Detailed explanation of Channel in JAVA
Note: Reprinted from Concurrent Programming Network – ifeve.comLink address of this article: Java NIO Series Tutorial (2) Channel
Channel
The channel of Java NIO is similar Stream, but there are some differences:
can both read data from the channel and write data to the channel. But reading and writing streams are usually one-way.
Channels can be read and written asynchronously.
The data in the channel must first be read into a Buffer, or always written from a Buffer.
As mentioned above, data is read from the channel to the buffer and data is written from the buffer to the channel. As shown in the figure below:
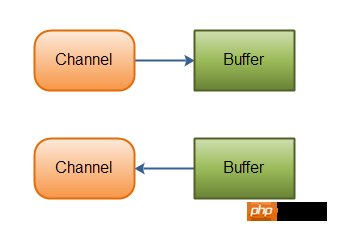
1. Implementation of Channel
These are the implementations of the most important channels in Java NIO:
- FileChannel
- DatagramChannel
- SocketChannel
- ServerSocketChannel
- FileChannel reads and writes data from files.
DatagramChannel can read and write data in the network through UDP.
SocketChannel can read and write data in the network through TCP.
ServerSocketChannel can monitor new incoming TCP connections, just like a web server. A SocketChannel is created for each new incoming connection.
2. Basic Channel Example
The following is an example of using FileChannel to read data into a Buffer:
public class Channel1 {public static void main(String[] args) {try {
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("./.gitignore","rw");
FileChannel channel = raf.getChannel(); //获取通道ByteBuffer bf = ByteBuffer.allocate(50); //通过静态allocate方法创建一个缓冲区,容量为50byte[] bytes = new byte[]{};
bytes = "123".getBytes();
bf = ByteBuffer.wrap(bytes); //通过静态wrap方法,byte数组生成缓冲区,缓冲区中保留了原数据while(bf.hasRemaining()){
System.out.print((char) bf.get());
}int bytesRead ;while ((bytesRead = channel.read(bf)) != -1) { //将通道中的数据写入缓冲区,并判断通道中的数据是否到末尾System.out.println("Read " + bytesRead);bf.flip(); //反转缓冲区 实际上就是将position置为0 后续buffer详细介绍while(bf.hasRemaining()){ //判断缓冲区中是否还有值System.out.print((char) bf.get()); //输出缓冲区中的值 }
bf.clear(); //清理缓冲区 }
raf.close(); //关闭RandomAccessFile} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of Channel in JAVA. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1381
1381
 52
52
 What does channel mean in Go language?
Dec 14, 2023 pm 02:21 PM
What does channel mean in Go language?
Dec 14, 2023 pm 02:21 PM
Channel in Go language is a mechanism for communication and data synchronization between coroutines. Can be thought of as a special data type, similar to a queue or pipe, used to transfer data between different coroutines. Channel provides two main operations: send and receive. Both send and receive operations in a channel are blocking, which means that if no sender or receiver is ready, the operation will be blocked until a coroutine is ready to perform the corresponding operation, etc.
 How does golang function communicate with goroutine through channel?
May 01, 2024 pm 09:42 PM
How does golang function communicate with goroutine through channel?
May 01, 2024 pm 09:42 PM
Go language uses channels and goroutines to communicate. After creating the channel, the goroutine can pass
 How to solve the problem of concurrent task reordering in Go language?
Oct 09, 2023 pm 10:55 PM
How to solve the problem of concurrent task reordering in Go language?
Oct 09, 2023 pm 10:55 PM
How to solve the problem of concurrent task reordering in Go language? In concurrent programming, the execution order of tasks is often uncertain, which may cause some problems, especially for tasks with dependencies. In Go language, we can solve the problem of concurrent task reordering by using channels and coroutines. Below we will explain in detail how to achieve this. Typically, we use channels to achieve task synchronization and communication. In the Go language, channels can be used as a higher-level synchronization primitive to ensure the execution order of tasks. By using buffered
 How to use java Channel
Apr 19, 2023 am 11:22 AM
How to use java Channel
Apr 19, 2023 am 11:22 AM
1. Explain that Channel is an object through which data can be read and written. It can be viewed as a stream in IO. But compared with streams, it has some differences: Channel is bidirectional and can be read or written, while streams are one-way. Channel can be read and written asynchronously. Channel reading and writing must go through the buffer object. 2. The example is completed using channels and indirect buffers. FileInputStreamfis=null;//Reference FileOutputStreamfout=null;FileChannelchannel=null;//Channel reference FileChanneloutchannel=null;try{fi
 How to use channel in Go language?
Jun 09, 2023 pm 08:13 PM
How to use channel in Go language?
Jun 09, 2023 pm 08:13 PM
In the Go language, channel is an important mechanism to achieve concurrent communication. It provides a way to pass data from one goroutine to another, thereby achieving data synchronization and collaboration. This article will introduce the basic usage of channels in Go language and some precautions. 1. Declaration and initialization of channel In Go language, declaring a channel requires using the make() function. Example code
 学习channel设计:从入门到放弃
Aug 08, 2023 pm 04:33 PM
学习channel设计:从入门到放弃
Aug 08, 2023 pm 04:33 PM
今天给大家带来的是Go语言中的channel。Go语言从出世以来就以高并发著称,得益于其Goroutine的设计,Goroutine也就是一个可执行的轻量级协程,有了Goroutine我们可以轻松的运行协程,但这并不能满足我们的需求,我们往往还希望多个线程/协程是能够通信的。
 learned! Use buffered channels as Mutexes
Aug 08, 2023 pm 04:21 PM
learned! Use buffered channels as Mutexes
Aug 08, 2023 pm 04:21 PM
The sync package provides basic synchronization primitives such as mutex locks. Except for the Once and WaitGroup types, most other types are intended for the underlying function library. Higher level synchronization is better accomplished through channels and communications.
 Tips for using channels and mutex in Golang functions
May 16, 2023 am 10:51 AM
Tips for using channels and mutex in Golang functions
May 16, 2023 am 10:51 AM
Golang is a very popular programming language that is widely used in network programming, cloud computing, concurrent programming and other fields. Among them, channel and mutex are important concepts in Golang programming. They can help us solve some problems in concurrent programming. This article will introduce how to use channels and mutex of Golang functions. 1. What is channel? In Golang, channel is a data type that can be used in different Gor




