What are the positioning models in CSS?
Positioning model June 8, 2017 fanbright
css supports 6 positioning models
static
Absolutely
Fixed
Relative
- ##Floating
- Relative floating
Set position
- position:static; you can cancel the positioning setting of the element and restore it to its original position. The display mode in the regular flow.static is the default value.
- position:relative; can offset the position of the element by a certain distance relative to the regular flow.
- position:absolute;You can offset the element by a certain distance relative to the position of the regular flow or the position of the nearest positioned ancestor element.
- position:fixed;You can make the element relative Offset a certain distance from the window.
- z-index can set the stacking order of elements. The larger the value, the higher the element is.
Recently positioned ancestor element
- If the element that sets the position does not have a positioned ancestor element, then
becomes Positioning ancestor elements, in other words,is the default position element.##The most recently positioned element must be a valid ancestor element (relative|absolute|fixed ), CSS does not support positioning relative to any element in the document. - position:relative; is a very good way to create positioned ancestor elements because it does not leave the routine Flow. Using this method, you can create a layout that maintains regular flow and achieves absolute positioning.
-
Atomic display
Atomic displayThe element whose position is set is, which means that external elements cannot appear between its static descendant elements, inline content and background. By using
relative positioning, absolute positioning and fixed positioningmodes, you can Elements are set to atomic display, and block-level elements set tooverflow:scroll|autoare also atomically displayed and are static block-level elements with no position set. When overlap occurs, their inline content will not overlap, but their
will overlap, but text will not.
- z-index is not a global attribute, but relative to the set numeric value The z-index is determined by the most recently positioned ancestor element. The root element html will create a root stacking context. Each positioned element with a specified numeric value z-index will create a local local stacking context.
- Static positioning elements are stacked from back to front according to the order in which the document appears.
- Setting the position element ignores the order in which the document elements appear, but changes from small to large based on the z-index value. The largest order is stacked from back to front. Negative value set position elements are located under static positioning elements and non-set position floating elements
position:static;The default is static;
- The starting position of a static element is determined by the position of the previous static element. The ## of the static element #Size
- ,
Padding
The vertical margins of adjacent elements will,Border, andMargindetermine the starting position of the next element.merge - together, and the final margin is the
larger value of the margins of the two adjacent elements
Set the left and right margins to auto to center the static block-level - elements with the
set size
.Two absolute positioning models
position:absolute;
##Percentage
- is relative to the nearest positioned ancestor The size of the element, and the size of
- non-parent element
.
autoSet the left, right, top, bottom of the element to, which can restore - its original position in the regular flow.
Unlike floating elements, absolute elements will not be automatically arranged and will not be affected by other elements. , will not affect other elements. - If all child elements of an element are set to absolute positioning, then its height will become
0
, all Its child elements have all left the regular flow. If there is no positioned ancestor element, it will be positioned based on- Absolutely Positioning and centering, general elements
div{ position:absolute; width:200px; height:200px; margin:0 auto; border:1px solid blue; /*left:0;*/ 这两条没用,没有影响 /*right:0;*/ }Copy after loginAbsolute positioning and centering, static inline elementsFor static inline elements, such as em, strong, span, etc., but does not include inline replaceable elements (input, img, textarea, etc.), when using the absolute positioning mode absolute, width and right can be used. In order to be centered, you need to addleft:0; and right:0;
so that margin:0 auto; can take effect normally. .Note that left and right
must be 0.
<div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false"> #em{ position:absolute; width:200px; height:200px; margin:0 auto; border:1px solid blue; left:0; right:0; }</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div>Three fixed positioning model
, andRemember: the position of the fixedly positioned element is relative to the
window
- Not
- relative to the nearest positioned ancestor`, and the element will not scroll as the page scrolls.
Because it is positioned relative to the page,
does not require the nearest ancestor to be positionedIt is best to use top and left when setting For offset positioning, when top, left, bottom, and right are set at the same time, the values of top and left will be
given priority. Only when top and leftdo not exist, bottom and right will be used. Only then will it take effect
Four relative positioning
position:relative;
Use left and top are used to change the position of the element. The default value of left and top is auto. Auto will keep the relatively positioned element in its original position in the regular flow.
Any element can be set to position:relative; Therefore, its absolutely positioned descendant elements can be positioned relative to it.
Five floating positioning and reset
Use float:left; and float:right; can make the element leave the regular flow.
