 Backend Development
Backend Development
 C#.Net Tutorial
C#.Net Tutorial
 Summary of EF general data layer encapsulation class examples detailed explanation
Summary of EF general data layer encapsulation class examples detailed explanation
Summary of EF general data layer encapsulation class examples detailed explanation
Brief Talk about ORM
I remember the first time I came into contact with Ling to Sql in school four years ago. At that time, I instantly realized how convenient it was to not write SQL statements by hand. Later, I gradually came into contact with many ORM frameworks. Like EF, Dapper, Hibernate, ServiceStack.OrmLite , etc. Of course, each ORM has its own advantages and disadvantages. There are also many masters in the garden who have open sourced the ORM they wrote, such as SqlSugar, Chloe.ORM, CYQ.Data wait. Let’s not talk about the usage of these open source ORMs. I think they are commendable at least in terms of the spirit of open source. I have also downloaded the source code of these great masters to study.
The ultimate point of all ORM is convenience, which reduces repetitive work for programmers. Of course, some companies still use handwritten SQL to do it. I think it is a bit idle to use handwritten SQL for the entire project. It hurts. It’s not that I don’t recommend handwriting SQL, but I personally think that if the most basic additions, deletions, modifications and queries are written by hand, the test is not ability, but endurance. Some people say that the handwritten SQL method has strong controllability and high performance. What I want to say is that ORM can also do it. The key is how you use it.
The advantages of ORM are very obvious, and development is convenient, but perhaps it is also because of this advantage that many lazy programmers will gradually forget how to write SQL statements. I have met many programmer friends who use EF and write by hand. I no longer want to use sql, views, and stored procedures. I personally feel that handwritten sql is still necessary. Otherwise, one day when you see "exec xxxx" written in someone else's program, you will suddenly think, "Ah, I seem to have seen it somewhere...". So what I want to say is "You still have to take action when it's time to take action."
A brief talk about Entity Framework
Entity Framework is Microsoft’s ORM framework. With the continuous improvement and strengthening of Entity Framework, I believe that the proportion of usage is still higher compared to other ORMs. The ones I currently use the most are EF and Dapper. Indeed, it will be much more convenient to use EF during the development process. After all, EF has gone through so many years, both in terms of maturity and performance, etc. have improved a lot. There are also many developers who have provided extended functions for EF, such as entity framework extended etc. Moreover, as a .net developer, the project is very versatile, there is a lot of information, and Microsoft’s updates in this area are also very powerful. However, the EF Core that was just released also has some pitfalls. After all, it is still in its early stages. I believe it will get better and better in the future.
Entity Framework provides three development modes, code first, db first, and model first. The most commonly used one at present is code first. As for the simple use and differences of these three modes, you can refer to this article.
I have heard some friends say that the performance of EF is poor and the generated SQL statements are ugly. I think you should check the code or read more EF articles before saying this. You should first make sure that you are not digging a hole for yourself before you can accuse others of their faults. If you really feel that EF or other ORMs are uncomfortable to use, then write one yourself. I once used Dapper with my colleagues to extend a general ORM, which was out of the convenience of learning and use.
Entity Framework Universal Data Layer Class
