Sample code sharing about reflection mechanism in Java (picture)
This article mainly introduces relevant information about the reflection mechanism in Java. Friends who need it can refer to
Detailed explanation of the reflection mechanism in Java
Reflection , I often heard them say that I had read some information and may have used it in Design Pattern, but I didn’t feel I had a deep understanding of it. I studied it again this time and it felt okay. Bar!
First, let’s take a look at the concept of reflection:
Mainly refers to the ability of a program to access, detect and modify its own status or behavior, and can The status and results of its own behavior, adjusting or modifying the status and related semantics of the behavior described by the application.
Reflection is a powerful tool in Java that allows us to easily create flexible code that can be assembled at runtime without source code linking between components. But improper use of reflection can be very costly!
If you are confused by the concept, continue reading.
2. The role of the reflection mechanism:
1, decompilation: .class-->.java
2, accessed through the reflection mechanism Properties, methods, Construction methods, etc. of java objects;
This seems to be easier to understand. Let’s look at how to implement these functions in detail.
Third, let’s take a look at the classes that sun provides us with in the reflection mechanism:
java.lang.Class; java.lang.reflect.Constructor; java.lang.reflect.Field; java.lang.reflect.Method; java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
Many reflections We can query methods, attributes and other operations from these four classes. Or should we learn to constantly query the API, that is our best teacher.
4. Specific function implementation:
1. There are three ways to obtain classes through the reflection mechanism. Let’s get the Employee type
//第一种方式:
Classc1 = Class.forName("Employee");
//第二种方式:
//java中每个类型都有class 属性.
Classc2 = Employee.class;
//第三种方式:
//java语言中任何一个java对象都有getClass 方法
Employeee = new Employee();
Classc3 = e.getClass(); //c3是运行时类 (e的运行时类是Employee)2, Create object: After obtaining the class, we create its object, using newInstance:
Class c =Class.forName("Employee");
//创建此Class 对象所表示的类的一个新实例
Objecto = c.newInstance(); //调用了Employee的无参数构造方法.3, get the attributes: Divided into all attributes and specified attributes:
a, first look at how to get all attributes:
##
//获取整个类
Class c = Class.forName("java.lang.Integer");
//获取所有的属性?
Field[] fs = c.getDeclaredFields();
//定义可变长的字符串,用来存储属性
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
//通过追加的方法,将每个属性拼接到此字符串中
//最外边的public定义
sb.append(Modifier.toString(c.getModifiers()) + " class " + c.getSimpleName() +"{\n");
//里边的每一个属性
for(Field field:fs){
sb.append("\t");//空格
sb.append(Modifier.toString(field.getModifiers())+" ");//获得属性的修饰符,例如public,static等等
sb.append(field.getType().getSimpleName() + " ");//属性的类型的名字
sb.append(field.getName()+";\n");//属性的名字+回车
}
sb.append("}");
System.out.println(sb);public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//以前的方式:
/*
User u = new User();
u.age = 12; //set
System.out.println(u.age); //get
*/
//获取类
Class c = Class.forName("User");
//获取id属性
Field idF = c.getDeclaredField("id");
//实例化这个类赋给o
Object o = c.newInstance();
//打破封装
idF.setAccessible(true); //使用反射机制可以打破封装性,导致了java对象的属性不安全。
//给o对象的id属性赋值"110"
idF.set(o, "110"); //set
//get
System.out.println(idF.get(o));
}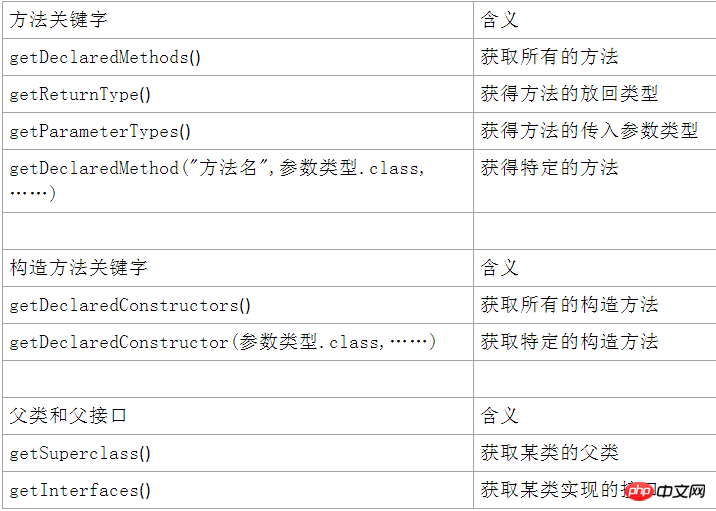
Object-oriented.
Fifth, reflection plus Configuration file makes our program more flexible:
In the design pattern learning, when learning the abstract factory Reflection was used to more conveniently read database connection strings, etc. I didn’t quite understand it at the time, so I just copied it. Take a look at the use of reflection + configuration files in .NET: The configuration file used at that time was the app.config file, the content was in XML format, and the content of the linked database was filled in: <configuration>
<appSettings>
<add key="" value=""/>
</appSettings>
</configuration> assembly.load("当前程序集的名称").CreateInstance("当前命名空间名称".要实例化的类名);The above is the detailed content of Sample code sharing about reflection mechanism in Java (picture). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.




