JS uses scroll to monitor resize image and text examples
This article mainly introduces you to the relevant information of using scroll to monitor resize in JS. The article introduces it in detail through the example code. It has certain reference and learning value for everyone's study or work. Friends who need it Let’s take a look below.
Preface
Everyone knows that the native resize event can only act on the defaultView, that is, the window, so what method should we use To monitor the size changes of other elements? The author recently discovered a magical method to indirectly implement the monitoring of the resize event through the scroll event. This article will analyze the principle and code implementation of this method.
Principle
First, let’s take a look at what the scroll event does.
The scroll event is fired when the document view or an element has been scrolled.
The scroll event is fired when the document view or an element has been scrolled.
That is to say, this event will be triggered when the element scrolls. So when will the element scroll? An element can be scrolled when it is larger than its parent element and the parent element allows it to scroll. In other words, elements that can be scrolled mean that parent and child elements are not sized the same, which is the core of this approach.
Then we need to make scrollLeft or scrollTop change when the element size changes, thereby triggering the scroll event and further knowing that its size has changed.
Listen for the element to become larger
When the element becomes larger, we can see more, and its internal scrollable area will slowly decrease Small, but this will not cause the position of the scroll bar to change, but when the element is large enough to make the scroll bar disappear, it will cause scrollLeft or scrollTop to become 0, so we know that the element has become larger, so we actually only need 1px To judge, the icon is as follows:

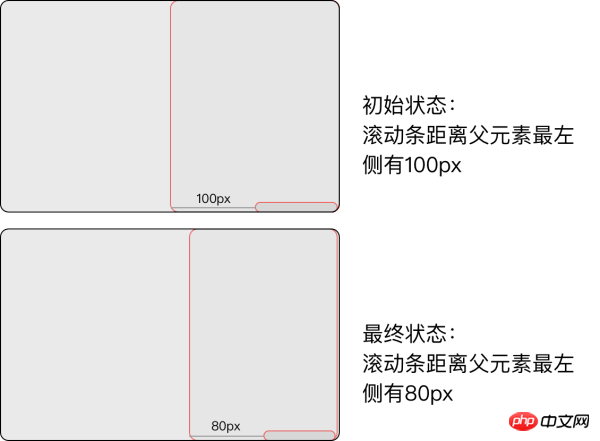
The listening element becomes smaller
When the element When it becomes smaller, the scrollable area will become larger, but the position of the scroll bar will not actually change. The approach taken here is to shrink the scrollable area and the parent element at a certain ratio, and let the parent element squeeze and scroll. area, thereby indirectly changing the size of the scroll bar scrollLeft or scrollTop. The text description may not be very clear. Let’s look at the picture below:
Through the above two methods, we can Get the resize event.
Implementation
First of all, in order not to affect the original element, we should create an element as large as the element to be monitored, and It performs related operations, and then we need two child elements to monitor the two situations of the element becoming larger and the element becoming smaller respectively. Therefore, the following HTML structure is constructed:
<p class="resize-triggers"> <p class="expand-trigger"> <p></p> </p> <p class="contract-trigger"></p> </p>
Their corresponding CSS is as follows:
##
.resize-triggers {
visibility: hidden;
opacity: 0;
}
.resize-triggers,
.resize-triggers > p,
.contract-trigger:before {
content: " ";
display: block;
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
height: 100%;
width: 100%;
overflow: hidden;
}
.resize-triggers > p {
overflow: auto;
}
.contract-triggers:before {
width: 200%;
height: 200%;
}. The width and height of the expand-triggers child element should remain 1px greater than the parent element, and both triggers should remain in the lower-right corner, so we can implement the following state reset function, And called during initialization and each scroll event:
/**
* 重置触发器
* @param element 要处理的元素
*/
const resetTrigger = function(element) {
const trigger = element.resizeTrigger; // 要重置的触发器
const expand = trigger.firstElementChild; // 第一个子元素,用来监听变大
const contract = trigger.lastElementChild; // 最后一个子元素,用来监听变小
const expandChild = expand.firstElementChild; // 第一个子元素的第一个子元素,用来监听变大
contract.scrollLeft = contract.scrollWidth; // 滚动到最右
contract.scrollTop = contract.scrollHeight; // 滚动到最下
expandChild.style.width = expand.offsetWidth + 1 + 'px'; // 保持宽度多1px
expandChild.style.height = expand.offsetHeight + 1 + 'px'; // 保持高度多1px
expand.scrollLeft = expand.scrollWidth; // 滚动到最右
expand.scrollTop = expand.scrollHeight; // 滚动到最右
};
/**
* 检测触发器状态
* @param element 要检查的元素
* @returns {boolean} 是否改变了大小
*/
const checkTriggers = function(element) {