The EF universal data layer parent class method is provided here. In fact, many people on the Internet have provided the EF universal data layer parent class method in their own projects, so here What is provided is not the optimal and best choice. It can only be said to be a universal class for everyone to learn and use. The specific code is as follows:
DbContextFactory DbContext Factory Class
public class DbContextFactory
{public DbContext GetDbContext()
{string key = typeof(DBContext.DbContextFactory).Name + "XJHDbContext";
DbContext dbContext = CallContext.GetData(key) as DbContext;if (dbContext == null)
{
dbContext = new XJHDbContext();
CallContext.SetData(key, dbContext);
}return dbContext;
}
}DbBase data layer general operation class
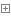

public class DbBase
{protected DbContext Db = new DbContextFactory().GetDbContext(); #region 自定义其他方法/// <summary>/// 执行存储过程或自定义sql语句--返回集合(自定义返回类型)/// </summary>/// <param name="sql"></param>/// <param name="parms"></param>/// <param name="cmdType"></param>/// <returns></returns>public List<TModel> Query<TModel>(string sql, List<SqlParameter> parms, CommandType cmdType = CommandType.Text)
{//存储过程(exec getActionUrlId @name,@ID)if (cmdType == CommandType.StoredProcedure)
{
StringBuilder paraNames = new StringBuilder();foreach (var sqlPara in parms)
{
paraNames.Append($" @{sqlPara},");
}
sql = paraNames.Length > 0 ? $"exec {sql} {paraNames.ToString().Trim(',')}" : $"exec {sql} ";
}var list = Db.Database.SqlQuery<TModel>(sql, parms.ToArray());var enityList = list.ToList();return enityList;
}/// <summary>/// 自定义语句和存储过程的增删改--返回影响的行数/// </summary>/// <param name="sql"></param>/// <param name="parms"></param>/// <param name="cmdType"></param>/// <returns></returns>public int Execute(string sql, List<SqlParameter> parms, CommandType cmdType = CommandType.Text)
{//存储过程(exec getActionUrlId @name,@ID)if (cmdType == CommandType.StoredProcedure)
{
StringBuilder paraNames = new StringBuilder();foreach (var sqlPara in parms)
{
paraNames.Append($" @{sqlPara},");
}
sql = paraNames.Length > 0 ?$"exec {sql} {paraNames.ToString().Trim(',')}" :
$"exec {sql} ";
}int ret = Db.Database.ExecuteSqlCommand(sql, parms.ToArray());return ret;
}#endregion 自定义其他方法}/// <summary>/// mssql数据库 数据层 父类/// </summary>/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>public class DbBase<T> : DbBase where T : class, new()
{#region INSERT/// <summary>/// 新增 实体/// </summary>/// <param name="model"></param>/// <returns></returns>public void Insert(T model)
{
Db.Set<T>().Add(model);
}/// <summary>/// 普通批量插入/// </summary>/// <param name="datas"></param>public void InsertRange(List<T> datas)
{
Db.Set<T>().AddRange(datas);
}#endregion INSERT#region DELETE/// <summary>/// 根据模型删除/// </summary>/// <param name="model">包含要删除id的对象</param>/// <returns></returns>public void Delete(T model)
{
Db.Set<T>().Attach(model);
Db.Set<T>().Remove(model);
}/// <summary>/// 删除/// </summary>/// <param name="whereLambda"></param>public void Delete(Expression<Func<T, bool>> whereLambda)
{
Db.Set<T>().Where(whereLambda).Delete();
}#endregion DELETE#region UPDATE/// <summary>/// 单个对象指定列修改/// </summary>/// <param name="model">要修改的实体对象</param>/// <param name="proNames">要修改的 属性 名称</param>/// <param name="isProUpdate"></param>/// <returns></returns>public void Update(T model, List<string> proNames, bool isProUpdate = true)
{//将 对象 添加到 EF中Db.Set<T>().Attach(model);var setEntry = ((IObjectContextAdapter)Db).ObjectContext.ObjectStateManager.GetObjectStateEntry(model);//指定列修改if (isProUpdate)
{foreach (string proName in proNames)
{
setEntry.SetModifiedProperty(proName);
}
}//忽略类修改else{
Type t = typeof(T);
List<PropertyInfo> proInfos = t.GetProperties(BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.Public).ToList();foreach (var item in proInfos)
{string proName = item.Name;if (proNames.Contains(proName))
{continue;
}
setEntry.SetModifiedProperty(proName);
}
}
}/// <summary>/// 单个对象修改/// </summary>/// <param name="model"></param>/// <returns></returns>public void Update(T model)
{
