python learning journey
In this chapter, the author briefly introduces the python data model, mainly some special methods of python. For example, __len__, __getitem__. And use a playing card program to explain these methods
First introduce the difference between Tuple and nametuple:
Nametuple is similar to a tuple type of data. In addition to being able to access data using indexes, it also supports accessing data using convenient property names.
Traditional tuple access is as follows. Access to each element must be found via index. This method of finding is very unintuitive
tup1=(,,) tup1[1]
Use nametuple to construct:
tup2=namedtuple(,[,,]) t1=tup2(,,) t1 t1.age t1.height t1.name
得到结果如下,namedtupel中tuple2是类型名,name,age,height是属性名字
从上面的访问可以看到,直接用t1.age的方法访问更加直观。当然也可以用索引比如t1[0]的方法来访问

namedtupe1 also supports iterative access:
t t1: t
和元组一样,namedtupel中的元素也是不可变更的。如果执行t1.age+=1。将会提示无法设置元素
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "E:/py_prj/fluent_py.py", line 17, in
t1.age+=1
AttributeError: can't set attribute
Let’s take a look at the playing card example in the book. The code is as follows:
collections namedtuple Card=namedtuple(,[,]) FrenchDeck: ranks=[str(n) n range(2,11)] + list() suits=.split() __init__(self): self._cards=[Card(rank,suit) suit self.suits
First, the card tuple Card is defined, rank represents the card number, and suit represents the card suit. Then FrenchDeck first defines the specific meaning of ranks and suit. Initialize self._cards in __init__.
__len__Feedback the length of self._cards. __getitem__ returns the specific card value.
The result is as follows, the length of the card is 52, where deck[1] is Card(rank='3',suit='spades')
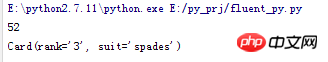
You can see that len(deck) actually calls the __len__ method. deck[1] calls __getitem__
Due to the __getitem__ method, iterative access can also be performed, as follows:
rank self.ranks] __len__(self): len(self._cards) __getitem__(self, position): self._cards[position] __name__==: deck=FrenchDeck() len(deck) deck[1]
Since it is iterable, Then we can simulate the mechanism of random card dealing.
d deck: d
from random import choice
Get the result:
Card(rank='9', suit='hearts')
Let's look at another example, about Vector operations. For example, there is vector 1 vector1(1,2) and vector 2 vector2(3,4). Then the result of vector1+vector2 should be (4,6). Vector1 and vector2 are both vectors, how to implement the operation? The method is __add__,__mul__
The code is as follows:
print choice(deck)
vector: __init__(self,x=0,y=0): self.x=x self.y=y __repr__(self): % (self.x,self.y) __abs__(self): hypot(self.x,self.y) __bool__(self): bool(abs(self)) __add__(self,other): x=self.x+other.x y=self.y+other.y vector(x,y) __mul__(self, scalar): vector(self.x*scalar,self.y*scalar)
The operation result is as follows:
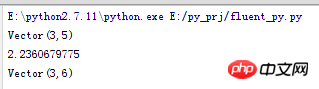
__name__==: v1=vector(1,2) v2=vector(2,3) v1+v2 abs(v1) v1*3
The above is the detailed content of python learning journey. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Google AI announces Gemini 1.5 Pro and Gemma 2 for developers
Jul 01, 2024 am 07:22 AM
Google AI announces Gemini 1.5 Pro and Gemma 2 for developers
Jul 01, 2024 am 07:22 AM
Google AI has started to provide developers with access to extended context windows and cost-saving features, starting with the Gemini 1.5 Pro large language model (LLM). Previously available through a waitlist, the full 2 million token context windo
 How to download deepseek Xiaomi
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:27 PM
How to download deepseek Xiaomi
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:27 PM
How to download DeepSeek Xiaomi? Search for "DeepSeek" in the Xiaomi App Store. If it is not found, continue to step 2. Identify your needs (search files, data analysis), and find the corresponding tools (such as file managers, data analysis software) that include DeepSeek functions.
 How do you ask him deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 04:42 PM
How do you ask him deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 04:42 PM
The key to using DeepSeek effectively is to ask questions clearly: express the questions directly and specifically. Provide specific details and background information. For complex inquiries, multiple angles and refute opinions are included. Focus on specific aspects, such as performance bottlenecks in code. Keep a critical thinking about the answers you get and make judgments based on your expertise.
 How to search deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:18 PM
How to search deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:18 PM
Just use the search function that comes with DeepSeek. Its powerful semantic analysis algorithm can accurately understand the search intention and provide relevant information. However, for searches that are unpopular, latest information or problems that need to be considered, it is necessary to adjust keywords or use more specific descriptions, combine them with other real-time information sources, and understand that DeepSeek is just a tool that requires active, clear and refined search strategies.
 How to program deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
How to program deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
DeepSeek is not a programming language, but a deep search concept. Implementing DeepSeek requires selection based on existing languages. For different application scenarios, it is necessary to choose the appropriate language and algorithms, and combine machine learning technology. Code quality, maintainability, and testing are crucial. Only by choosing the right programming language, algorithms and tools according to your needs and writing high-quality code can DeepSeek be successfully implemented.
 How to use deepseek to settle accounts
Feb 19, 2025 pm 04:36 PM
How to use deepseek to settle accounts
Feb 19, 2025 pm 04:36 PM
Question: Is DeepSeek available for accounting? Answer: No, it is a data mining and analysis tool that can be used to analyze financial data, but it does not have the accounting record and report generation functions of accounting software. Using DeepSeek to analyze financial data requires writing code to process data with knowledge of data structures, algorithms, and DeepSeek APIs to consider potential problems (e.g. programming knowledge, learning curves, data quality)
 The Key to Coding: Unlocking the Power of Python for Beginners
Oct 11, 2024 pm 12:17 PM
The Key to Coding: Unlocking the Power of Python for Beginners
Oct 11, 2024 pm 12:17 PM
Python is an ideal programming introduction language for beginners through its ease of learning and powerful features. Its basics include: Variables: used to store data (numbers, strings, lists, etc.). Data type: Defines the type of data in the variable (integer, floating point, etc.). Operators: used for mathematical operations and comparisons. Control flow: Control the flow of code execution (conditional statements, loops).
 Problem-Solving with Python: Unlock Powerful Solutions as a Beginner Coder
Oct 11, 2024 pm 08:58 PM
Problem-Solving with Python: Unlock Powerful Solutions as a Beginner Coder
Oct 11, 2024 pm 08:58 PM
Pythonempowersbeginnersinproblem-solving.Itsuser-friendlysyntax,extensivelibrary,andfeaturessuchasvariables,conditionalstatements,andloopsenableefficientcodedevelopment.Frommanagingdatatocontrollingprogramflowandperformingrepetitivetasks,Pythonprovid






