a*b' does not refer to a and b but a is repeated 0 or more times and then contains b
. The above are the wildcards and regular expressions under Linux introduced by the editor. I hope it will be helpful to you. If you have any questions, please leave me a message. , the editor will reply to everyone in time. I would also like to thank everyone for your support of the Script House website!
The above is the detailed content of Wildcards and regular expressions under linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1389
1389
 52
52
 How to view the docker process
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:48 AM
How to view the docker process
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:48 AM
Docker process viewing method: 1. Docker CLI command: docker ps; 2. Systemd CLI command: systemctl status docker; 3. Docker Compose CLI command: docker-compose ps; 4. Process Explorer (Windows); 5. /proc directory (Linux).
 What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
VS Code system requirements: Operating system: Windows 10 and above, macOS 10.12 and above, Linux distribution processor: minimum 1.6 GHz, recommended 2.0 GHz and above memory: minimum 512 MB, recommended 4 GB and above storage space: minimum 250 MB, recommended 1 GB and above other requirements: stable network connection, Xorg/Wayland (Linux)
 vscode cannot install extension
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:18 PM
vscode cannot install extension
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:18 PM
The reasons for the installation of VS Code extensions may be: network instability, insufficient permissions, system compatibility issues, VS Code version is too old, antivirus software or firewall interference. By checking network connections, permissions, log files, updating VS Code, disabling security software, and restarting VS Code or computers, you can gradually troubleshoot and resolve issues.
 Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
VS Code is available on Mac. It has powerful extensions, Git integration, terminal and debugger, and also offers a wealth of setup options. However, for particularly large projects or highly professional development, VS Code may have performance or functional limitations.
 What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
VS Code is the full name Visual Studio Code, which is a free and open source cross-platform code editor and development environment developed by Microsoft. It supports a wide range of programming languages and provides syntax highlighting, code automatic completion, code snippets and smart prompts to improve development efficiency. Through a rich extension ecosystem, users can add extensions to specific needs and languages, such as debuggers, code formatting tools, and Git integrations. VS Code also includes an intuitive debugger that helps quickly find and resolve bugs in your code.
 What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of Linux include: 1. Server operating system, 2. Embedded system, 3. Desktop operating system, 4. Development and testing environment. Linux excels in these areas, providing stability, security and efficient development tools.
 How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
Although Notepad cannot run Java code directly, it can be achieved by using other tools: using the command line compiler (javac) to generate a bytecode file (filename.class). Use the Java interpreter (java) to interpret bytecode, execute the code, and output the result.
 How to use VSCode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
How to use VSCode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is a cross-platform, open source and free code editor developed by Microsoft. It is known for its lightweight, scalability and support for a wide range of programming languages. To install VSCode, please visit the official website to download and run the installer. When using VSCode, you can create new projects, edit code, debug code, navigate projects, expand VSCode, and manage settings. VSCode is available for Windows, macOS, and Linux, supports multiple programming languages and provides various extensions through Marketplace. Its advantages include lightweight, scalability, extensive language support, rich features and version