DbEntityEntry entry = Db.Entry<T>(model);
Db.Set<T>().Attach(model);
entry.State = EntityState.Modified;
}/// <summary>/// 批量修改/// </summary>/// <param name="whereLambda"></param>/// <param name="updateExpression"></param>public void Update(Expression<Func<T, bool>> whereLambda, Expression<Func<T, T>> updateExpression)
{
Db.Set<T>().Where(whereLambda).Update(updateExpression);
}/// <summary>/// 批量修改/// </summary>/// <param name="models"></param>/// <returns></returns>public void UpdateAll(List<T> models)
{foreach (var model in models)
{
DbEntityEntry entry = Db.Entry(model);
entry.State = EntityState.Modified;
}
}/// <summary>/// 批量统一修改/// </summary>/// <param name="model">要修改的实体对象</param>/// <param name="whereLambda">查询条件</param>/// <param name="modifiedProNames"></param>/// <returns></returns>public void Update(T model, Expression<Func<T, bool>> whereLambda, params string[] modifiedProNames)
{//查询要修改的数据List<T> listModifing = Db.Set<T>().Where(whereLambda).ToList();
Type t = typeof(T);
List<PropertyInfo> proInfos = t.GetProperties(BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.Public).ToList();
Dictionary<string, PropertyInfo> dictPros = new Dictionary<string, PropertyInfo>();
proInfos.ForEach(p =>{if (modifiedProNames.Contains(p.Name))
{
dictPros.Add(p.Name, p);
}
});if (dictPros.Count <= 0)
{throw new Exception("指定修改的字段名称有误或为空");
}foreach (var item in dictPros)
{
PropertyInfo proInfo = item.Value;//取出 要修改的值object newValue = proInfo.GetValue(model, null);//批量设置 要修改 对象的 属性foreach (T oModel in listModifing)
{//为 要修改的对象 的 要修改的属性 设置新的值proInfo.SetValue(oModel, newValue, null);
}
}
}#endregion UPDATE#region SELECT/// <summary>/// 根据主键查询/// </summary>/// <param name="id"></param>/// <returns></returns>public T FindById(dynamic id)
{return Db.Set<T>().Find(id);
}/// <summary>/// 获取默认一条数据,没有则为NULL/// </summary>/// <param name="whereLambda"></param>/// <returns></returns>public T FirstOrDefault(Expression<Func<T, bool>> whereLambda = null)
{if (whereLambda == null)
{return Db.Set<T>().FirstOrDefault();
}return Db.Set<T>().FirstOrDefault(whereLambda);
}/// <summary>/// 获取全部数据/// </summary>/// <returns></returns>public List<T> GetAll(string ordering = null)
{return ordering == null? Db.Set<T>().ToList()
: Db.Set<T>().OrderBy(ordering).ToList();
}/// <summary>/// 带条件查询获取数据/// </summary>/// <param name="whereLambda"></param>/// <param name="ordering"></param>/// <returns></returns>public List<T> GetAll(Expression<Func<T, bool>> whereLambda, string ordering = null)
{var iQueryable = Db.Set<T>().Where(whereLambda);return ordering == null? iQueryable.ToList()
: iQueryable.OrderBy(ordering).ToList();
}/// <summary>/// 带条件查询获取数据/// </summary>/// <param name="whereLambda"></param>/// <returns></returns>public IQueryable<T> GetAllIQueryable(Expression<Func<T, bool>> whereLambda = null)
{return whereLambda == null ? Db.Set<T>() : Db.Set<T>().Where(whereLambda);
}/// <summary>/// 获取数量/// </summary>/// <param name="whereLambd"></param>/// <returns></returns>public int GetCount(Expression<Func<T, bool>> whereLambd = null)
{return whereLambd == null ? Db.Set<T>().Count() : Db.Set<T>().Where(whereLambd).Count();
}/// <summary>/// 判断对象是否存在/// </summary>/// <param name="whereLambd"></param>/// <returns></returns>public bool Any(Expression<Func<T, bool>> whereLambd)
{return Db.Set<T>().Where(whereLambd).Any();
}/// <summary>/// 分页查询/// </summary>/// <param name="pageIndex">当前页码</param>/// <param name="pageSize">每页大小</param>/// <param name="rows">总条数</param>/// <param name="orderBy">排序条件(一定要有)</param>/// <param name="whereLambda">查询添加(可有,可无)</param>/// <param name="isOrder">是否是Order排序</param>/// <returns></returns>public List<T> Page<TKey>(int pageIndex, int pageSize, out int rows, Expression<Func<T, TKey>> orderBy, Expression<Func<T, bool>> whereLambda = null, bool isOrder = true)
{
IQueryable<T> data = isOrder ?Db.Set<T>().OrderBy(orderBy) :
Db.Set<T>().OrderByDescending(orderBy);if (whereLambda != null)
{
data = data.Where(whereLambda);
}