- ##Use float:none; the default is none, which can override other floating rules of the element and avoid inheriting float
- Floating elements will not affect the position of the block-level box, but only affect the inline elements ##clear:left;clear:right;clear;both;
- Any element can be set as a floating element, clear is applicable to tables, block-level elements and floating elements
- clear is not applicable
- Inline
,
Absolute positioningorFixed positioningelements ##Six relative floating positioning
Use float to make some elements floating elements. Floating elements can be set to relative positioning through relative. Relative floating elements are still in the regular flow where the floating elements are located. You can use left and top to set its offset position in the flow. .
##Only positon:relative; and position:static; are applicable to floating elements. When set to absolute and fixed, the display result is uncertain.
- sporadic
In css, if the parameter value is 0, do not add units,
-
Before rendering the content of an element, the browser will first render its frame, starting with the background color, then the background image, then the border, and finally, the browser will render the content of the frame on top of the frame
The above is the detailed content of What are the positioning models in CSS?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 KAN, which replaces MLP, has been extended to convolution by open source projects
Jun 01, 2024 pm 10:03 PM
KAN, which replaces MLP, has been extended to convolution by open source projects
Jun 01, 2024 pm 10:03 PM
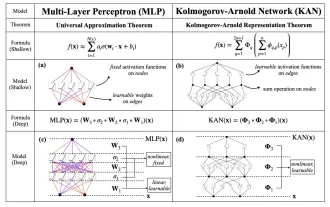
Earlier this month, researchers from MIT and other institutions proposed a very promising alternative to MLP - KAN. KAN outperforms MLP in terms of accuracy and interpretability. And it can outperform MLP running with a larger number of parameters with a very small number of parameters. For example, the authors stated that they used KAN to reproduce DeepMind's results with a smaller network and a higher degree of automation. Specifically, DeepMind's MLP has about 300,000 parameters, while KAN only has about 200 parameters. KAN has a strong mathematical foundation like MLP. MLP is based on the universal approximation theorem, while KAN is based on the Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theorem. As shown in the figure below, KAN has
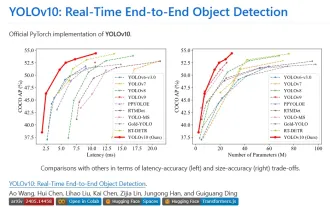 Yolov10: Detailed explanation, deployment and application all in one place!
Jun 07, 2024 pm 12:05 PM
Yolov10: Detailed explanation, deployment and application all in one place!
Jun 07, 2024 pm 12:05 PM
1. Introduction Over the past few years, YOLOs have become the dominant paradigm in the field of real-time object detection due to its effective balance between computational cost and detection performance. Researchers have explored YOLO's architectural design, optimization goals, data expansion strategies, etc., and have made significant progress. At the same time, relying on non-maximum suppression (NMS) for post-processing hinders end-to-end deployment of YOLO and adversely affects inference latency. In YOLOs, the design of various components lacks comprehensive and thorough inspection, resulting in significant computational redundancy and limiting the capabilities of the model. It offers suboptimal efficiency, and relatively large potential for performance improvement. In this work, the goal is to further improve the performance efficiency boundary of YOLO from both post-processing and model architecture. to this end
 Comprehensively surpassing DPO: Chen Danqi's team proposed simple preference optimization SimPO, and also refined the strongest 8B open source model
Jun 01, 2024 pm 04:41 PM
Comprehensively surpassing DPO: Chen Danqi's team proposed simple preference optimization SimPO, and also refined the strongest 8B open source model
Jun 01, 2024 pm 04:41 PM
In order to align large language models (LLMs) with human values and intentions, it is critical to learn human feedback to ensure that they are useful, honest, and harmless. In terms of aligning LLM, an effective method is reinforcement learning based on human feedback (RLHF). Although the results of the RLHF method are excellent, there are some optimization challenges involved. This involves training a reward model and then optimizing a policy model to maximize that reward. Recently, some researchers have explored simpler offline algorithms, one of which is direct preference optimization (DPO). DPO learns the policy model directly based on preference data by parameterizing the reward function in RLHF, thus eliminating the need for an explicit reward model. This method is simple and stable
 No OpenAI data required, join the list of large code models! UIUC releases StarCoder-15B-Instruct
Jun 13, 2024 pm 01:59 PM
No OpenAI data required, join the list of large code models! UIUC releases StarCoder-15B-Instruct
Jun 13, 2024 pm 01:59 PM
At the forefront of software technology, UIUC Zhang Lingming's group, together with researchers from the BigCode organization, recently announced the StarCoder2-15B-Instruct large code model. This innovative achievement achieved a significant breakthrough in code generation tasks, successfully surpassing CodeLlama-70B-Instruct and reaching the top of the code generation performance list. The unique feature of StarCoder2-15B-Instruct is its pure self-alignment strategy. The entire training process is open, transparent, and completely autonomous and controllable. The model generates thousands of instructions via StarCoder2-15B in response to fine-tuning the StarCoder-15B base model without relying on expensive manual annotation.
