
In many scenarios, we do not need to use JdbcTemplate to directly operate SQL statements. At this time, we can use ORM tools to save a lot of code and development time. . ORM tools can shift the focus from error-prone SQL code to how to implement the real needs of the application.
Spring's support for ORM frameworks provides integration points with these frameworks and some additional services:
Supports integration of Spring declarative transactions;
Transparent exception handling;
Thread-safe, lightweight template class;
DAO support class ;
Resource management.
Hibernate is an open source ORM framework that is very popular in the developer community.
mysqlCreate a new database store, and then execute the following sql:


1 create table Category (2 Id int not null,3 Name varchar(80) null,4 constraint pk_category primary key (Id)5 );6 7 INSERT INTO category(id,Name) VALUES (1,'女装');8 INSERT INTO category(id,Name) VALUES (2,'美妆');9 INSERT INTO category(id,Name) VALUES (3,'书籍');
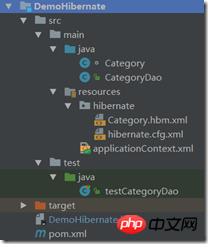
The IDE I use is IdeaIU and I build the project through maven , configure spring through xml. The completed code structure is:
class Category{
private int cateId;
private String cateName;
//次数省略get,set方法
@Override
public String toString() {
return "id="+cateId+" name="+cateName;
}
}
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>4.3.5.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.30</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx ">
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/store"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="sessionFactory"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.LocalSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:hibernate/hibernate.cfg.xml"/>
</bean>
<tx:annotation-driven/>
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.HibernateTransactionManager">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory"/>
</bean>
<bean id="categoryDao" class="CategoryDao">
<constructor-arg ref="sessionFactory"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
dataSource is nothing special, just No more explanation. Take a look at a few other points:
①hibernate sessionFactory:
The main interface required to use Hibernate is org.hibernate.Session. The Session interface provides the most basic CRUD and other Data access capabilities. Through Hibernate's Session interface, the application's Repository can meet all persistence needs. The standard way to obtain a Hibernate Session object is to use the implementation class of the Hibernate SessionFactory interface.
There are two main properties set in the sessionFactory configuration: dataSource sets the data connection, and configLocation sets the path to the hibernate configuration file.
②Transaction
If the database operation supports transactions, you need to configure
①hibernate.cfg.xml
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<mapping resource="hibernate/Category.hbm.xml"/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
②Category.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="Category" table="Category">
<id name="cateId" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="cateName" column="name"/>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
If the method wants to support transactions, it needs to be annotated @Transactional.
public class CategoryDao {
private SessionFactory sessionFactory;
public CategoryDao(SessionFactory sessionFactory) {
this.sessionFactory = sessionFactory;
}
private Session currentSession() {
return sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
}
@Transactional
public void save(Category category) {
currentSession().save(category);
}
@Transactional
public void update(Category category){
currentSession().update(category);
}
@Transactional
public void delete(int id) {
Query query = currentSession().createSQLQuery("DELETE FROM category WHERE Id=::ID");
query.setInteger("::ID", id);
query.executeUpdate();
}
@Transactional
public int count() {
return getAll().size();
}
@Transactional
public Category getById(int id) {
Criteria criteria=currentSession().createCriteria(Category.class);
criteria.add(Restrictions.eq("id",id));
return (Category) criteria.uniqueResult();
}
@Transactional
public List<Category> getAll() {
return currentSession().createCriteria(Category.class).list();
}
}
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:applicationContext.xml")
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
public class testCategoryDao {
@Autowired
private CategoryDao categoryDao;
@Test
public void testAdd() {
Category category = new Category();
category.setCateId(4);
category.setCateName("母婴");
categoryDao.save(category);
}
@Test
public void testUpdate() {
Category category = new Category();
category.setCateId(4);
category.setCateName("男装");
categoryDao.update(category);
}
@Test
public void testGetById() {
int id = 4;
Category category = categoryDao.getById(id);
if(category==null){
System.out.println("not exist");
}else {
System.out.println(category.toString());
}
}
@Test
public void testGetAll() {
List<Category> categories = categoryDao.getAll();
for (Category item : categories) {
System.out.println(item);
}
}
@Test
public void testCount() {
int count = categoryDao.count();
System.out.println(count);
}
@Test
public void testDelete() {
int id = 4;
categoryDao.delete(id);
}
}The above is the detailed content of Introduction to Hibernate and examples. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