// 宽度或高度不一致就返回true
return element.offsetWidth !== element.resizeLast.width || element.offsetHeight !== element.resizeLast.height;
};##
/**
* 添加大小更改监听
* @param element 要监听的元素
* @param fn 回调函数
*/
export const addResizeListener = function(element, fn) {
if (isServer) return; // 服务器端直接返回
if (attachEvent) { // 处理低版本ie
element.attachEvent('onresize', fn);
} else {
if (!element.resizeTrigger) { // 如果没有触发器
if (getComputedStyle(element).position === 'static') {
element.style.position = 'relative'; // 将static改为relative
}
createStyles();
element.resizeLast = {}; // 初始化触发器最后的状态
element.resizeListeners = []; // 初始化触发器的监听器
const resizeTrigger = element.resizeTrigger = document.createElement('p'); // 创建触发器
resizeTrigger.className = 'resize-triggers';
resizeTrigger.innerHTML = '<p class="expand-trigger"><p></p></p><p class="contract-trigger"></p>';
element.appendChild(resizeTrigger); // 添加触发器
resetTrigger(element); // 重置触发器
element.addEventListener('scroll', scrollListener, true); // 监听滚动事件
/* Listen for a css animation to detect element display/re-attach */
// 监听CSS动画来检测元素显示或者重新添加
if (animationStartEvent) { // 动画开始
resizeTrigger.addEventListener(animationStartEvent, function(event) { // 增加动画开始的事件监听
if (event.animationName === RESIZE_ANIMATION_NAME) { // 如果是大小改变事件
resetTrigger(element); // 重置触发器
}
});
}
}
element.resizeListeners.push(fn); // 加入该回调
}
};and the following function to remove the event
/**
* 移除大小改变的监听
* @param element 被监听的元素
* @param fn 对应的回调函数
*/
export const removeResizeListener = function(element, fn) {
if (attachEvent) { // 处理ie
element.detachEvent('onresize', fn);
} else {
element.resizeListeners.splice(element.resizeListeners.indexOf(fn), 1); // 移除对应的回调函数
if (!element.resizeListeners.length) { // 如果全部时间被移除
element.removeEventListener('scroll', scrollListener); // 移除滚动监听
element.resizeTrigger = !element.removeChild(element.resizeTrigger); // 移除对应的触发器,但保存下来
}
}
};OthersSome of the content is for optimization and does not affect the basics Functions, such as the distinction between server rendering and client rendering, special processing for IE, and solving bugs on chrome through opacity animation.
The above is the detailed content of JS uses scroll to monitor resize image and text examples. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 Monitor iframe scrolling behavior
Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:40 PM
Monitor iframe scrolling behavior
Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:40 PM
How to monitor the scrolling of an iframe requires specific code examples. When we use the iframe tag to embed other web pages in a web page, sometimes we need to perform some specific operations on the content in the iframe. One of the common needs is to listen for the scroll event of the iframe so that the corresponding code can be executed when the scroll occurs. The following will introduce how to use JavaScript to monitor the scrolling of an iframe, and provide specific code examples for reference. Get the iframe element First, we need
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
Introduction to the method of obtaining HTTP status code in JavaScript: In front-end development, we often need to deal with the interaction with the back-end interface, and HTTP status code is a very important part of it. Understanding and obtaining HTTP status codes helps us better handle the data returned by the interface. This article will introduce how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide specific code examples. 1. What is HTTP status code? HTTP status code means that when the browser initiates a request to the server, the service
 The relationship between the number of Oracle instances and database performance
Mar 08, 2024 am 09:27 AM
The relationship between the number of Oracle instances and database performance
Mar 08, 2024 am 09:27 AM
The relationship between the number of Oracle instances and database performance Oracle database is one of the well-known relational database management systems in the industry and is widely used in enterprise-level data storage and management. In Oracle database, instance is a very important concept. Instance refers to the running environment of Oracle database in memory. Each instance has an independent memory structure and background process, which is used to process user requests and manage database operations. The number of instances has an important impact on the performance and stability of Oracle database.