rows = data.Count();return data.PageBy((pageIndex - 1) * pageSize, pageSize).ToList();
}/// <summary>/// 分页查询/// </summary>/// <param name="pageIndex">当前页码</param>/// <param name="pageSize">每页大小</param>/// <param name="rows">总条数</param>/// <param name="ordering">排序条件(一定要有)</param>/// <param name="whereLambda">查询添加(可有,可无)</param>/// <returns></returns>public List<T> Page(int pageIndex, int pageSize, out int rows, string ordering, Expression<Func<T, bool>> whereLambda = null)
{// 分页 一定注意: Skip 之前一定要 OrderByvar data = Db.Set<T>().OrderBy(ordering);if (whereLambda != null)
{
data = data.Where(whereLambda);
}
rows = data.Count();return data.PageBy((pageIndex - 1) * pageSize, pageSize).ToList();
}/// <summary>/// 查询转换/// </summary>/// <typeparam name="TDto"></typeparam>/// <param name="whereLambda"></param>/// <returns></returns>public List<TDto> Select<TDto>(Expression<Func<T, bool>> whereLambda)
{return Db.Set<T>().Where(whereLambda).Select<TDto>().ToList();
}#endregion SELECT#region ORTHER/// <summary>/// 执行存储过程或自定义sql语句--返回集合/// </summary>/// <param name="sql"></param>/// <param name="parms"></param>/// <param name="cmdType"></param>/// <returns></returns>public List<T> Query(string sql, List<SqlParameter> parms, CommandType cmdType = CommandType.Text)
{return Query<T>(sql, parms, cmdType);
}/// <summary>/// 提交保存/// </summary>/// <returns></returns>public int SaveChanges()
{return Db.SaveChanges();
}/// <summary>/// 回滚/// </summary>public void RollBackChanges()
{var items = Db.ChangeTracker.Entries().ToList();
items.ForEach(o => o.State = EntityState.Unchanged);
}#endregion ORTHER}扩展类,实现读写分离
上面的通用类是比较基础简单通用的,适合于单库读写操作。对于EF实现读写分离,之前网上找过类似的参考文章,很多人文章都是使用 DbCommandInterceptor拦截器 来实现,具体的做法是通过拦截到sql语句,然后根据具体条件去判断是走主库还是从库。这种做法不是不行,只是个人感觉不是很好扩展,而且要在拦截器里面做限制判断。
其实说白了EF本身就是一个读写分离的orm。用过EF的人知道,EF提供访问数据库的是 DbContext 这个对象,所以想实现读写分离的就很简单了,只要在程序中使用两个不同的DbContext对象,一个负责读,一个负责写就好了。
所以在上面提供的通用封装类中稍微做下修改,修改如下DbContextFactory中获取DbContext的方法,实现一个读的DbContext和一个写的DbContext对象的获取。
这里要注意下,对于读的DbContext来说,要做下设置
1.使用 Database.SetInitializer(new NullDatabaseInitializer
2.重写 SaveChanges 方法,对应从库来说,只提供读取的功能,所以防止误操作,这里禁用掉SaveChanges方法,一般需要使用从读的保存方法,就对外抛出异常。
代码如下:
支持读写分离的 DbContextFactory 类
public class DbContextFactory
{public DbContext GetWriteDbContext(){string key = typeof(DbContextFactory).Name + "WriteDbContext";
DbContext dbContext = CallContext.GetData(key) as DbContext;if (dbContext == null)
{
dbContext = new WriteDbContext();
CallContext.SetData(key, dbContext);
}return dbContext;
}public DbContext GetReadDbContext(){string key = typeof(DbContextFactory).Name + "ReadDbContext";
DbContext dbContext = CallContext.GetData(key) as DbContext;if (dbContext == null)
{
dbContext = new ReadDbContext();
CallContext.SetData(key, dbContext);
}return dbContext;
}
}对应的 DbBase 类也做下修改,主要将上面的Db对象改作 MasterDb 和 SlaveDb 对象,并且把上面的读写方法坐下调整,修改后如下:
支持读写分离的 DbBase类


public class DbBase
{//是否读写分离(可以配置在配置文件中)private static readonly bool IsReadWriteSeparation = true;#region EF上下文对象(主库)protected DbContext MasterDb => _masterDb.Value;private readonly Lazy<DbContext> _masterDb = new Lazy<DbContext>(() => new DbContextFactory().GetWriteDbContext());#endregion EF上下文对象(主库)#region EF上下文对象(从库)protected DbContext SlaveDb => IsReadWriteSeparation ? _slaveDb.Value : _masterDb.Value;private readonly Lazy<DbContext> _slaveDb = new Lazy<DbContext>(() => new DbContextFactory().GetReadDbContext());#endregion EF上下文对象(从库)#region 自定义其他方法/// <summary>/// 执行存储过程或自定义sql语句--返回集合(自定义返回类型)/// </summary>/// <param name="sql"></param>/// <param name="parms"></param>/// <param name="cmdType"></param>/// <returns></returns>public List<TModel> Query<TModel>(string sql, List<SqlParameter> parms, CommandType cmdType = CommandType.Text)
{//存储过程(exec getActionUrlId @name,@ID)if (cmdType == CommandType.StoredProcedure)
{
StringBuilder paraNames = new StringBuilder();foreach (var sqlPara in parms)
{
paraNames.Append($" @{sqlPara},");
}
sql = paraNames.Length > 0 ? $"exec {sql} {paraNames.ToString().Trim(',')}" : $"exec {sql} ";
