Detailed introduction to java memory area and memory overflow exception
java memory area and memory overflow exception
1. Runtime data area

1. Program counter: thread private , used to store the location of the currently executed instruction
2. Java virtual machine stack: thread private, describing the Java method execution model; when executing a method, a stack frame will be created to store local variables and basic type variables. Reference and other information
3.Java native method stack: thread private, serving the Native methods used by the virtual machine
4.Java heap: thread shared, is the main working place of the garbage collector ;Storage object instances, etc.
5. Method area: thread sharing; storage class information, constants, static variables, etc.
Runtime constants: store various literals and symbol references generated during compilation
6. Direct memory: machine memory
2. Virtual machine object
1. Creation of object
Check first Can the constant pool locate the symbol reference of this class and check whether the class has been loaded and initialized, otherwise the loading process must be performed first;
Allocate memory for the object: calculate the space and extract it from the heap Divide a continuous or discontinuous area; use cas+failure retry to avoid thread safety issues (because objects are created very frequently, I don’t know whether the current memory has been allocated)
Initialize memory space: Initialize the allocated memory space to 0 value
Set basic information of the object: metadata, hash code, gc, etc.
Execute Java's init initialization:
2. Memory layout of the object
Object header: stores the hash code, lock status, etc. of the object and the type pointer (the class pointed to by the object) Metadata)
Instance data: the information actually stored by the object
Alignment filling: filling conforms to the rules
3. Object access positioning
Object access , through the reference data on the java stack, it maintains a reference to the object
Access method: Handle and direct access
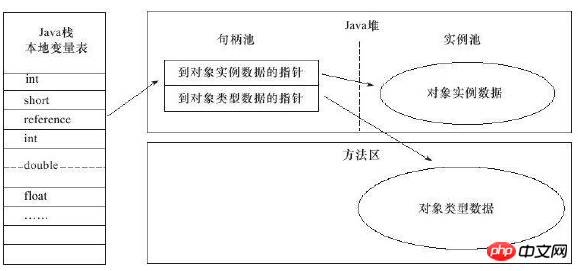
Handle: A handle pool is maintained in the heap, reference points to the handle, and the handle contains the address information of the object instance data and type data
It is easy to move, just modify the instance data in the handle directly; the overhead is high, and there are more One-time pointer positioning

Direct: reference points directly to the object address
##
##
# will be made by pointing directly to the object address vis will point directly to the address of the object三、actual combat OutofMemoryERROR .java heap overflow
Parameters
: -Xms heap minimum value; -Xmx heap maximum value; -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError Memory snapshot analysis when overflow occurs Heap storage Objects: A large number of objects can be created to achieve heap overflow: heap space2. Stack overflow
Parameter
: -Xss sets the stack value Stack depth can be achieved by increasing the stack depth through infinite recursion or creating a large number of threads//递归来StackOverFlowerpublic class JavaVMStackSOF {private int stackLength = 1;public void stackLeak(){
stackLength++;
stackLeak();
}public static void main(String[] args)throws Throwable{
JavaVMStackSOF oom = new JavaVMStackSOF();try {
oom.stackLeak();
} catch(Throwable e){
System.out.println("stack length:" + oom.stackLength);throw e;
}
}
}3. Method area and constant pool overflow
Parameters :-XX:PermSize method area size; -XX:MaxPermSize maximum size of method area
Before JDK1.6, you can create a large number of Strings, and the virtual machine will copy the objects and put them into the constant pool, thereby overflowing ##
In 1.7 and later, this cannot be done, because the virtual machine will only save the reference to the object when the object first appears in the constant poolpublic class JavaMethodAreaOOM{public static void main(String[]args){while(true){//创建大量的动态类,动态代理OOMObjectEnhancer enhancer=new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(OOMObject.class);
enhancer.setUseCache(false);
enhancer.setCallback(new MethodInterceptor(){public Object intercept(Object obj,Method method,Object[]args,MethodProxy proxy)throws Throwable{return proxy.invokeSuper(obj,args);
}}
);
enhancer.create();
}}static class OOMObject{
}
}
String.intern() is a Native method. Its function is: if the string constant pool already contains a string equal to this String object, return the String object representing the string in the pool; Otherwise, add the string contained in this String object to the constant pool, and return the reference of this String object
JDK6 and before: the method area (permanent generation) is separate, and the constant pool is in the method area
public class RuntimeConstantPoolOOM{public static void main(String[]args){
String str1=new StringBuilder("计算机").append("软件").toString();
System.out.println(str1.intern()==str1);
String str2=new StringBuilder("ja").append("va").toString();
System.out.println(str2.intern()==str2);
}
}When this code is run in JDK 1.6, it will get two false, but when it is run in JDK 1.7, it will get one true and one false.