 Tsinghua University took over and YOLOv10 came out: the performance was greatly improved and it was on the GitHub hot list
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:20 PM
Tsinghua University took over and YOLOv10 came out: the performance was greatly improved and it was on the GitHub hot list
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:20 PM
The benchmark YOLO series of target detection systems has once again received a major upgrade. Since the release of YOLOv9 in February this year, the baton of the YOLO (YouOnlyLookOnce) series has been passed to the hands of researchers at Tsinghua University. Last weekend, the news of the launch of YOLOv10 attracted the attention of the AI community. It is considered a breakthrough framework in the field of computer vision and is known for its real-time end-to-end object detection capabilities, continuing the legacy of the YOLO series by providing a powerful solution that combines efficiency and accuracy. Paper address: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2405.14458 Project address: https://github.com/THU-MIG/yo
 Li Feifei reveals the entrepreneurial direction of 'spatial intelligence': visualization turns into insight, seeing becomes understanding, and understanding leads to action
Jun 01, 2024 pm 02:55 PM
Li Feifei reveals the entrepreneurial direction of 'spatial intelligence': visualization turns into insight, seeing becomes understanding, and understanding leads to action
Jun 01, 2024 pm 02:55 PM
After Stanford's Feifei Li started his business, he unveiled the new concept "spatial intelligence" for the first time. This is not only her entrepreneurial direction, but also the "North Star" that guides her. She considers it "the key puzzle piece to solve the artificial intelligence problem." Visualization leads to insight; seeing leads to understanding; understanding leads to action. Based on Li Feifei's 15-minute TED talk, which is fully open to the public, it starts from the origin of life evolution hundreds of millions of years ago, to how humans are not satisfied with what nature has given them and develops artificial intelligence, to how to build spatial intelligence in the next step. Nine years ago, Li Feifei introduced the newly born ImageNet to the world on the same stage - one of the starting points for this round of deep learning explosion. She herself also encouraged netizens: If you watch both videos, you will be able to understand the computer vision of the past 10 years.
 Beating GPT-4o in seconds, beating Llama 3 70B in 22B, Mistral AI opens its first code model
Jun 01, 2024 pm 06:32 PM
Beating GPT-4o in seconds, beating Llama 3 70B in 22B, Mistral AI opens its first code model
Jun 01, 2024 pm 06:32 PM
French AI unicorn MistralAI, which is targeting OpenAI, has made a new move: Codestral, the first large code model, was born. As an open generative AI model designed specifically for code generation tasks, Codestral helps developers write and interact with code by sharing instructions and completion API endpoints. Codestral's proficiency in coding and English allows software developers to design advanced AI applications. The parameter size of Codestral is 22B, it complies with the new MistralAINon-ProductionLicense, and can be used for research and testing purposes, but commercial use is prohibited. Currently, the model is available for download on HuggingFace. download link
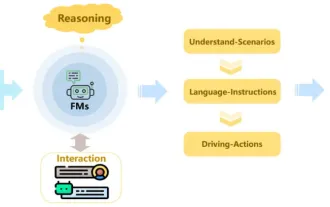 Review! Comprehensively summarize the important role of basic models in promoting autonomous driving
Jun 11, 2024 pm 05:29 PM
Review! Comprehensively summarize the important role of basic models in promoting autonomous driving
Jun 11, 2024 pm 05:29 PM
Written above & the author’s personal understanding: Recently, with the development and breakthroughs of deep learning technology, large-scale foundation models (Foundation Models) have achieved significant results in the fields of natural language processing and computer vision. The application of basic models in autonomous driving also has great development prospects, which can improve the understanding and reasoning of scenarios. Through pre-training on rich language and visual data, the basic model can understand and interpret various elements in autonomous driving scenarios and perform reasoning, providing language and action commands for driving decision-making and planning. The base model can be data augmented with an understanding of the driving scenario to provide those rare feasible features in long-tail distributions that are unlikely to be encountered during routine driving and data collection.