}var list = SlaveDb.Database.SqlQuery<TModel>(sql, parms.ToArray());var enityList = list.ToList();return enityList;
}/// <summary>/// 自定义语句和存储过程的增删改--返回影响的行数/// </summary>/// <param name="sql"></param>/// <param name="parms"></param>/// <param name="cmdType"></param>/// <returns></returns>public int Execute(string sql, List<SqlParameter> parms, CommandType cmdType = CommandType.Text)
{//存储过程(exec getActionUrlId @name,@ID)if (cmdType == CommandType.StoredProcedure)
{
StringBuilder paraNames = new StringBuilder();foreach (var sqlPara in parms)
{
paraNames.Append($" @{sqlPara},");
}
sql = paraNames.Length > 0 ?$"exec {sql} {paraNames.ToString().Trim(',')}" :
$"exec {sql} ";
}int ret = MasterDb.Database.ExecuteSqlCommand(sql, parms.ToArray());return ret;
}#endregion 自定义其他方法}/// <summary>/// mssql数据库 数据层 父类/// </summary>/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>public class DbBase<T> : DbBase where T : class, new()
{#region INSERT/// <summary>/// 新增 实体/// </summary>/// <param name="model"></param>/// <returns></returns>public void Insert(T model)
{
MasterDb.Set<T>().Add(model);
}/// <summary>/// 普通批量插入/// </summary>/// <param name="datas"></param>public void InsertRange(List<T> datas)
{
MasterDb.Set<T>().AddRange(datas);
}#endregion INSERT#region DELETE/// <summary>/// 根据模型删除/// </summary>/// <param name="model">包含要删除id的对象</param>/// <returns></returns>public void Delete(T model)
{
MasterDb.Set<T>().Attach(model);
MasterDb.Set<T>().Remove(model);
}/// <summary>/// 删除/// </summary>/// <param name="whereLambda"></param>public void Delete(Expression<Func<T, bool>> whereLambda)
{
MasterDb.Set<T>().Where(whereLambda).Delete();
}#endregion DELETE#region UPDATE/// <summary>/// 单个对象指定列修改/// </summary>/// <param name="model">要修改的实体对象</param>/// <param name="proNames">要修改的 属性 名称</param>/// <param name="isProUpdate"></param>/// <returns></returns>public void Update(T model, List<string> proNames, bool isProUpdate = true)
{//将 对象 添加到 EF中MasterDb.Set<T>().Attach(model);var setEntry = ((IObjectContextAdapter)MasterDb).ObjectContext.ObjectStateManager.GetObjectStateEntry(model);//指定列修改if (isProUpdate)
{foreach (string proName in proNames)
{
setEntry.SetModifiedProperty(proName);
}
}//忽略类修改else{
Type t = typeof(T);
List<PropertyInfo> proInfos = t.GetProperties(BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.Public).ToList();foreach (var item in proInfos)
{string proName = item.Name;if (proNames.Contains(proName))
{continue;
}
setEntry.SetModifiedProperty(proName);
}
}
}/// <summary>/// 单个对象修改/// </summary>/// <param name="model"></param>/// <returns></returns>public void Update(T model)
{
DbEntityEntry entry = MasterDb.Entry<T>(model);
MasterDb.Set<T>().Attach(model);
entry.State = EntityState.Modified;
}/// <summary>/// 批量修改/// </summary>/// <param name="whereLambda"></param>/// <param name="updateExpression"></param>public void Update(Expression<Func<T, bool>> whereLambda, Expression<Func<T, T>> updateExpression)
{
MasterDb.Set<T>().Where(whereLambda).Update(updateExpression);
}/// <summary>/// 批量修改/// </summary>/// <param name="models"></param>/// <returns></returns>public void UpdateAll(List<T> models)
{foreach (var model in models)
{
DbEntityEntry entry = MasterDb.Entry(model);
entry.State = EntityState.Modified;
}
}/// <summary>/// 批量统一修改/// </summary>/// <param name="model">要修改的实体对象</param>/// <param name="whereLambda">查询条件</param>/// <param name="modifiedProNames"></param>/// <returns></returns>public void Update(T model, Expression<Func<T, bool>> whereLambda, params string[] modifiedProNames)
{//查询要修改的数据List<T> listModifing = MasterDb.Set<T>().Where(whereLambda).ToList();
Type t = typeof(T);
List<PropertyInfo> proInfos = t.GetProperties(BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.Public).ToList();
Dictionary<string, PropertyInfo> dictPros = new Dictionary<string, PropertyInfo>();
proInfos.ForEach(p =>{if (modifiedProNames.Contains(p.Name))
{
dictPros.Add(p.Name, p);
}
});if (dictPros.Count <= 0)
{throw new Exception("指定修改的字段名称有误或为空");
}foreach (var item in dictPros)