The reason for the difference is: in JDK 1.6, the intern() method will copy the first encountered string instance to the permanent generation, and return a reference to the string instance in the permanent generation, and The string instance created by StringBuilder is on the Java heap, so it must not be the same reference, and false will be returned.
And JDK 1.7: the intern() implementation will no longer copy the instance, but only records the first instance reference of in the constant pool, so the reference returned by intern() is the same as the one created by StringBuilder That string instance is the same.
The comparison of str2 returns false because the string "java" has already appeared before executing StringBuilder.toString(), and there is already a reference to it in the string constant pool, which does not meet the requirements of "first occurrence" principle, and the string "computer software" appears for the first time, so true is returned
Note: 1.7 and later save the reference that appears for the first time; understand the above analysis
4. Native direct memory
Parameters: -XX: MaxDirectMemorySize direct memory size; default == maximum heap memory
The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to java memory area and memory overflow exception. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 Top 10 virtual currency trading platforms in the 2025 cryptocurrency circle
Mar 12, 2025 pm 05:27 PM
Top 10 virtual currency trading platforms in the 2025 cryptocurrency circle
Mar 12, 2025 pm 05:27 PM
Top 10 virtual currency trading platforms in the 2025 cryptocurrency circle: 1. OKX, known for its high liquidity, low fees and abundant products; 2. Binance, one of the world's largest exchanges, with a huge user base; 3. Gate.io, a veteran exchange, safe and stable; 4. Kraken, focusing on professional traders, safe and compliant; 5. Huobi Global, a world-renowned, strong technical strength; 6. Coinbase, a leading exchange in the United States, easy to use compliance; 7. KuCoin, rich trading pairs, low fees.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.
 How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Spring Boot simplifies the creation of robust, scalable, and production-ready Java applications, revolutionizing Java development. Its "convention over configuration" approach, inherent to the Spring ecosystem, minimizes manual setup, allo
 Java Made Simple: A Beginner's Guide to Programming Power
Oct 11, 2024 pm 06:30 PM
Java Made Simple: A Beginner's Guide to Programming Power
Oct 11, 2024 pm 06:30 PM
Java Made Simple: A Beginner's Guide to Programming Power Introduction Java is a powerful programming language used in everything from mobile applications to enterprise-level systems. For beginners, Java's syntax is simple and easy to understand, making it an ideal choice for learning programming. Basic Syntax Java uses a class-based object-oriented programming paradigm. Classes are templates that organize related data and behavior together. Here is a simple Java class example: publicclassPerson{privateStringname;privateintage;
 Can you make money by mining virtual coins? Is it true?
Mar 04, 2025 am 07:09 AM
Can you make money by mining virtual coins? Is it true?
Mar 04, 2025 am 07:09 AM
Virtual currency mining: Opportunities and challenges coexist in virtual currency mining, that is, using computer algorithms to solve complex mathematical problems to obtain virtual currency. It is the core mechanism of proof-of-work blockchains such as Bitcoin and is crucial to maintaining network security and stably issuing new coins. However, as mining costs rise, its profitability is highly questioned. This article will explore in-depth the profit potential of virtual currency mining and the key factors that affect its returns. Mining Profit Analysis Mining receives virtual currency rewards by participating in the computing and verification of blockchain networks. With the rise of technologies such as cloud mining, the threshold for participation has been lowered. Mining can provide a relatively stable source of income, but only if the mining machine is operating normally and the power supply is sufficient. In addition, the price of virtual currency fluctuates dramatically, which may bring high returns and may also create
 Java Program to insert an element at the Bottom of a Stack
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:59 AM
Java Program to insert an element at the Bottom of a Stack
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:59 AM
A stack is a data structure that follows the LIFO (Last In, First Out) principle. In other words, The last element we add to a stack is the first one to be removed. When we add (or push) elements to a stack, they are placed on top; i.e. above all the