{
PropertyInfo proInfo = item.Value;//取出 要修改的值object newValue = proInfo.GetValue(model, null);//批量设置 要修改 对象的 属性foreach (T oModel in listModifing)
{//为 要修改的对象 的 要修改的属性 设置新的值proInfo.SetValue(oModel, newValue, null);
}
}
}#endregion UPDATE#region SELECT/// <summary>/// 根据主键查询/// </summary>/// <param name="id"></param>/// <returns></returns>public T FindById(dynamic id)
{return SlaveDb.Set<T>().Find(id);
}/// <summary>/// 获取默认一条数据,没有则为NULL/// </summary>/// <param name="whereLambda"></param>/// <returns></returns>public T FirstOrDefault(Expression<Func<T, bool>> whereLambda = null)
{if (whereLambda == null)
{return SlaveDb.Set<T>().FirstOrDefault();
}return SlaveDb.Set<T>().FirstOrDefault(whereLambda);
}/// <summary>/// 获取全部数据/// </summary>/// <returns></returns>public List<T> GetAll(string ordering = null)
{return ordering == null? SlaveDb.Set<T>().ToList()
: SlaveDb.Set<T>().OrderBy(ordering).ToList();
}/// <summary>/// 带条件查询获取数据/// </summary>/// <param name="whereLambda"></param>/// <param name="ordering"></param>/// <returns></returns>public List<T> GetAll(Expression<Func<T, bool>> whereLambda, string ordering = null)
{var iQueryable = SlaveDb.Set<T>().Where(whereLambda);return ordering == null? iQueryable.ToList()
: iQueryable.OrderBy(ordering).ToList();
}/// <summary>/// 带条件查询获取数据/// </summary>/// <param name="whereLambda"></param>/// <returns></returns>public IQueryable<T> GetAllIQueryable(Expression<Func<T, bool>> whereLambda = null)
{return whereLambda == null ? SlaveDb.Set<T>() : SlaveDb.Set<T>().Where(whereLambda);
}/// <summary>/// 获取数量/// </summary>/// <param name="whereLambd"></param>/// <returns></returns>public int GetCount(Expression<Func<T, bool>> whereLambd = null)
{return whereLambd == null ? SlaveDb.Set<T>().Count() : SlaveDb.Set<T>().Where(whereLambd).Count();
}/// <summary>/// 判断对象是否存在/// </summary>/// <param name="whereLambd"></param>/// <returns></returns>public bool Any(Expression<Func<T, bool>> whereLambd)
{return SlaveDb.Set<T>().Where(whereLambd).Any();
}/// <summary>/// 分页查询/// </summary>/// <param name="pageIndex">当前页码</param>/// <param name="pageSize">每页大小</param>/// <param name="rows">总条数</param>/// <param name="orderBy">排序条件(一定要有)</param>/// <param name="whereLambda">查询添加(可有,可无)</param>/// <param name="isOrder">是否是Order排序</param>/// <returns></returns>public List<T> Page<TKey>(int pageIndex, int pageSize, out int rows, Expression<Func<T, TKey>> orderBy, Expression<Func<T, bool>> whereLambda = null, bool isOrder = true)
{
IQueryable<T> data = isOrder ?SlaveDb.Set<T>().OrderBy(orderBy) :
SlaveDb.Set<T>().OrderByDescending(orderBy);if (whereLambda != null)
{
data = data.Where(whereLambda);
}
rows = data.Count();return data.PageBy((pageIndex - 1) * pageSize, pageSize).ToList();
}/// <summary>/// 分页查询/// </summary>/// <param name="pageIndex">当前页码</param>/// <param name="pageSize">每页大小</param>/// <param name="rows">总条数</param>/// <param name="ordering">排序条件(一定要有)</param>/// <param name="whereLambda">查询添加(可有,可无)</param>/// <returns></returns>public List<T> Page(int pageIndex, int pageSize, out int rows, string ordering, Expression<Func<T, bool>> whereLambda = null)
{// 分页 一定注意: Skip 之前一定要 OrderByvar data = SlaveDb.Set<T>().OrderBy(ordering);if (whereLambda != null)
{
data = data.Where(whereLambda);
}
rows = data.Count();return data.PageBy((pageIndex - 1) * pageSize, pageSize).ToList();
}/// <summary>/// 查询转换/// </summary>/// <typeparam name="TDto"></typeparam>/// <param name="whereLambda"></param>/// <returns></returns>public List<TDto> Select<TDto>(Expression<Func<T, bool>> whereLambda)
{return SlaveDb.Set<T>().Where(whereLambda).Select<TDto>().ToList();
}#endregion SELECT#region ORTHER/// <summary>/// 执行存储过程或自定义sql语句--返回集合/// </summary>/// <param name="sql"></param>/// <param name="parms"></param>/// <param name="cmdType"></param>/// <returns></returns>public List<T> Query(string sql, List<SqlParameter> parms, CommandType cmdType = CommandType.Text)
{return Query<T>(sql, parms, cmdType);
}/// <summary>/// 提交保存/// </summary>/// <returns></returns>public int SaveChanges()
{return MasterDb.SaveChanges();
}/// <summary>/// 回滚/// </summary>public void RollBackChanges()
{var items = MasterDb.ChangeTracker.Entries().ToList();
items.ForEach(o => o.State = EntityState.Unchanged);
}#endregion ORTHER}这样简单的读写分离就实现了,实现逻辑也比较清晰,方便扩展。
进一步改造,实现多从库读取
一般做读写分离,都会做一主多从,特别对读取量比较大的项目,这样多库读取就能减轻读库的压力。所以对于上面的方法,做下改造。
上面可以看到,主库和从库都是通过 DbContextFactory 这个类来获取的,在GetReadDbContext 方法中每次都是获取 ReadDbContext 这个对象。那么对于多个从库的情况下,每次读取到底要去哪个库读取数据呢?这里就是一个算法规则的问题了,或者说是策略吧,如果使用过nginx的朋友就知道,nginx本身内部在实现负载均衡的时候提供了多种策略,比如轮询,加权轮询,ip_hash等策略。其实上面获取同一个ReadDbContext 的方法也算一种策略,叫单一策略,每次都获取单一的对象。
多从库的情况下,我们简单的来实现另一种获取策略,随机策略,每次都随机获取到一个从库的对象,这种是最简单的策略,当然,正式使用的话大家可以发挥自己的创造力,写出多了的算法策略。
首先,定义一个策略接口,方便策略的扩展和切换,代码如下:
IReadDbStrategy 接口
/// <summary>
/// 从数据库获取策略接口 /// </summary>
public interface IReadDbStrategy
{ /// <summary> /// 获取读库 /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> DbContext GetDbContext();
}单从库情况下,定义一个单一策略,代码如下:
单一策略
/// <summary>
/// 单一策略 /// </summary>
public class SingleStrategy : IReadDbStrategy
{ public DbContext GetDbContext()
{ return new ReadDbContext();
}
}多从库情况下,定义一个随机策略,代码如下:
随机策略
/// <summary>/// 随机策略/// </summary>public class RandomStrategy : IReadDbStrategy
{//所有读库类型public static List<Type> DbTypes; static RandomStrategy()
{
LoadDbs();
} //加载所有的读库类型static void LoadDbs()
{
DbTypes = new List<Type>();var assembly = Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly();var types = assembly.GetTypes();foreach (var type in types)
{if (type.BaseType == typeof(BaseReadDbContext))
{
DbTypes.Add(type);
}
}
} public DbContext GetDbContext()
{int randomIndex = new Random().Next(0, DbTypes.Count);var dbType = DbTypes[randomIndex];var dbContext = Activator.CreateInstance(dbType) as DbContext;return dbContext;
}
}这样,所有从库我们都基于策略去获取,扩展也比较方便。修改下 DbContextFactory 类的 GetReadDbContext 方法,通过策略接口来获取,代码如下:
支持一主多从的 DbContextFactory 类
public class DbContextFactory
{//todo:这里可以自己通过注入的方式来实现,就会更加灵活private static readonly IReadDbStrategy ReadDbStrategy = new RandomStrategy();public DbContext GetWriteDbContext()
{string key = typeof(DbContextFactory).Name + "WriteDbContext";
DbContext dbContext = CallContext.GetData(key) as DbContext;if (dbContext == null)
{
dbContext = new WriteDbContext();
CallContext.SetData(key, dbContext);
}return dbContext;
}public DbContext GetReadDbContext()
{string key = typeof(DbContextFactory).Name + "ReadDbContext";
DbContext dbContext = CallContext.GetData(key) as DbContext;if (dbContext == null)
{
dbContext = ReadDbStrategy.GetDbContext();CallContext.SetData(key, dbContext);
}return dbContext;
}
}这样简单的一主多从也实现了。
参考文章
源码分享
所有的代码提供给大家的更多的是一种思路和学习的参考,如果有什么不足的地方也欢迎大家批评指正,如果觉得对你有帮助,不要吝啬你的鼠标,帮忙点个星,点个赞吧。
The above is the detailed content of Summary of EF general data layer encapsulation class examples detailed explanation. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Use ddrescue to recover data on Linux
Mar 20, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
Use ddrescue to recover data on Linux
Mar 20, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
DDREASE is a tool for recovering data from file or block devices such as hard drives, SSDs, RAM disks, CDs, DVDs and USB storage devices. It copies data from one block device to another, leaving corrupted data blocks behind and moving only good data blocks. ddreasue is a powerful recovery tool that is fully automated as it does not require any interference during recovery operations. Additionally, thanks to the ddasue map file, it can be stopped and resumed at any time. Other key features of DDREASE are as follows: It does not overwrite recovered data but fills the gaps in case of iterative recovery. However, it can be truncated if the tool is instructed to do so explicitly. Recover data from multiple files or blocks to a single
 Open source! Beyond ZoeDepth! DepthFM: Fast and accurate monocular depth estimation!
Apr 03, 2024 pm 12:04 PM
Open source! Beyond ZoeDepth! DepthFM: Fast and accurate monocular depth estimation!
Apr 03, 2024 pm 12:04 PM
0.What does this article do? We propose DepthFM: a versatile and fast state-of-the-art generative monocular depth estimation model. In addition to traditional depth estimation tasks, DepthFM also demonstrates state-of-the-art capabilities in downstream tasks such as depth inpainting. DepthFM is efficient and can synthesize depth maps within a few inference steps. Let’s read about this work together ~ 1. Paper information title: DepthFM: FastMonocularDepthEstimationwithFlowMatching Author: MingGui, JohannesS.Fischer, UlrichPrestel, PingchuanMa, Dmytr
 Google is ecstatic: JAX performance surpasses Pytorch and TensorFlow! It may become the fastest choice for GPU inference training
Apr 01, 2024 pm 07:46 PM
Google is ecstatic: JAX performance surpasses Pytorch and TensorFlow! It may become the fastest choice for GPU inference training
Apr 01, 2024 pm 07:46 PM
The performance of JAX, promoted by Google, has surpassed that of Pytorch and TensorFlow in recent benchmark tests, ranking first in 7 indicators. And the test was not done on the TPU with the best JAX performance. Although among developers, Pytorch is still more popular than Tensorflow. But in the future, perhaps more large models will be trained and run based on the JAX platform. Models Recently, the Keras team benchmarked three backends (TensorFlow, JAX, PyTorch) with the native PyTorch implementation and Keras2 with TensorFlow. First, they select a set of mainstream
 Slow Cellular Data Internet Speeds on iPhone: Fixes
May 03, 2024 pm 09:01 PM
Slow Cellular Data Internet Speeds on iPhone: Fixes
May 03, 2024 pm 09:01 PM
Facing lag, slow mobile data connection on iPhone? Typically, the strength of cellular internet on your phone depends on several factors such as region, cellular network type, roaming type, etc. There are some things you can do to get a faster, more reliable cellular Internet connection. Fix 1 – Force Restart iPhone Sometimes, force restarting your device just resets a lot of things, including the cellular connection. Step 1 – Just press the volume up key once and release. Next, press the Volume Down key and release it again. Step 2 – The next part of the process is to hold the button on the right side. Let the iPhone finish restarting. Enable cellular data and check network speed. Check again Fix 2 – Change data mode While 5G offers better network speeds, it works better when the signal is weaker
 The vitality of super intelligence awakens! But with the arrival of self-updating AI, mothers no longer have to worry about data bottlenecks
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:55 PM
The vitality of super intelligence awakens! But with the arrival of self-updating AI, mothers no longer have to worry about data bottlenecks
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:55 PM
I cry to death. The world is madly building big models. The data on the Internet is not enough. It is not enough at all. The training model looks like "The Hunger Games", and AI researchers around the world are worrying about how to feed these data voracious eaters. This problem is particularly prominent in multi-modal tasks. At a time when nothing could be done, a start-up team from the Department of Renmin University of China used its own new model to become the first in China to make "model-generated data feed itself" a reality. Moreover, it is a two-pronged approach on the understanding side and the generation side. Both sides can generate high-quality, multi-modal new data and provide data feedback to the model itself. What is a model? Awaker 1.0, a large multi-modal model that just appeared on the Zhongguancun Forum. Who is the team? Sophon engine. Founded by Gao Yizhao, a doctoral student at Renmin University’s Hillhouse School of Artificial Intelligence.
 Tesla robots work in factories, Musk: The degree of freedom of hands will reach 22 this year!
May 06, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
Tesla robots work in factories, Musk: The degree of freedom of hands will reach 22 this year!
May 06, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
The latest video of Tesla's robot Optimus is released, and it can already work in the factory. At normal speed, it sorts batteries (Tesla's 4680 batteries) like this: The official also released what it looks like at 20x speed - on a small "workstation", picking and picking and picking: This time it is released One of the highlights of the video is that Optimus completes this work in the factory, completely autonomously, without human intervention throughout the process. And from the perspective of Optimus, it can also pick up and place the crooked battery, focusing on automatic error correction: Regarding Optimus's hand, NVIDIA scientist Jim Fan gave a high evaluation: Optimus's hand is the world's five-fingered robot. One of the most dexterous. Its hands are not only tactile
 The first robot to autonomously complete human tasks appears, with five fingers that are flexible and fast, and large models support virtual space training
Mar 11, 2024 pm 12:10 PM
The first robot to autonomously complete human tasks appears, with five fingers that are flexible and fast, and large models support virtual space training
Mar 11, 2024 pm 12:10 PM
This week, FigureAI, a robotics company invested by OpenAI, Microsoft, Bezos, and Nvidia, announced that it has received nearly $700 million in financing and plans to develop a humanoid robot that can walk independently within the next year. And Tesla’s Optimus Prime has repeatedly received good news. No one doubts that this year will be the year when humanoid robots explode. SanctuaryAI, a Canadian-based robotics company, recently released a new humanoid robot, Phoenix. Officials claim that it can complete many tasks autonomously at the same speed as humans. Pheonix, the world's first robot that can autonomously complete tasks at human speeds, can gently grab, move and elegantly place each object to its left and right sides. It can autonomously identify objects
 The U.S. Air Force showcases its first AI fighter jet with high profile! The minister personally conducted the test drive without interfering during the whole process, and 100,000 lines of code were tested for 21 times.
May 07, 2024 pm 05:00 PM
The U.S. Air Force showcases its first AI fighter jet with high profile! The minister personally conducted the test drive without interfering during the whole process, and 100,000 lines of code were tested for 21 times.
May 07, 2024 pm 05:00 PM
Recently, the military circle has been overwhelmed by the news: US military fighter jets can now complete fully automatic air combat using AI. Yes, just recently, the US military’s AI fighter jet was made public for the first time and the mystery was unveiled. The full name of this fighter is the Variable Stability Simulator Test Aircraft (VISTA). It was personally flown by the Secretary of the US Air Force to simulate a one-on-one air battle. On May 2, U.S. Air Force Secretary Frank Kendall took off in an X-62AVISTA at Edwards Air Force Base. Note that during the one-hour flight, all flight actions were completed autonomously by AI! Kendall said - "For the past few decades, we have been thinking about the unlimited potential of autonomous air-to-air combat, but it has always seemed out of reach." However now,



